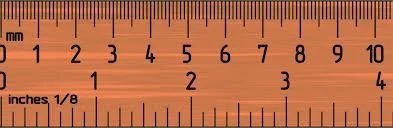
Primary Lesions Summary
- 1. Macule: Flat circumscribed area of change in skin color
- 2. Papule: small circumscribed elevation of the skin
- 3. Nodule: Solid, circumscribed elevation of the skin whose greater part is beneath skin surface (felt more than seen)
- 4. Plaque: flat topped palpable lesion (gathering of papules)
- 5. Vesicle: collection of clear fluid (<5mm in diameter)
- 6. Bulla: like vesicle, but > 5 mm
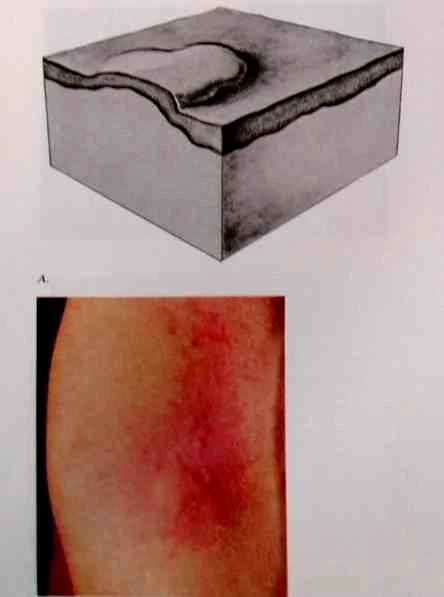
- 7. Wheal: Transient, slightly raised lesion with pale center and pink margin. Seen in urticaria.
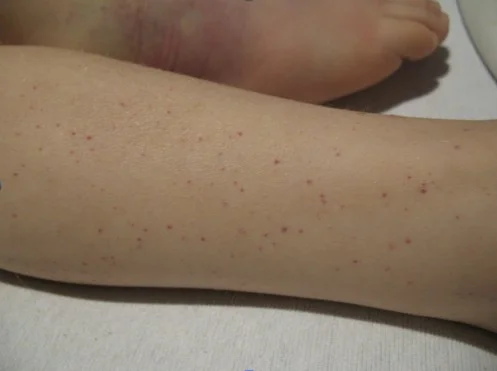
- 8. Purpura: Visible collection of blood under the skin e.g. Vasculitis
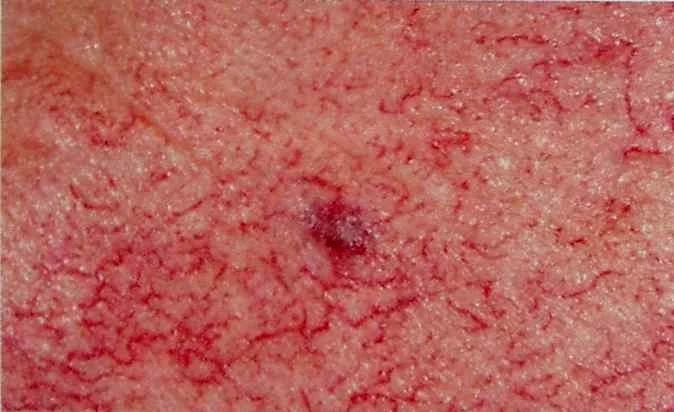
- 9. Telangectasia: Dilated capillaries visible on skin surface
- 10. Burrow: Tunnel in the skin (e.g. Scabies)
Morphology
- The word morphology is used by dermatologists to describe the form and structure of skin lesions
- The morphologic characteristics of skin lesions are key elements in establishing the diagnosis and communicating skin findings
- There are two steps in establishing the morphology of any given skin condition:
- Careful visual and tactile inspection
- Application of correct descriptors
Visual and Tactile Inspection
- Accumulate detailed information about the visual and tactile aspects of the skin findings
- Be able to communicate an accurate description so someone on the other end of a phone can get a mental picture of what you see.
- Question 1
- How would you fill in the description of the item depicted on the next slide?
Question 1
- How would you describe the object to the right?
- Be as detailed as you can be!

- This is a red, circular, shiny object with a small invagination on top. It measures 8 cm. It is in a white background and casts a shadow.
- The above description identifies:
- Palpability (indicated by shadow)
- Color
- Shape
- Texture
- Size
- Location
Application of the correct descriptors
- We have just reviewed careful visual inspection
- We will now define the terms dermatologists use to describe skin lesions
- We will then have a series of cases for you to practice describing so you can use the correct descriptors.
Primary skin lesions
Macule
- (L. macula, “spot”)
- A macule is flat; if you can feel it, then it is not a macule.

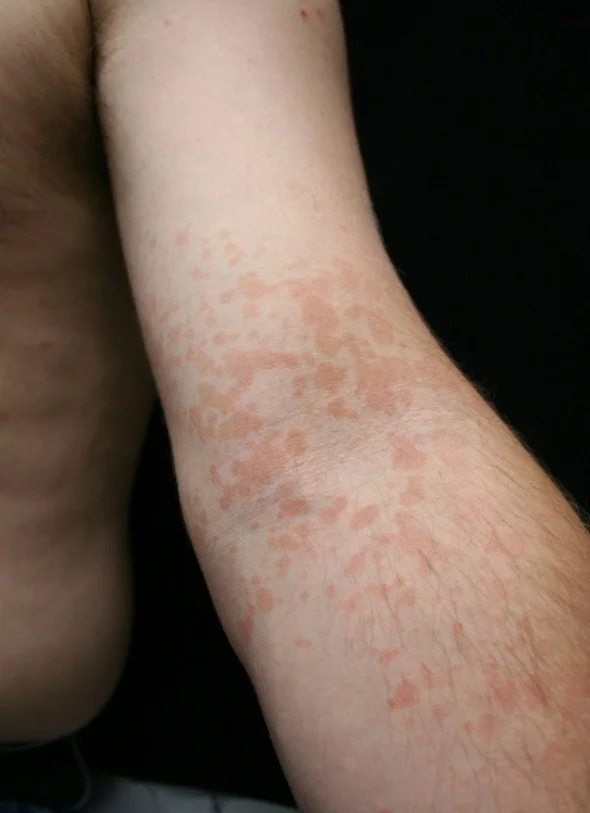
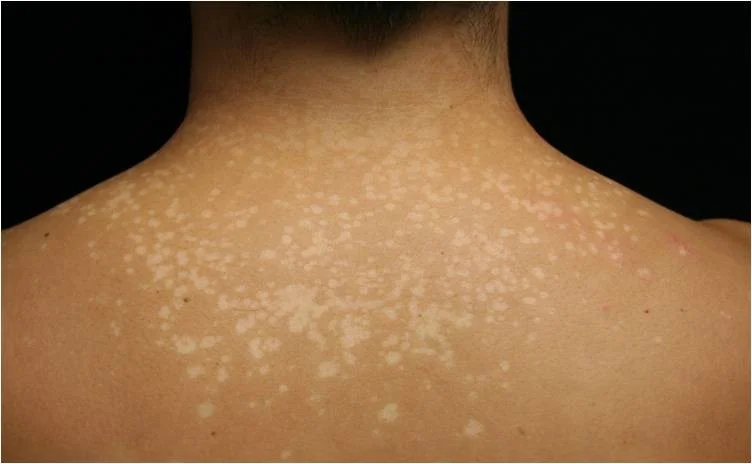

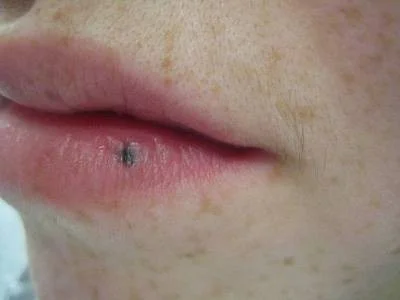
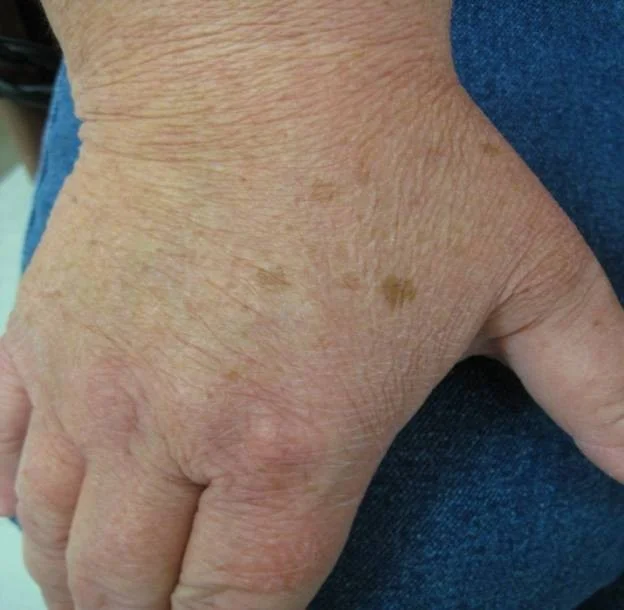
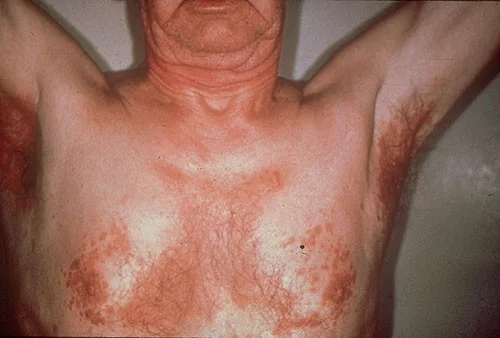
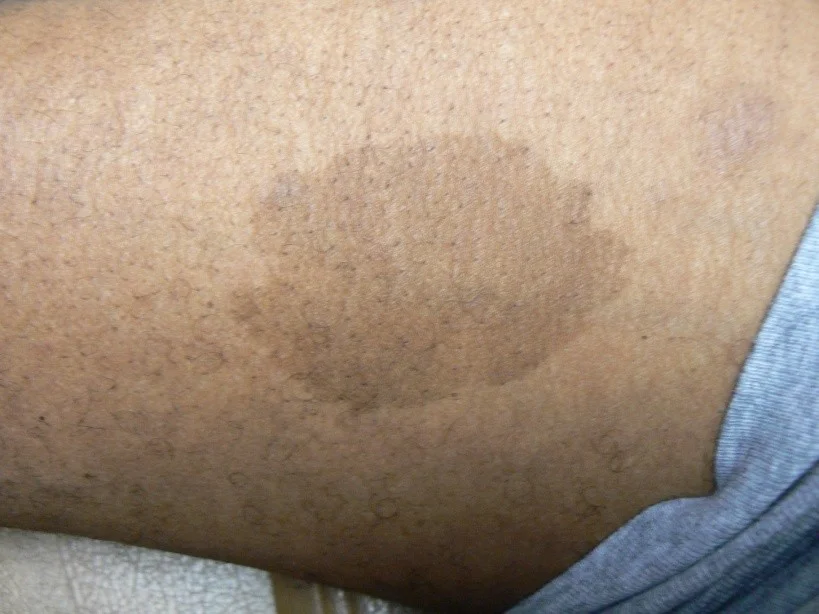
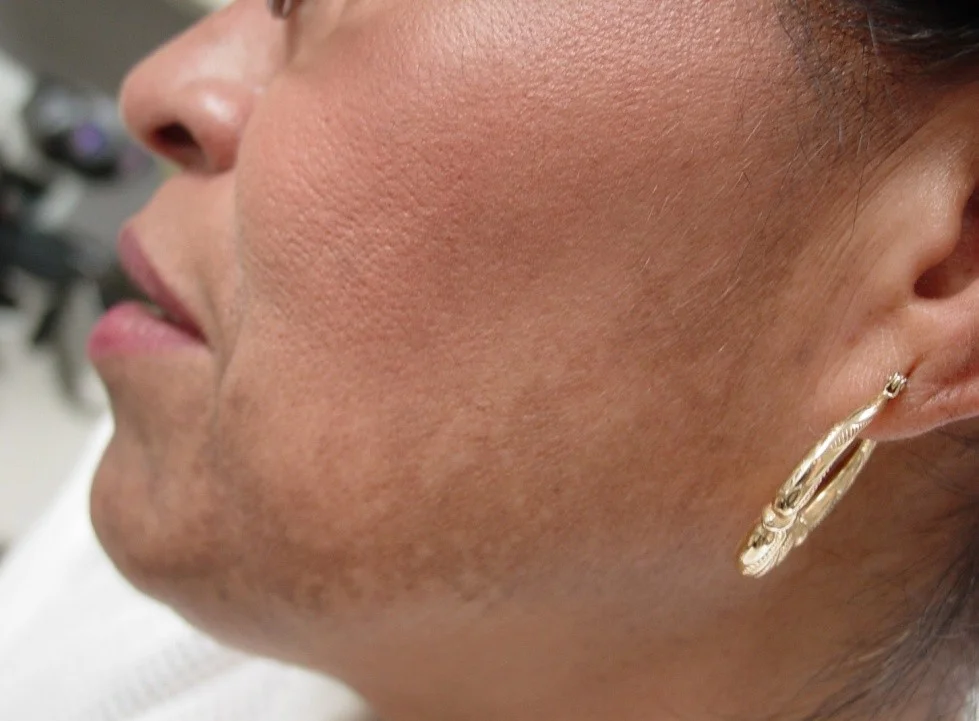
Patch
- Patches are flat but larger than macules
- If it’s flat and larger than 1 cm, it is a patch

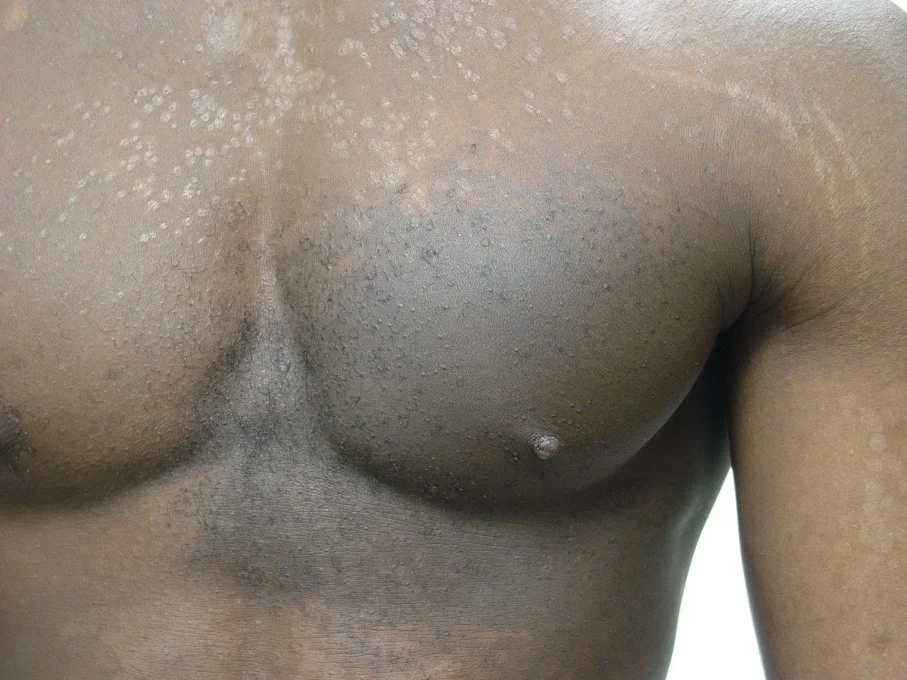

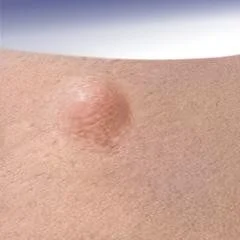
Papule
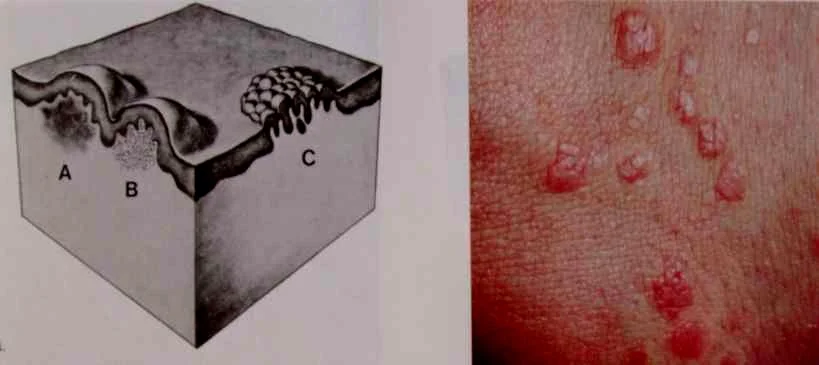
- (L. papula, “pimple”)
- A papule is a circumscribed palpable elevation of the skin less than 1 cm in diameter
- Dermal (drug eruption, lipid deposits), epidermal (warts, molluscum), or both (lichen planus)
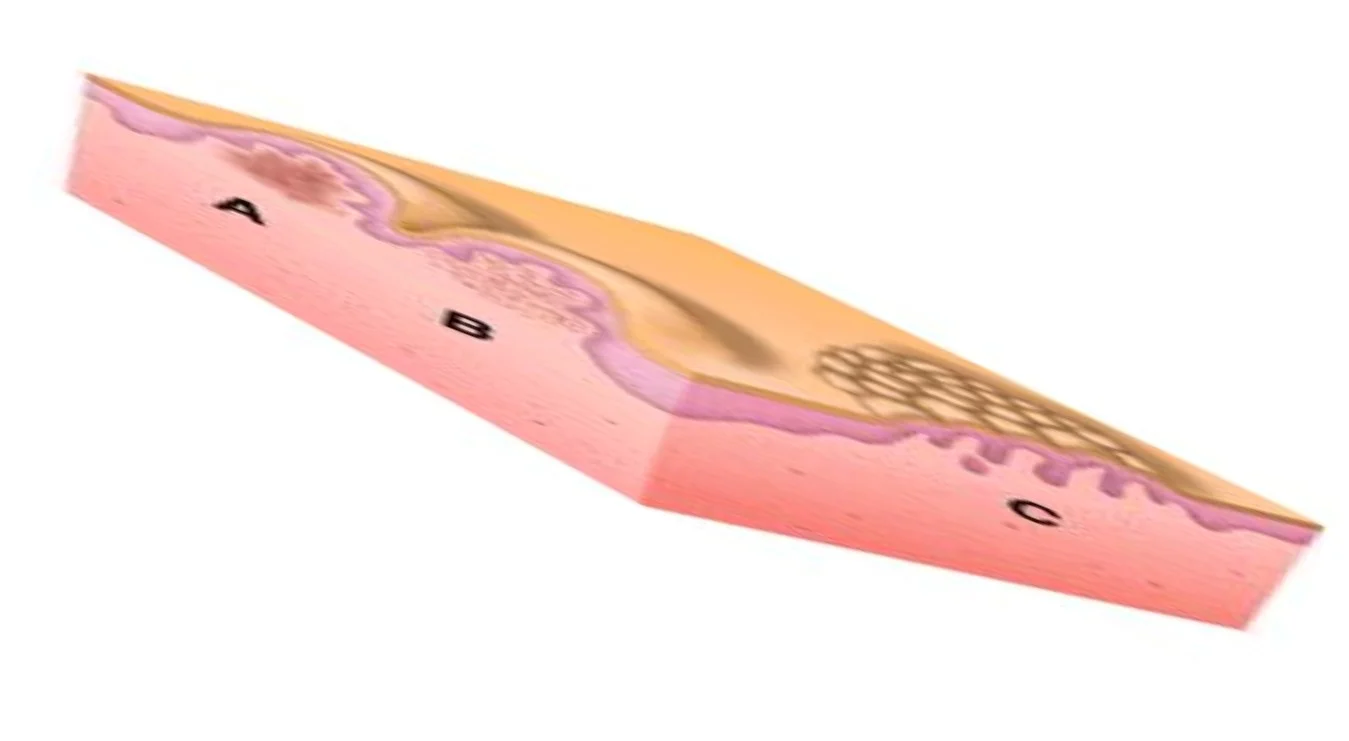

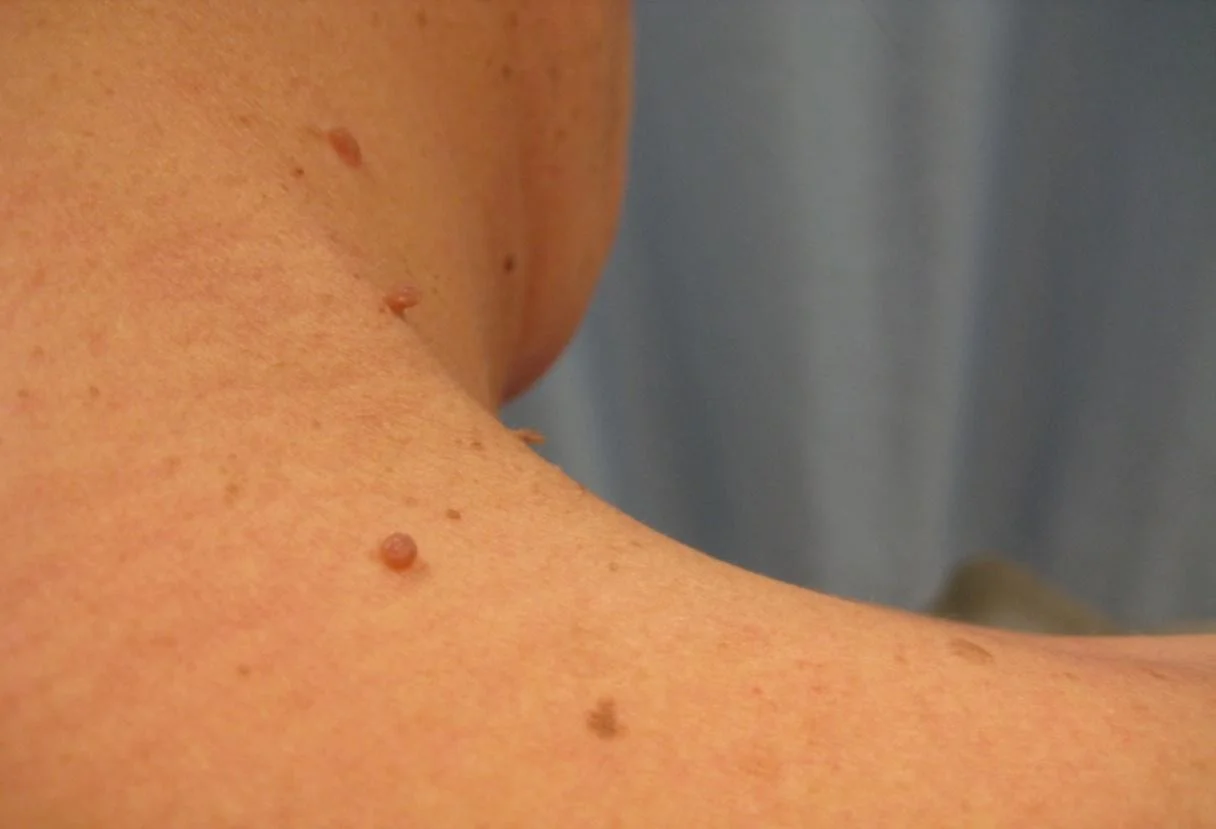
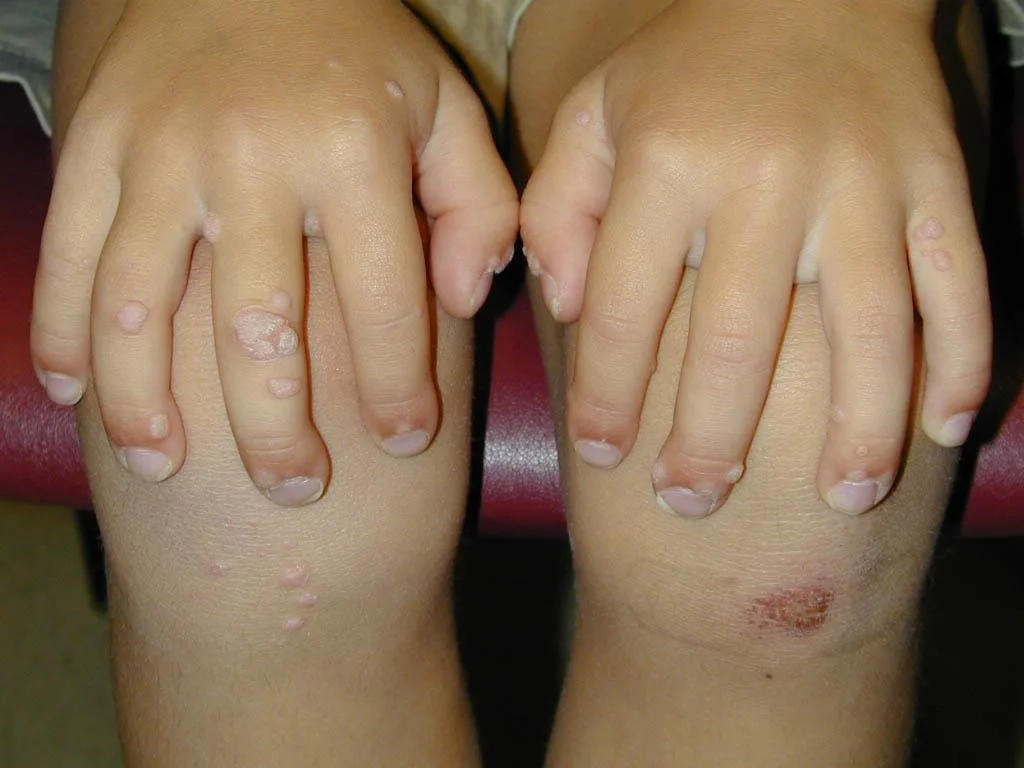
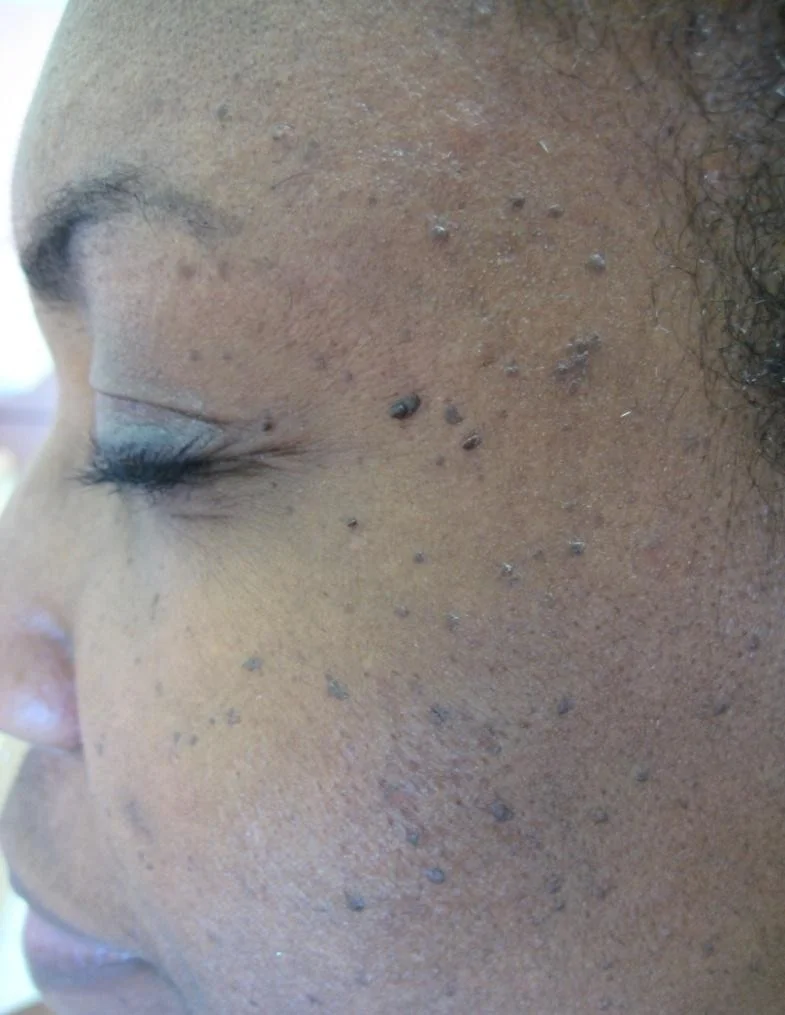
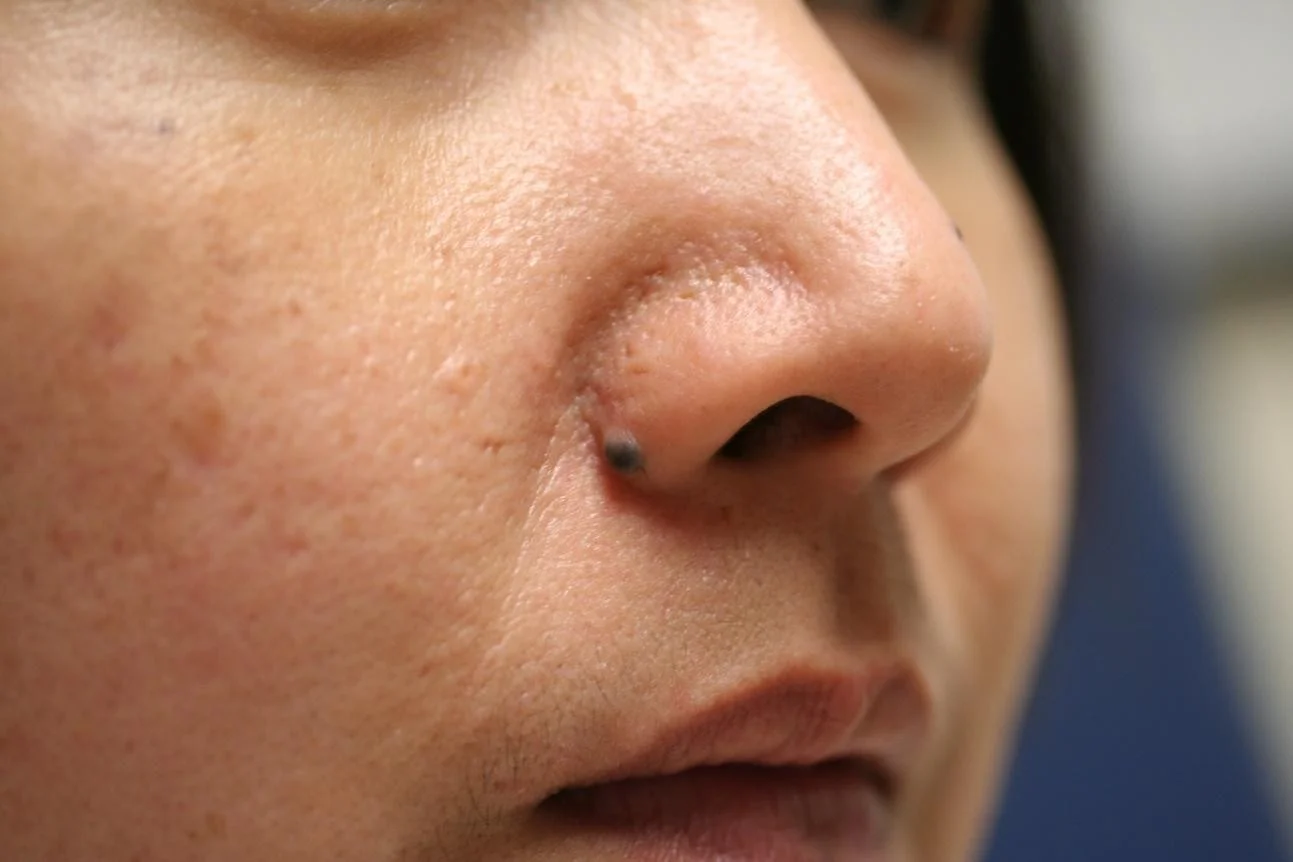
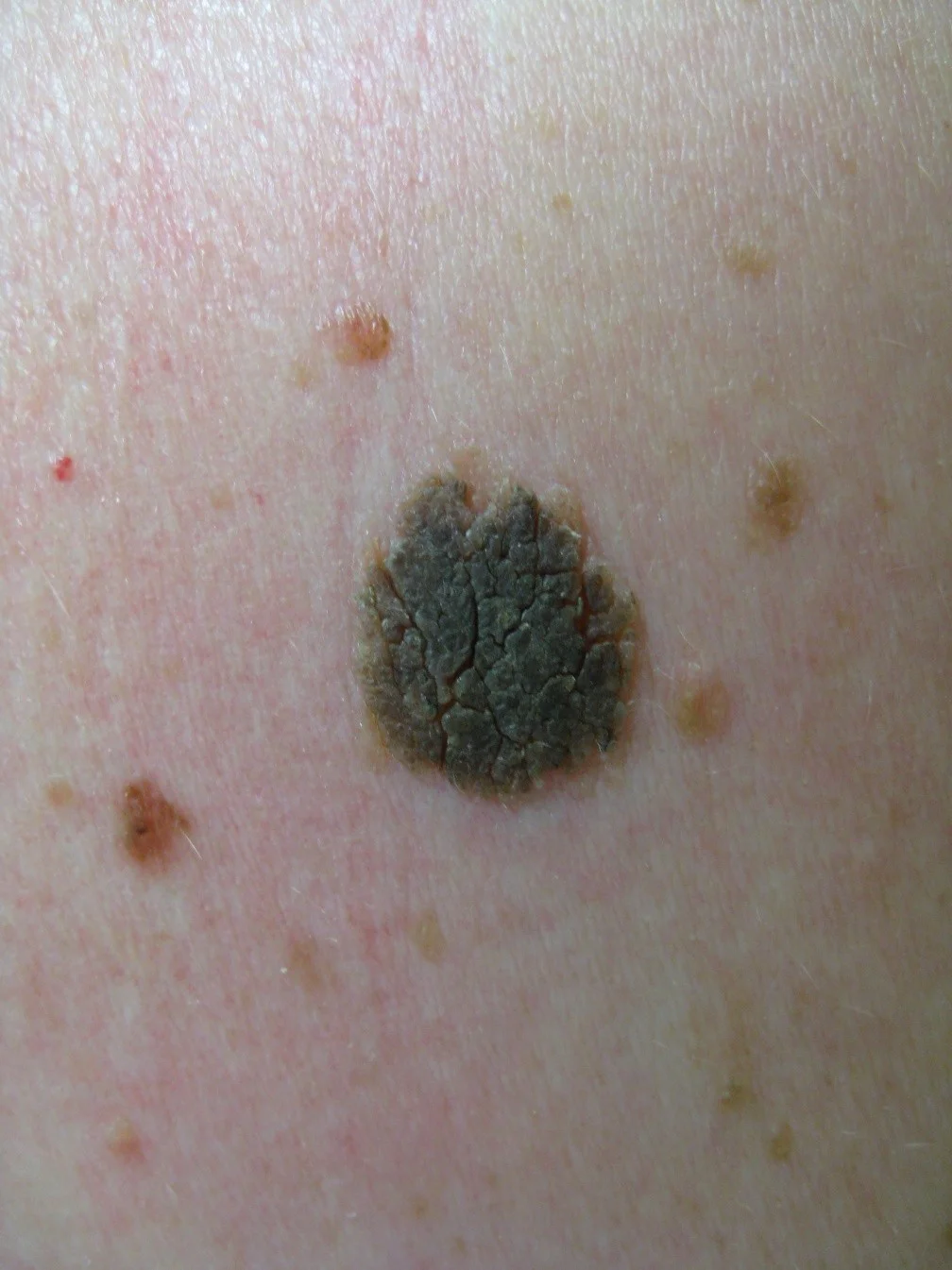
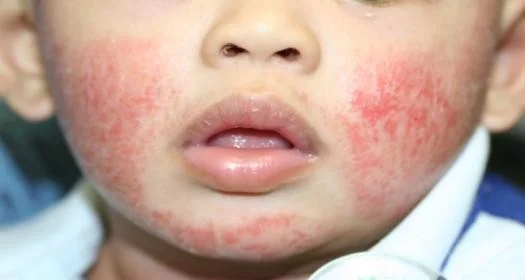
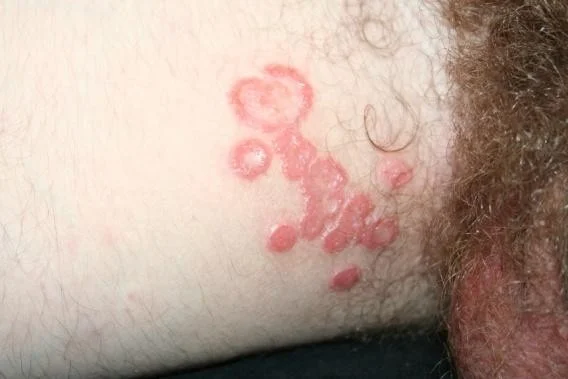
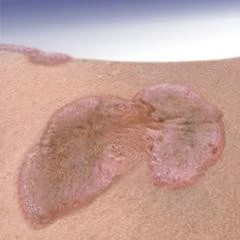
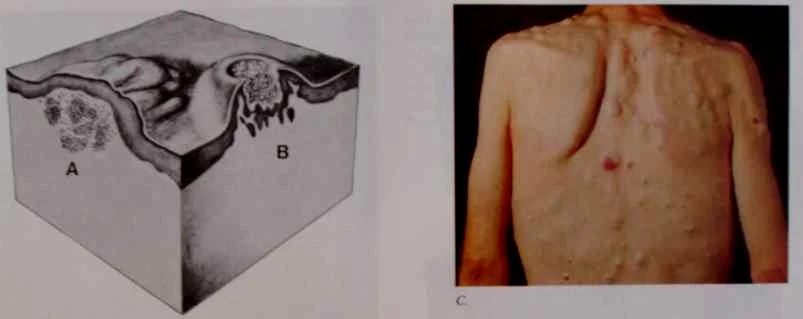
Plaque
- Plaques > 1 cm - A slightly raised lesion greater than 1 cm in diameter - They cast a shadow with side lighting
- Papules confluence (psoriasis)
- Patch thickening (mycosis fungoides the lymphoma of the skin)
- It is caused by a proliferation of cells in epidermis or superficial dermis

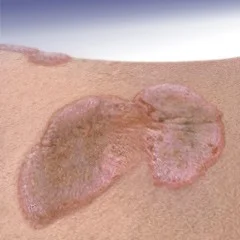
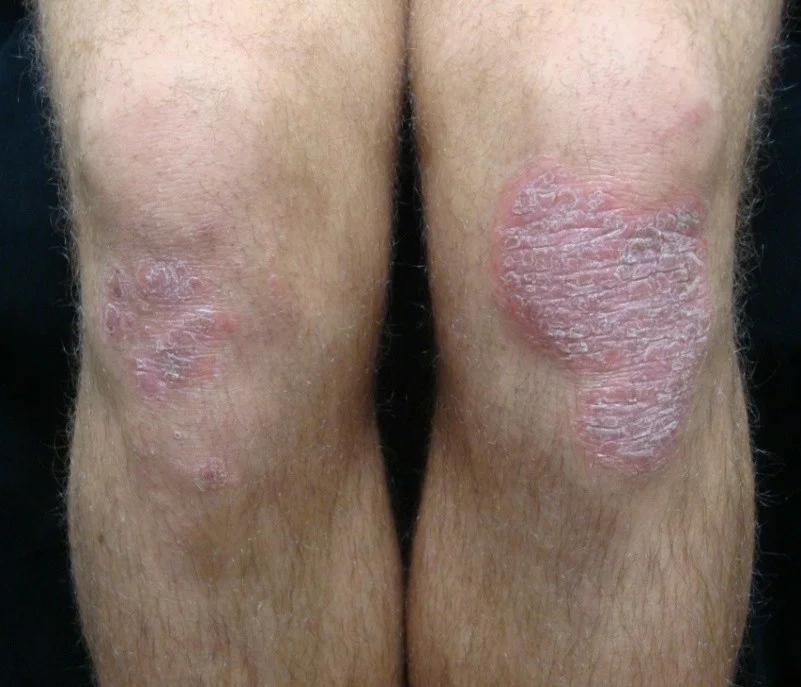
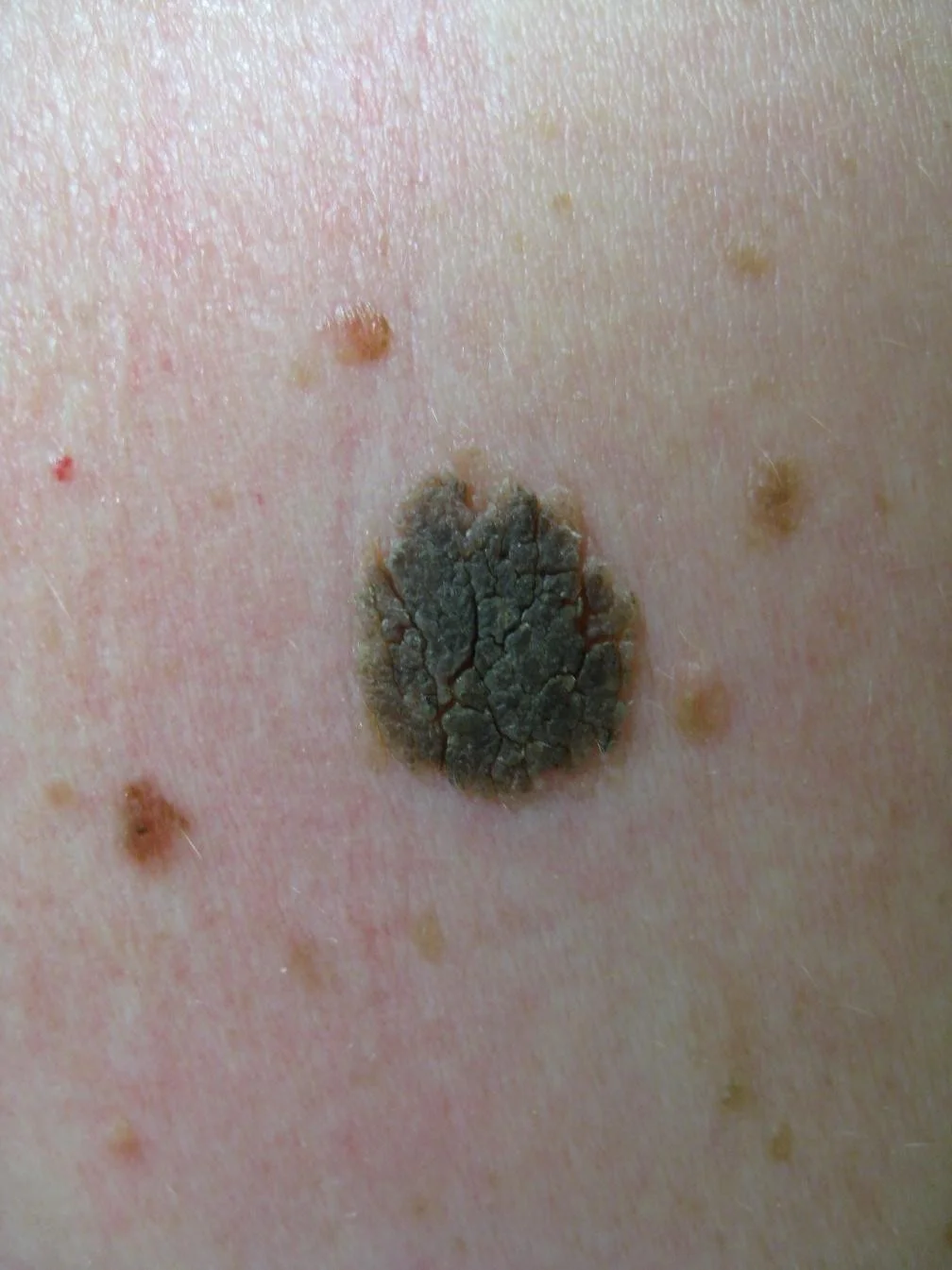
Nodule
Palpable solid deep lesion (depth > diameter)
- Epidermal
- Dermal
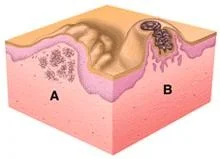
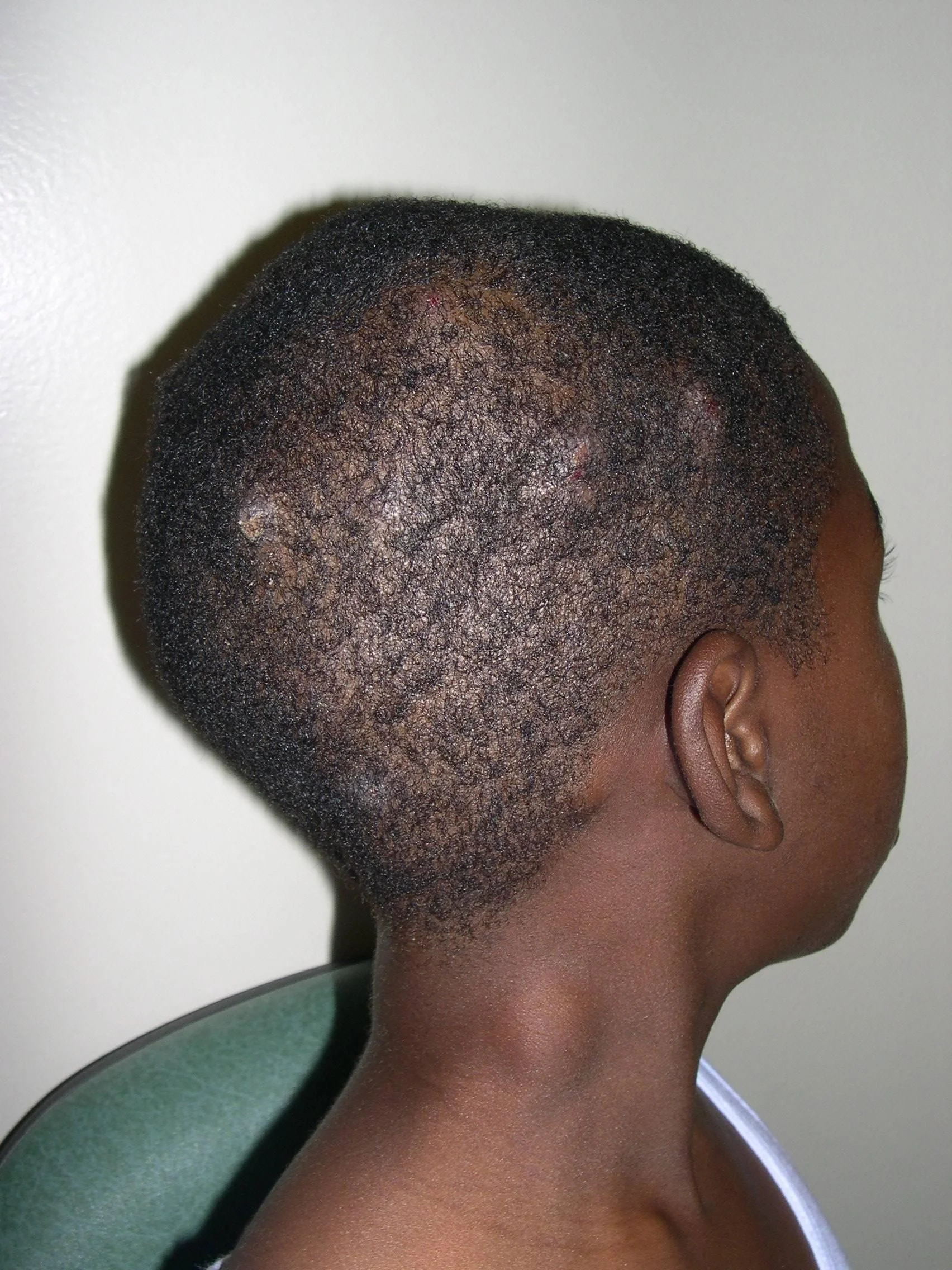
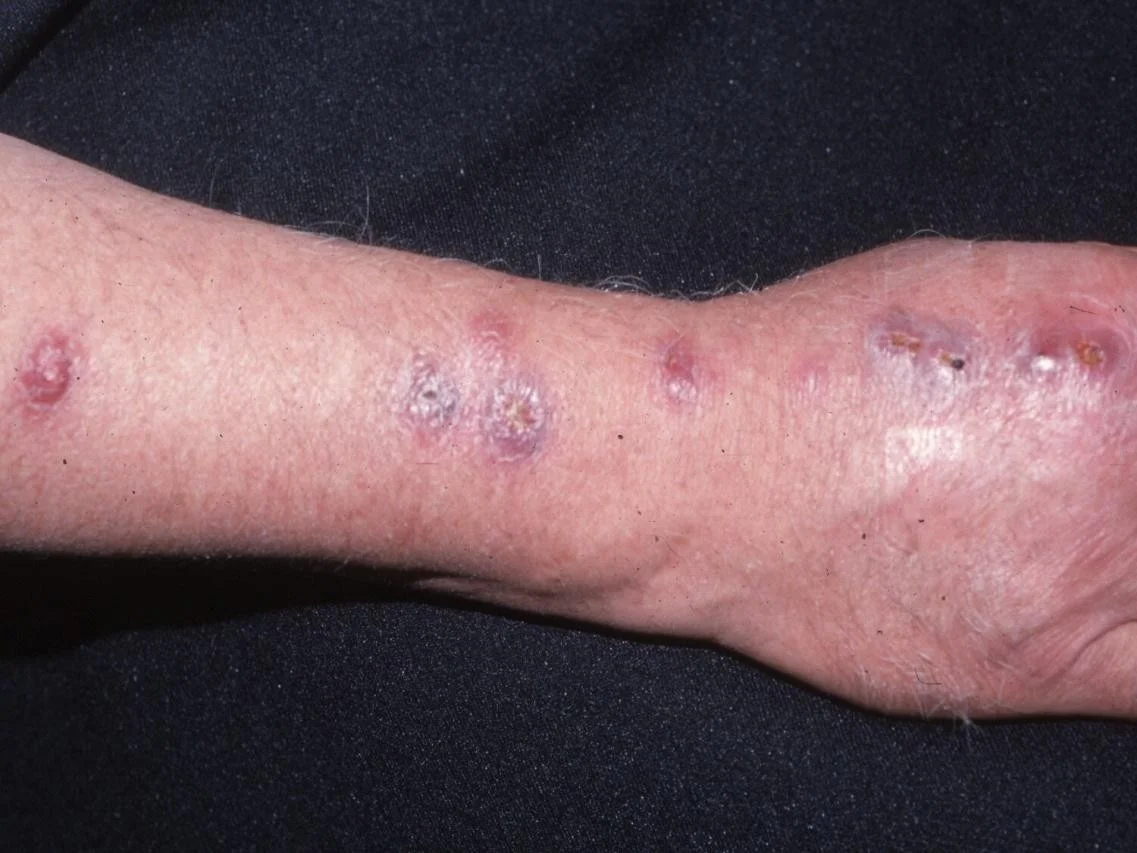
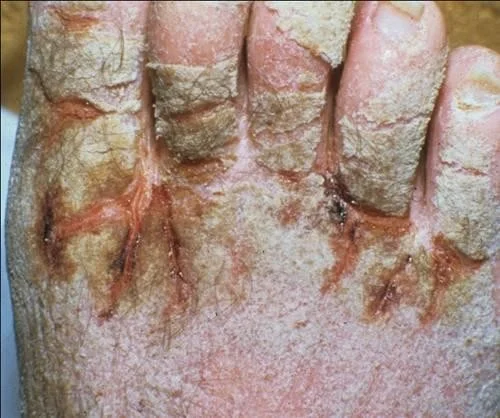
Vesicle
- A raised lesion less than 0.5 cm in diameter containing clear fluid
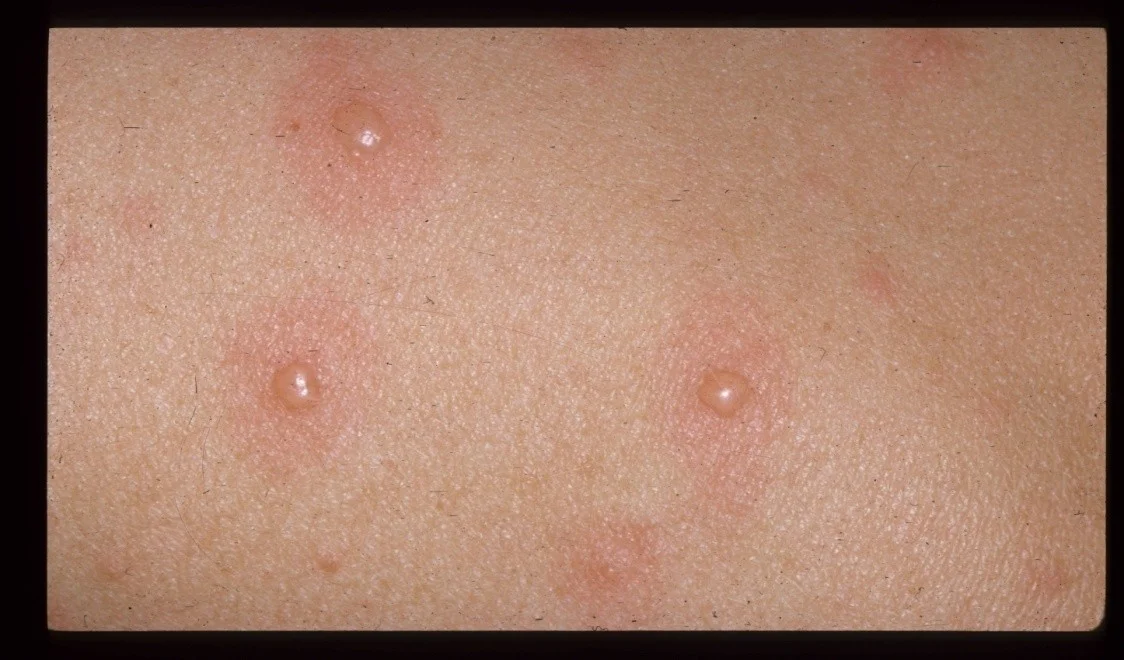
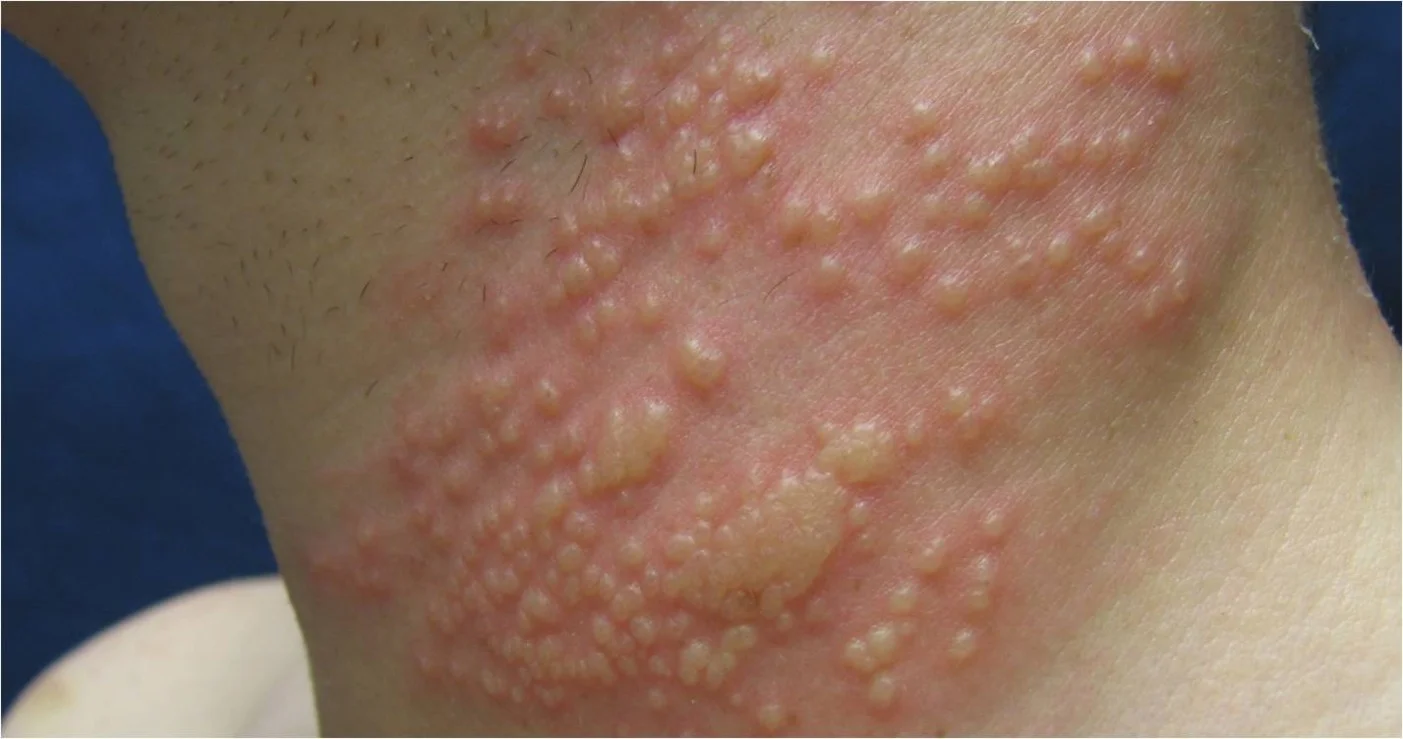
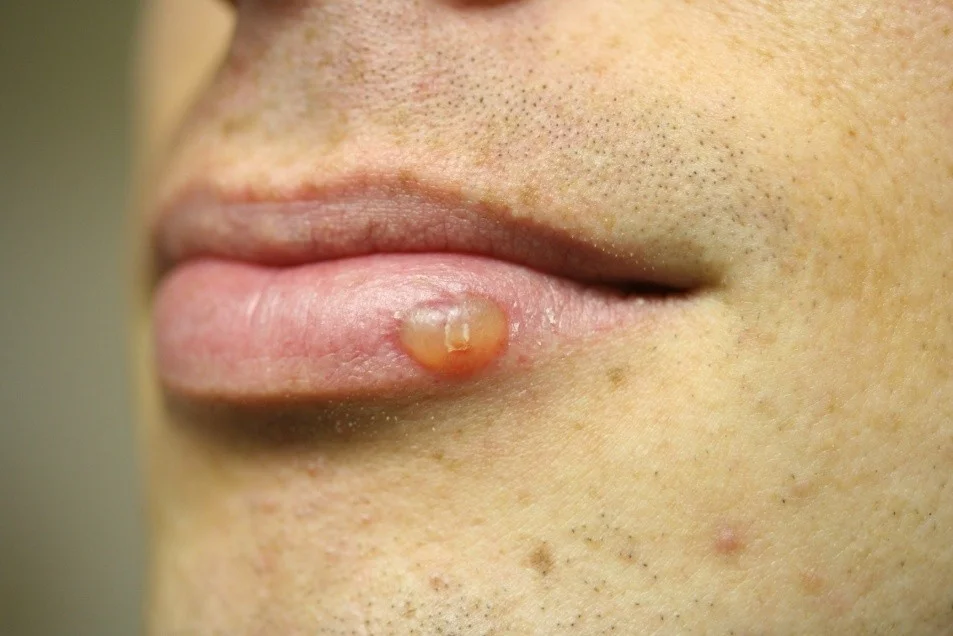
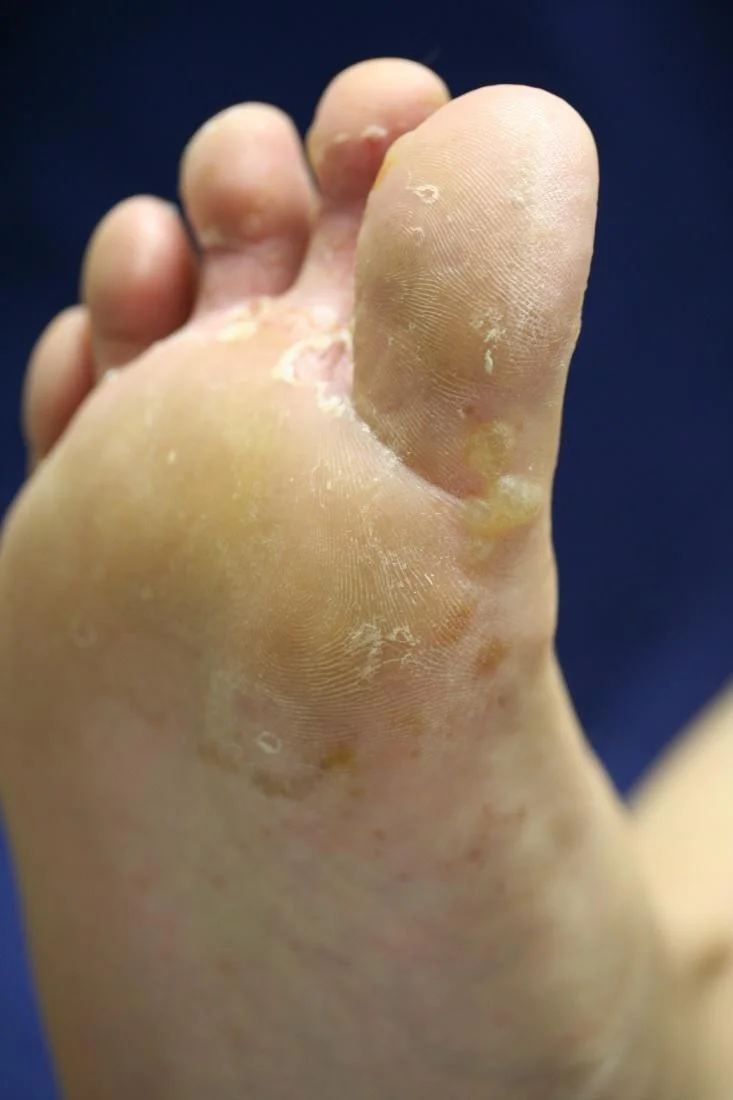
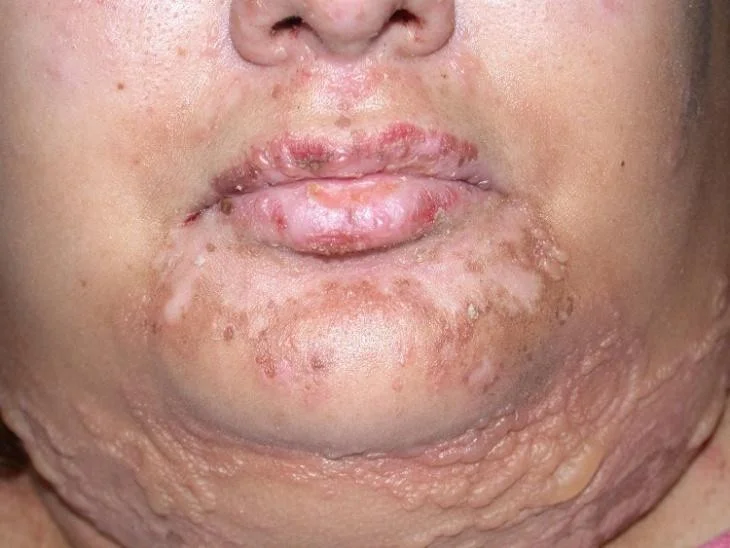
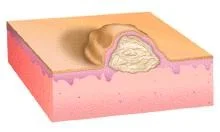
Vesicles - Bulla

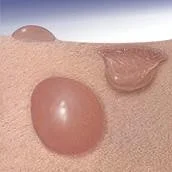
Bulla
- A vesicle that is greater than 0.5 cm in diameter is known as a bulla.
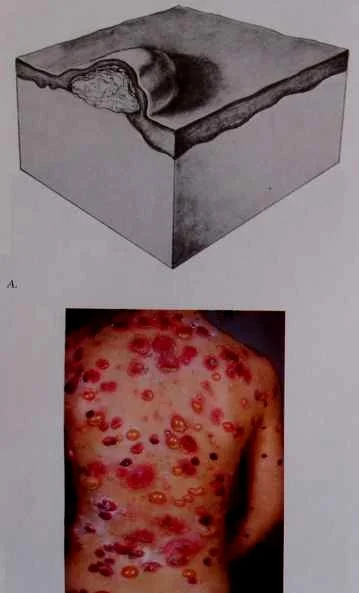
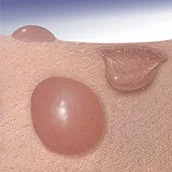
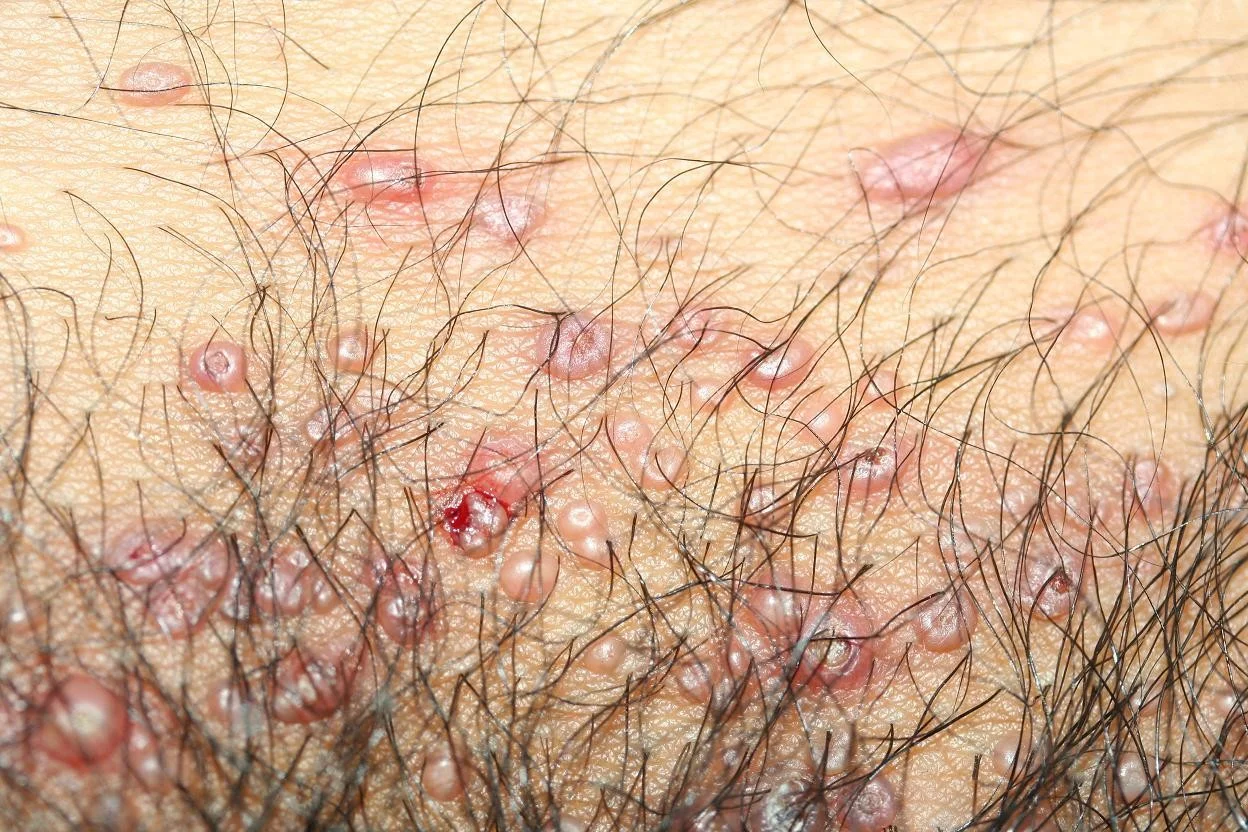
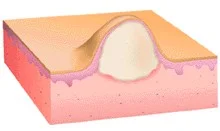
Pustule
Pus is made up of leukocytes and a thin fluid called liquor puris (L.“pus liquid”)
- A pustule is a raised lesion less than 0.5 cm in diameter containing yellow fluid, which may be sterile as in acne and pustular psoriasis, or infected.
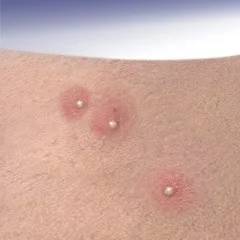
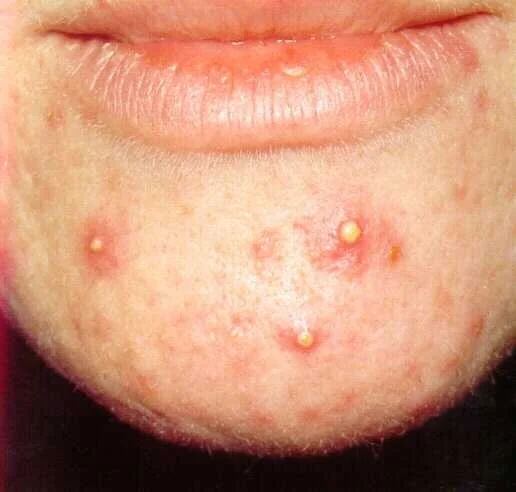
Sterile pastules; ABCD - seen in acne, psoarsos, bacterial staph, commidone?
4s
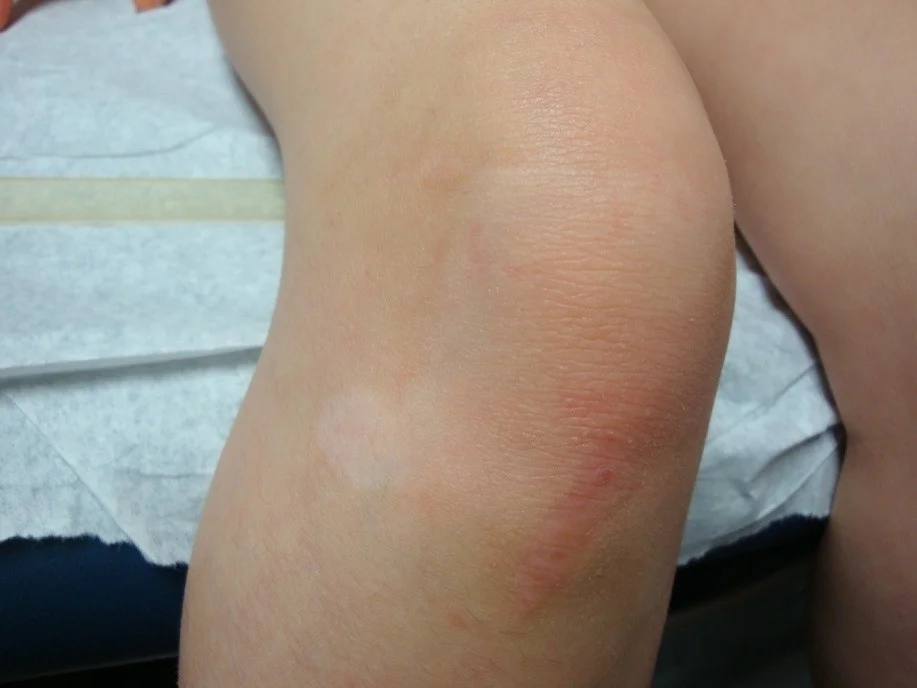
Wheal
- A wheal is a transient, itchy, pink or red swelling of the skin, often with central pallor.
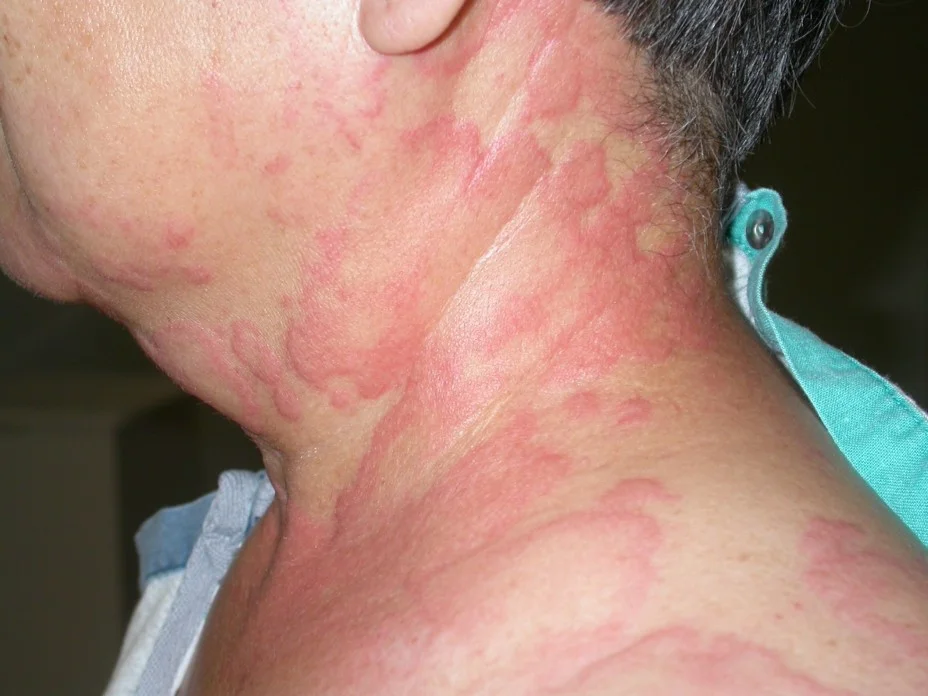
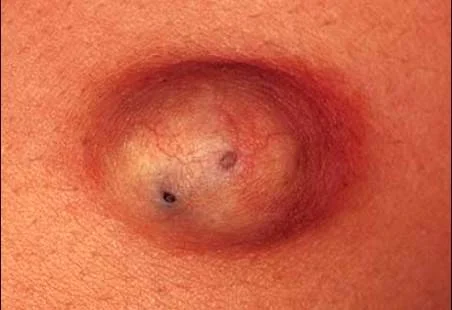
Cyst
palpable soft sac containing fluid.
- Epidermal
- Dermal
Telangiectasia
- Dilatation of capillaries gives rise to this skin condition.
rosseta .. C