Complex neuropsychatric syndrome complicating acute or chronic liver disease .
Pathogenesis:
many factors with lack of detoxification of toxic substaces absorbed from intestine due to:
A) severe hepatocellular damage
B) vascular shunt (in portal hypertension).
Theories
1- Ammonia theory: Increase blood ammonia level (unionized) which when reach the brain combine with alpha ketoglutaric acid to be converted to glutamine which decrease oxygen consumption in Krebs cycle to produce diffuse cerebral inhibition.
Source of ammonia:
- GIT: (dietary protein- GI hemorrhage ) by bacterial deamination of amino acids in the intestine .
- hepatic (decrease urea synthesis).
- renal (in hepatorenal syndrome )
2-Synergism theory: Include ammonia and long chain fatty acids (elevated in cirrhosis) These long chain fatty acids displace neuroactive chemicals e.g tryptophan from serum albumin.
3-False neurotransmitters theory:
-
With increase aromatic amino acids level e.g phenyl alanine which compete with tyrosine so, there is less conversion to NE and dopamine but increase level of octopamine (weak chemical transmitter) leading to manifestations of extrapyramidal syndrome which is improved with L, dopa and branched chain amino acids.
-
Also, increased level of tryptophan which is strong inhibitory chemical transmitter.
4-GBAB theory: GABA level is increased in the brain which produce diffuse cerebral inhibition (act as endogenous benzodiazepines)
5-Inflammation and infection theory: Infection act to synergizes ammonia effect in the brain.
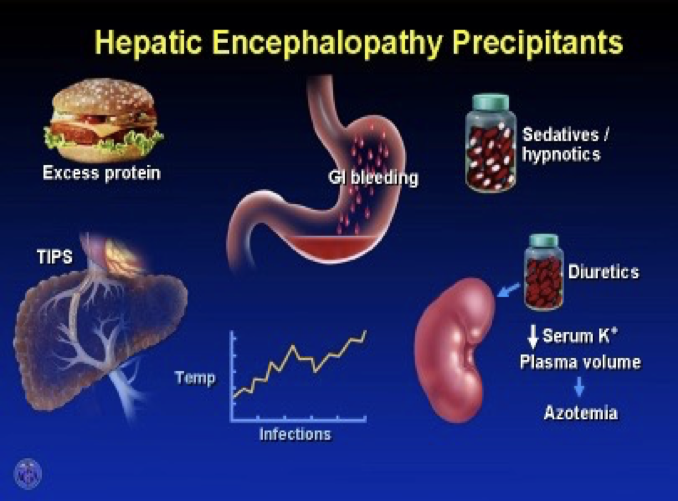
P.P.F:
- A: azotemia; dysfunction of renal functions
- B: bleeding.
- C: constipation (increased ammonia formation due to increased gut transit time).
- D: diet(protein) and drugs (diuretics,, CNS inhibitors as benzodiazepines, alcohol;, narcotics…etc)
- E: electrolyte imbalance ( hypo or hyperkalaemia)
- F: febrile illness (tissue catabolism = infection). ((may result in increased ammonia))
Clinical picture:
1- Hepatic precoma: Psychiatric ( lack of concentration, disturbed mood, altered personality…)
- Neurological :( tremor, rigidity)
- imperfect performance.
- Disturbed conscious state (insomnia and hypersomnia).
- Flapping tremors.
- Dysarthria.
2- Hepatic coma.
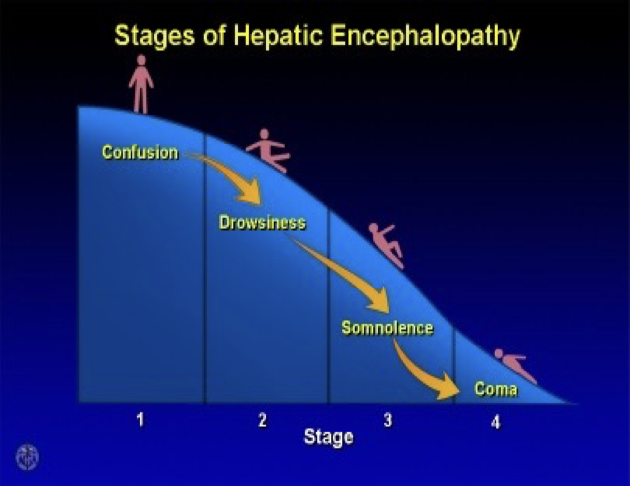
Four Stages of Hepatic Encephalopathy
May be 2 week sudden manifestation
Stage Symptom I Mild confusion, agitation, irritability, sleep disturbance, decreased attention II Lethargy, disorientation, inappropriate behavior, drowsiness III Somnolence but arousable, incomprehensible speech, confusion, aggression when awake IV Coma

Treatment of
A) Ammonia theory= hyperammoniaemia 1-Decrease ammoniogenic substances:
- prevention of GIT bleeding.
- dietary protein restriction to decrease ammonia formation.
- give vegetable proteins (high in branched chain and low in aromatic amino-acids )so, this help to restore balance between both.
- use lactulose cleansing enema and orally.
2- Inhibit production and absorption of ammonia:
- Antibiotics:
- pre and probitics; ((Replacement of bacterial flora))
- Lactulose. ((if healthy patient = laxative, otherwise in this case looseformed, used for life, very few side effects))
- Lactitol.
B) For GABA theory: give flumazenil I.V which give response within minute but 2/3 of patients deteriorates after 3-4 hours.
C) For false neurotransimitter theory: -infusion of BCAA -oral BCAA supplement.