DERMATOPHYTE
Dermatophytes group of fungi (ringworm) have the ability to infect and survive only on dead keratin on the top layer of the skin hair and the nails.
CLASSIFICATION
The ringworm fungi belong to three genera (types):
- Microsporum
- Trichophyton
- Epidermophyton
There are several species of Microsporum and Trichophyton and one species of Epidermophyton.
The Dermatophyte Genera and Diseases
| Genus | Name of Disease | Principal Targets | How Transmitted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trichophyton | Ringworm of the scalp, body, beard, and nails | Hair, skin, nails | Human to human, animal to human |
| Microsporum | Ringworm of scalp Ringworm of skin | Scalp hair Skin; not nails | Animal to human, soil to human, human to human |
| Epidermophyton | Ringworm of the groin and nails | Skin, nails; not hair | Strictly human to human |
CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION
Tinea means fungal infection. Clinically, dermatophyte infections are classified by body region:
Types by Body Region
- .Corporis → body
- .Cruris → groin
- .Pedis → foot
- .Unguium → nail
- .Capitis → scalp
Tinea corporis

more active by the borders, raised margin more likely fungal infection
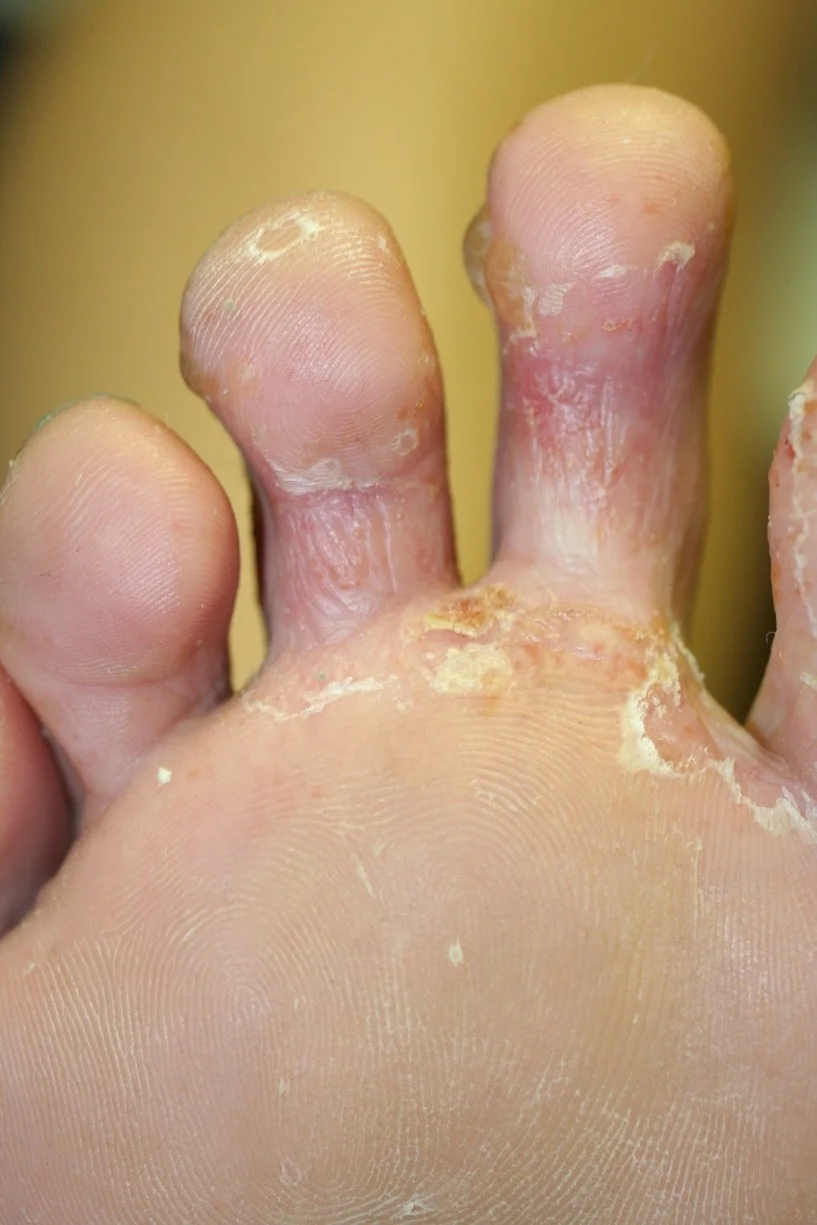
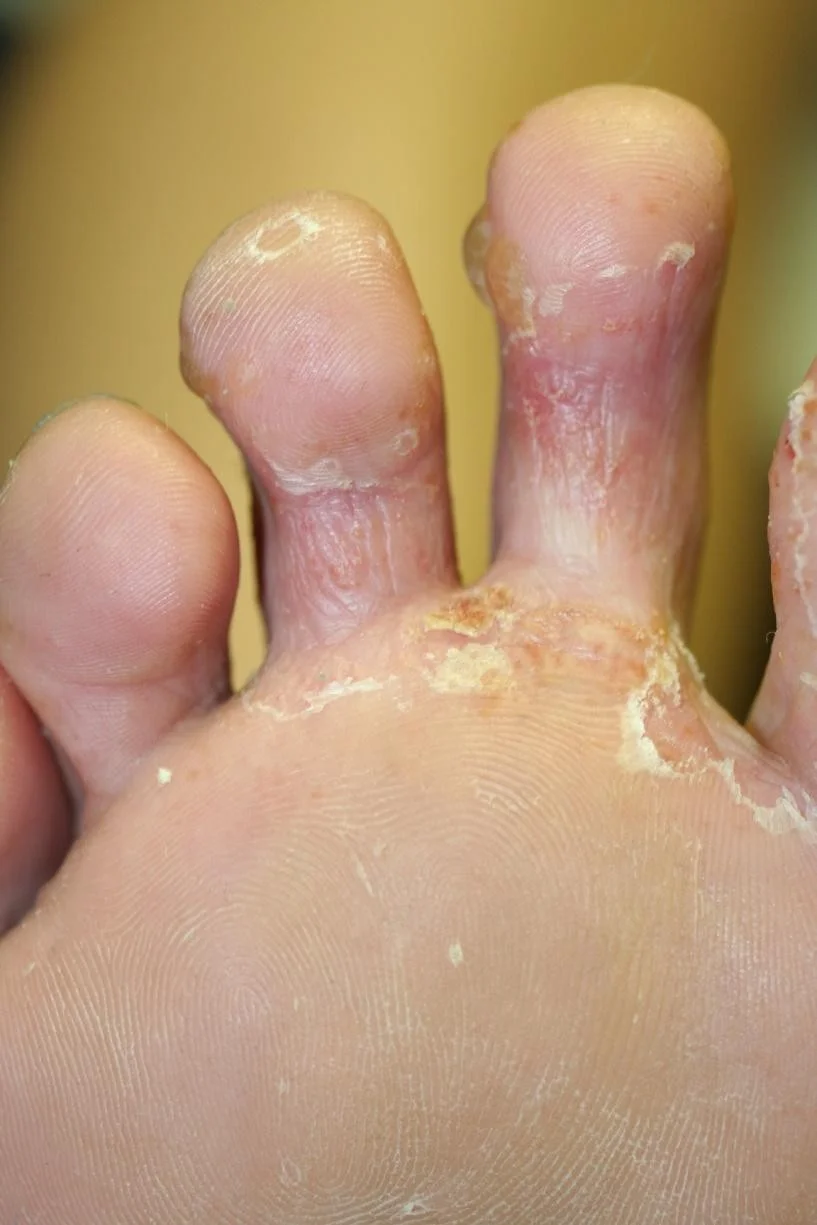
Tinea pedis
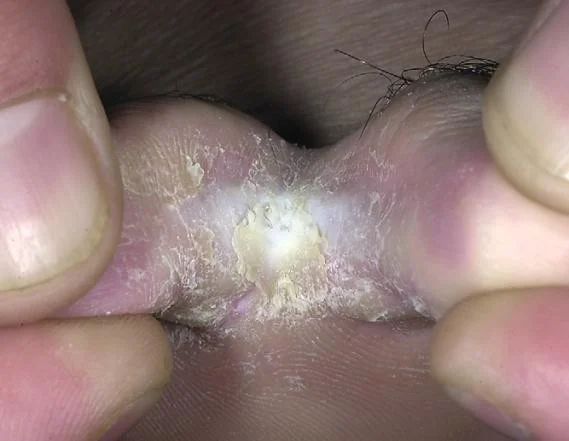
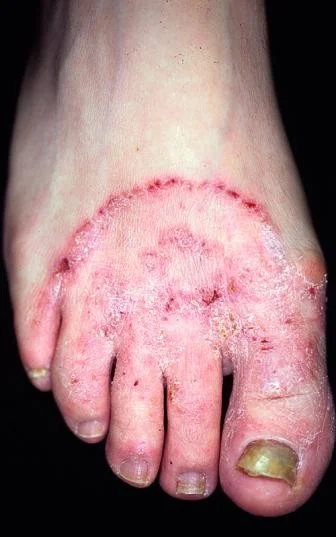
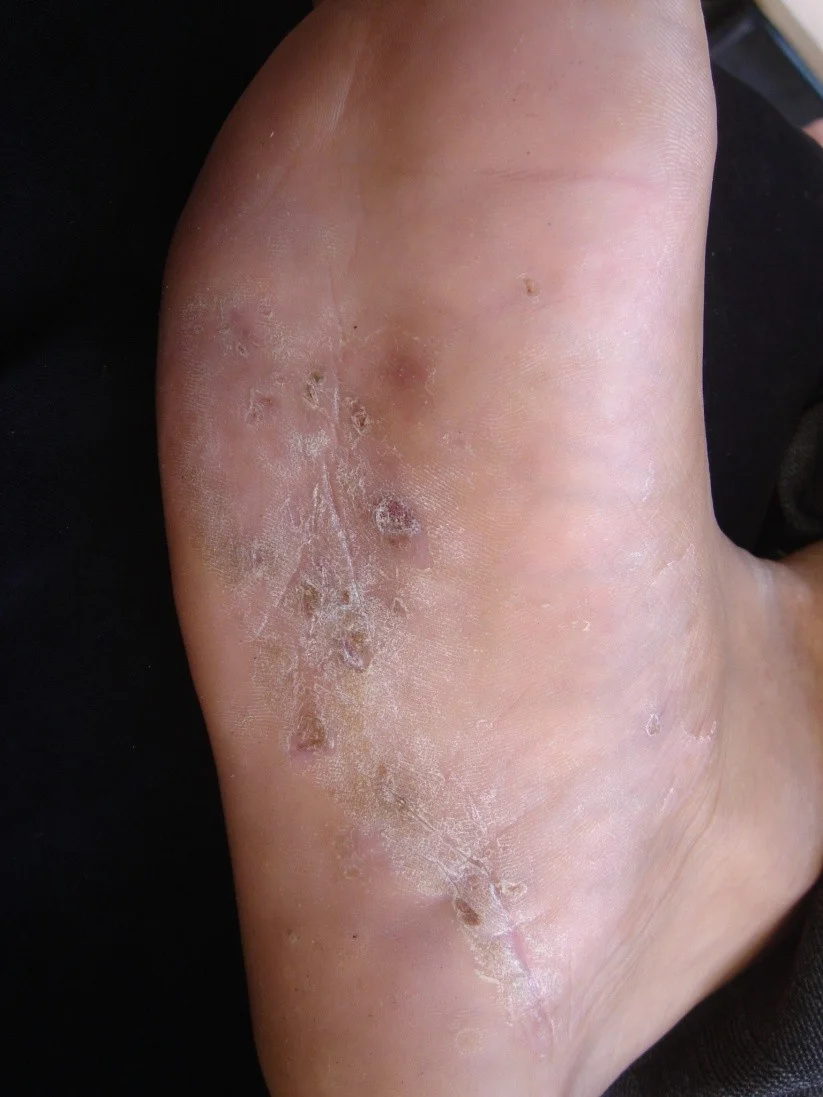
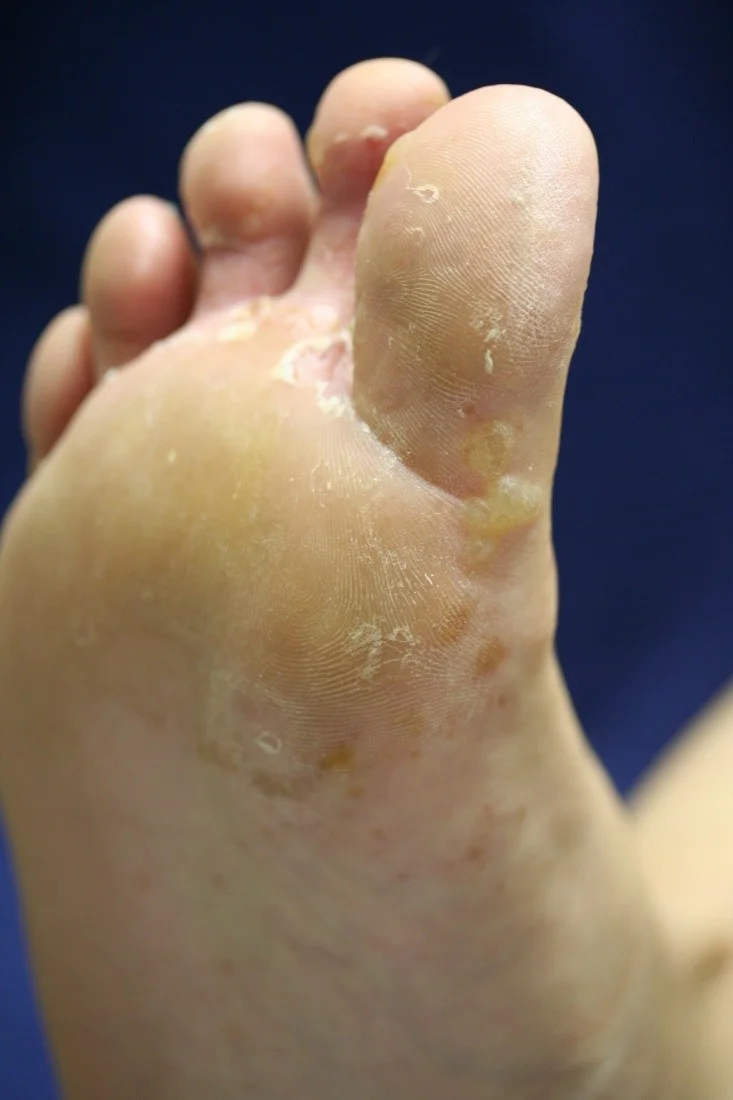
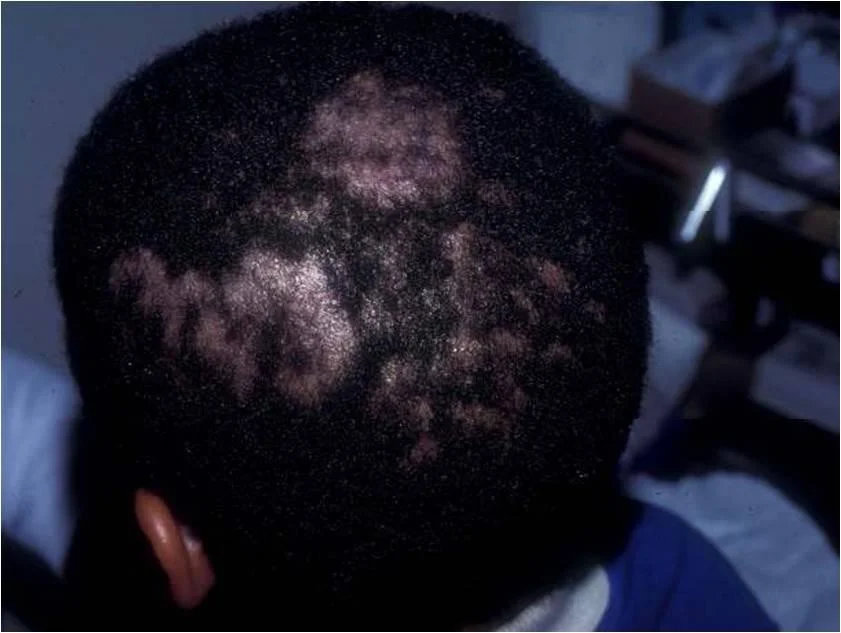
Tinea capitis
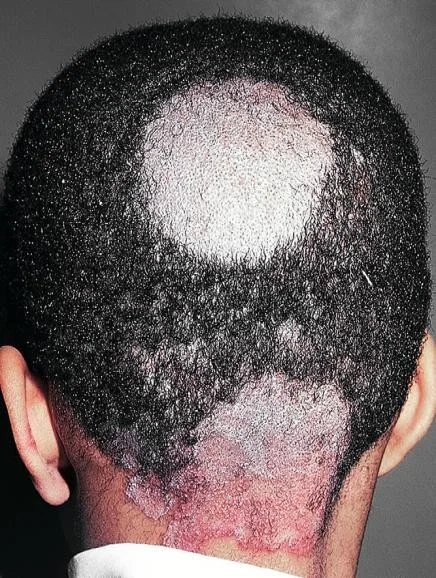 erythema, scales, broken hair
erythema, scales, broken hair
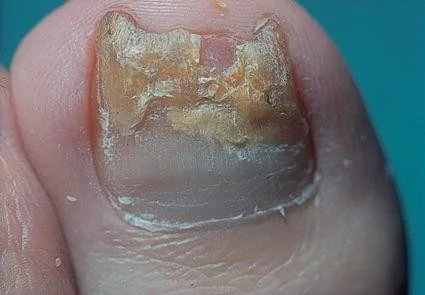
Chronic tinea of the big toe nail (T. Unguium)
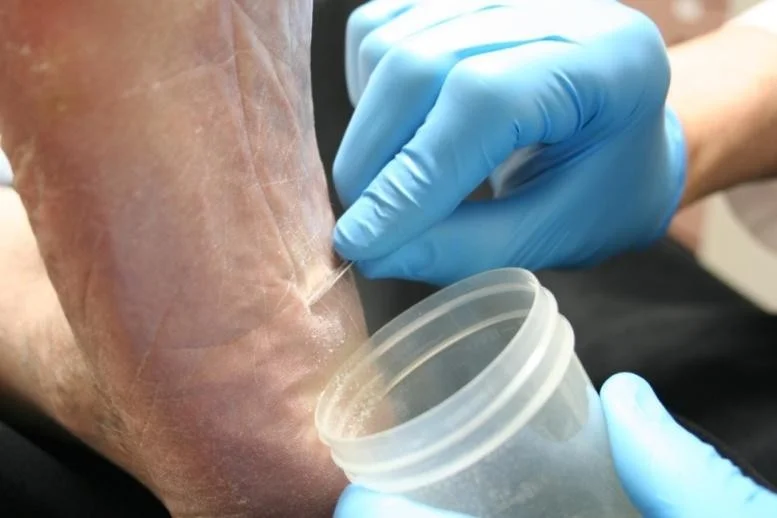
KOH exam
- Excellent choice.
- You decide to do a KOH exam in the office.
- Scrape the leading edge for fine scale
Case One
Case One: History
- HPI: Sali is a 31-year-old woman who presents with red circles on her arms and trunk for the past 7 months. They don’t itch.
- PMH: none
- Allergies: erythromycin (rash)
- Medications: none
- Family history: noncontributory
- Social history: stay-at-home mom
- ROS: negative
Case One: Skin Exam
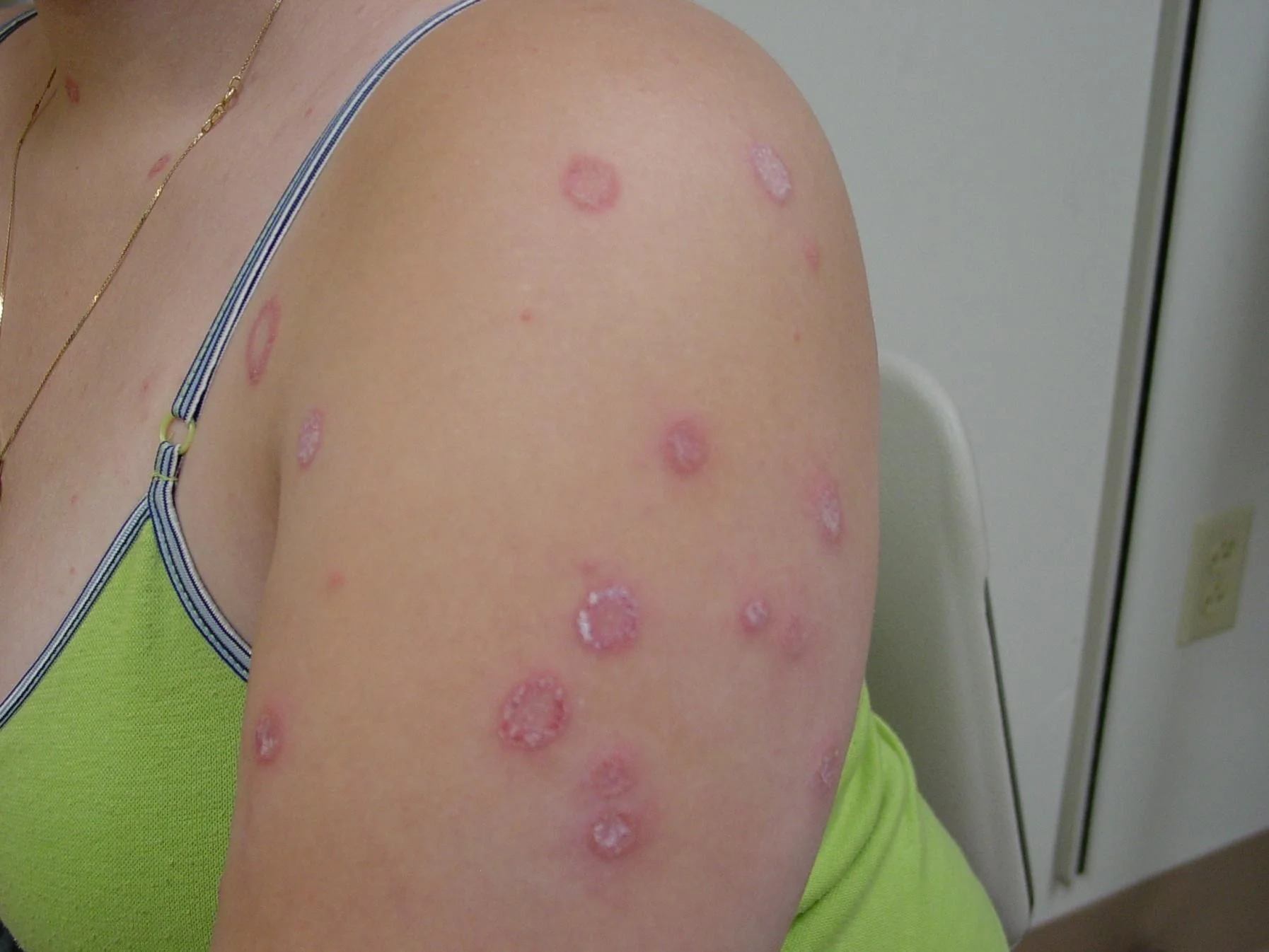
Case One, Question 1
- Mrs. Sali’s exam shows annular erythematous patches with scale on the advancing edges and central clearing. Which is the best test to confirm the diagnosis? a. Bacterial culture (would only get normal skin flora) b. Direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) test (for herpes virus) c. Fungal culture (more expensive, takes longer) d. Potassium hydroxide (KOH) exam (can make the diagnosis in the office; inexpensive test) e. Wood’s light (this does not fluoresce)
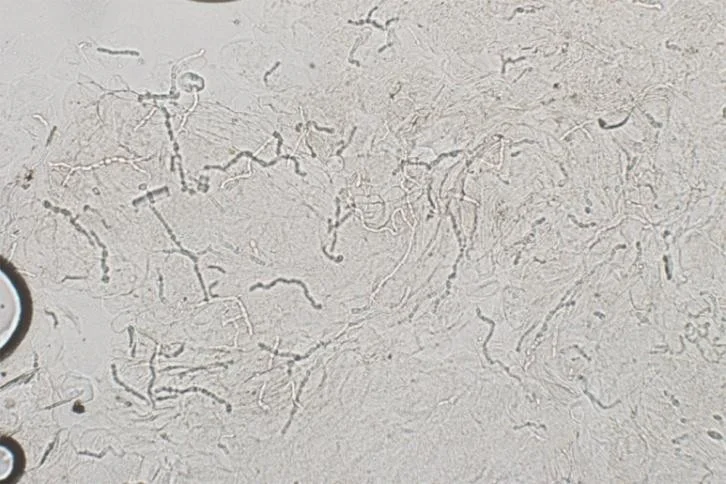
Case One, KOH exam
Translucent branching, septate hyphae
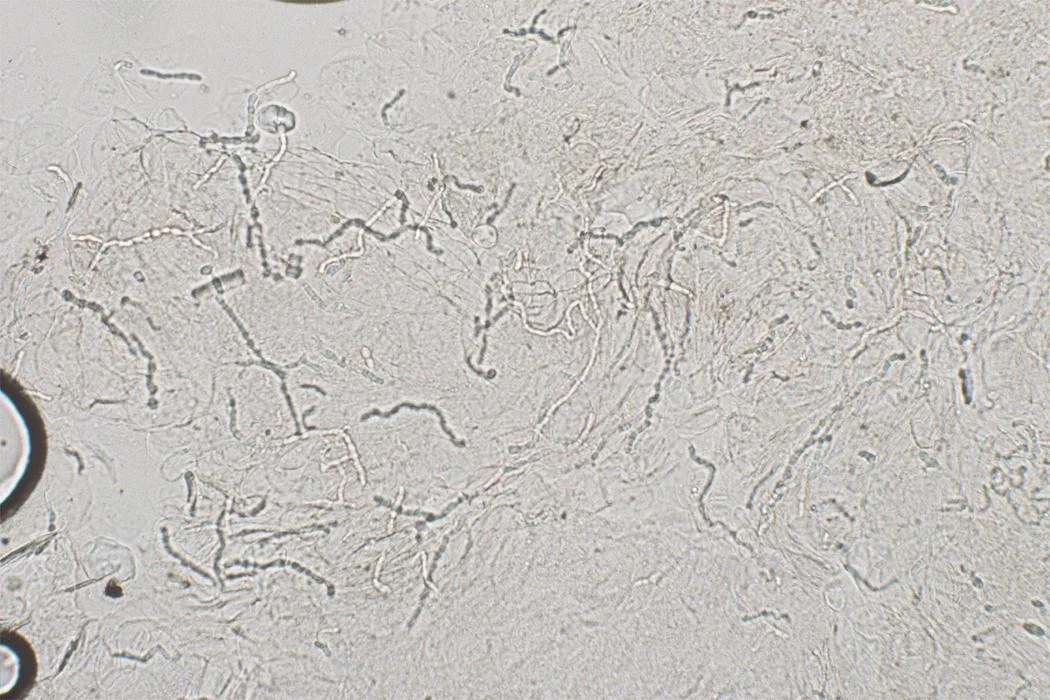
Potassium hydroxide exam
- The first step in diagnosing a scaling annular rash on the body is to perform a KOH exam to rule out fungus
- “All that scales must be scraped” is a common mantra in dermatology
- Rule out dermatophyte infections before moving forward on scaling rashes
Case One, Question 2
- Mrs. Sali’s KOH exam is positive. Which of the following questions are important to ask? a. Do you have a rash in your groin? (associated tinea cruris) b. Do you have a rash on your feet? (associated tinea pedis) c. Do you have any pets? (cats can transmit a type of ringworm) d. Do you take care of young children? (kids may have fungal infections on the scalp) e. All of the above
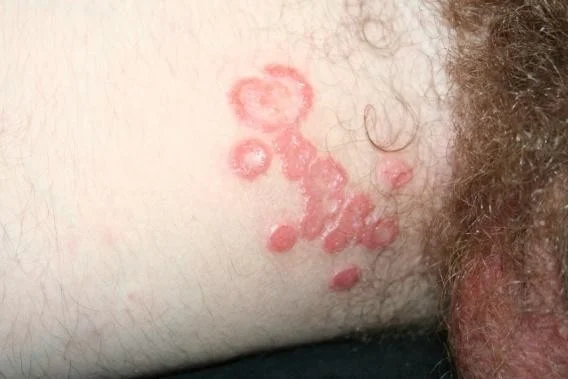
Tinea corporis
- Tinea corporis (“ringworm”) classically presents as annular patches with peripheral scaling at the advancing edge and central clearing
- Complete skin exam often reveals tinea cruris (“jock itch”) and tinea pedis (“athlete’s foot”). Check these areas on full skin exam.
- Tinea corporis is usually caused by Trichophyton and Microsporum species.
- These dermatophytes appear as translucent branching, septate hyphae. They do not have yeast forms.
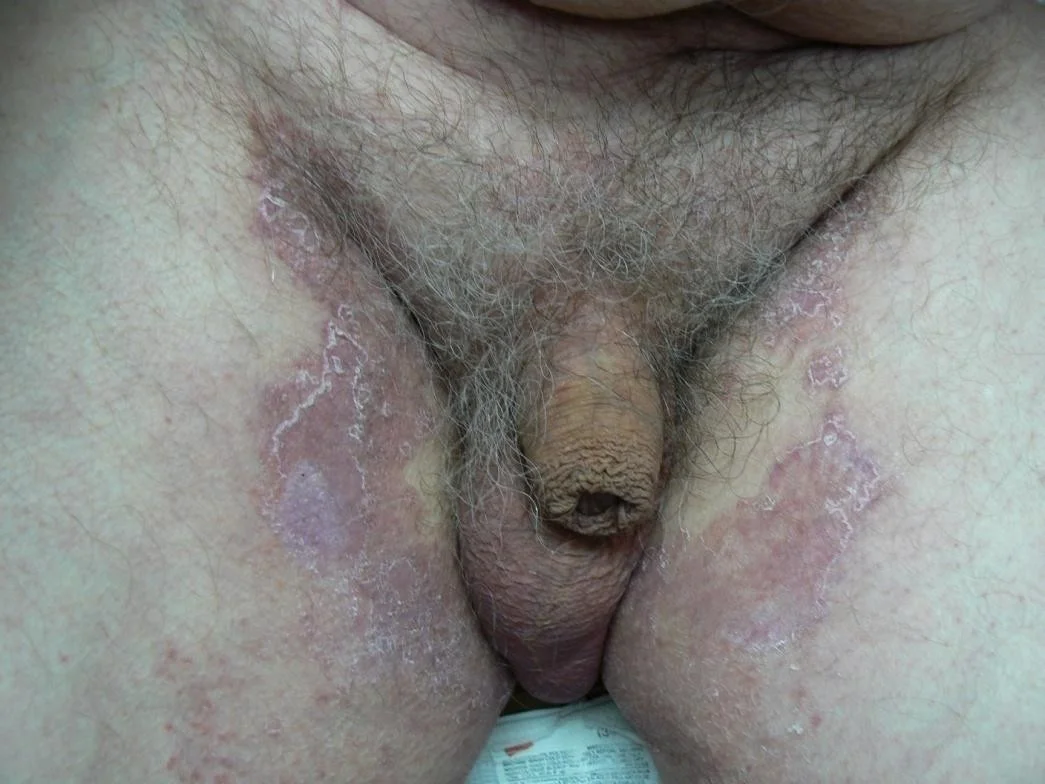
Tinea cruris
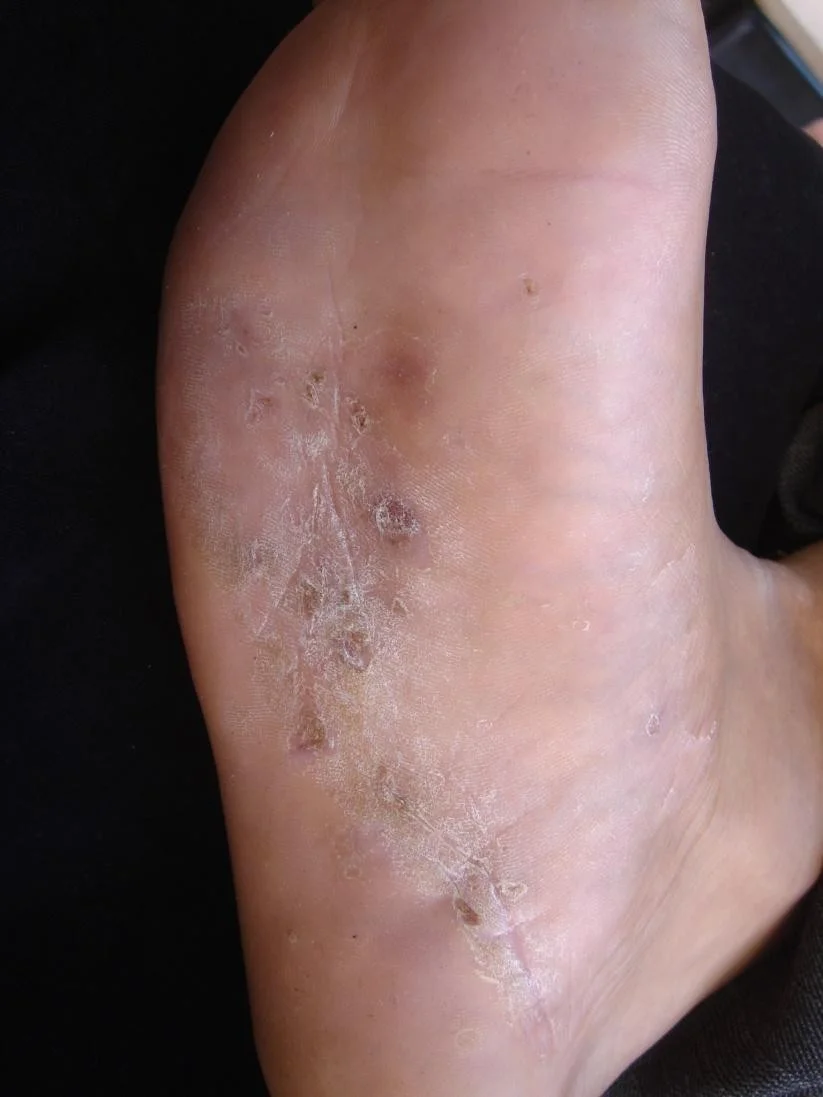
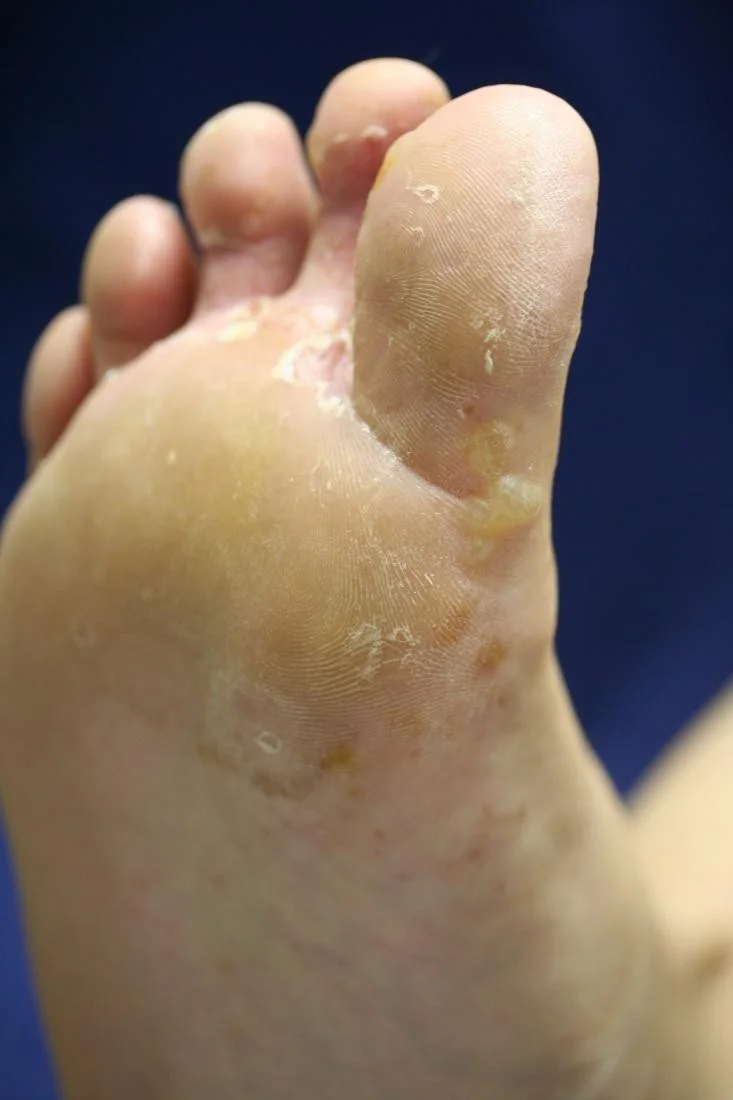
Tinea pedis
Tinea capitis
Case One, Question 3
- Mrs. Sali has athlete’s foot and extensive tinea corporis on her abdomen, chest, back, and arms. What is the best therapy for her? a. Nystatin cream (only works for Candida species) b. Oral terbinafine (necessary for extensive tinea corporis) c. Terbinafine cream (not good for extensive involvement) d. Triamcinolone cream (could worsen infection or create tinea incognito) e. Ultraviolet B (UVB) phototherapy (will not kill fungus)
Tinea corporis treatment
- Counsel on foot care to prevent recurrence
- Localized involvement
- Azoles (miconazole, clotrimazole) are fungistatic and must be used BID
- Allylamines (terbinafine, naftifine) and benzylamines (butenafine) are fungicidal
- Better cure rates and lower recurrence than azoles
- Extensive involvement may require oral antifungals (14-28 days of terbinafine)