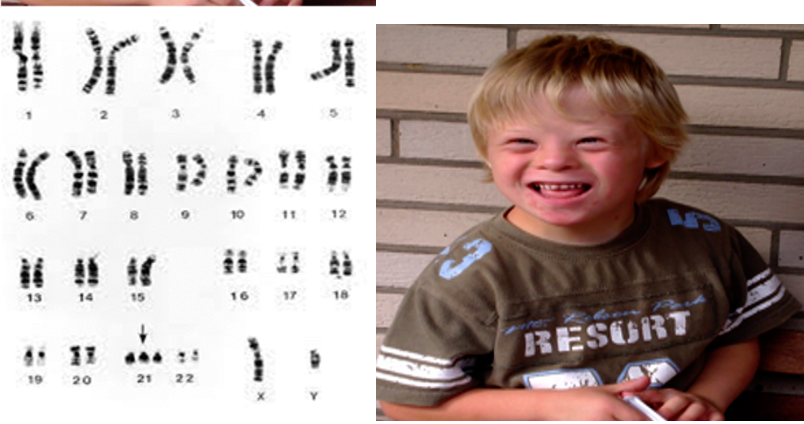
Typical Craniofacial Appearance
- Round face and flat nasal bridge
- Upslanted palpebral fissures
- Epicanthic folds (a fold of skin running across the inner edge of the palpebral fissure)
- Brushfield spots in iris (pigmented spots)
- Small mouth and protruding tongue
- Small ears (75%)
- Flat occiput and third fontanelle
Later Medical Problems
- Delayed motor milestones
- Learning difficulties (severity is variable, usually mild to moderate but may be severe)
- Short stature
- Increased susceptibility to infections
- Hearing impairment from secretory otitis media
- Visual impairment from cataracts (15%), squints, myopia (50%)
- Increased risk of leukemia and solid tumors (<1%)
- Acquired hip dislocation and atlantoaxial instability
- Obstructive sleep apnea (50% to 75%)
- Increased risk of hypothyroidism (15%) and celiac disease
- Epilepsy
- Early-onset Alzheimer disease
Other Anomalies
- Short Neck
- Single palmar creases, incurved and short fifth finger, and wide ‘sandal’ gap between first and second toes
- Hypotonia
- Congenital heart defects (in 40%)
- Duodenal atresia
- Hirschsprung disease (<1%)
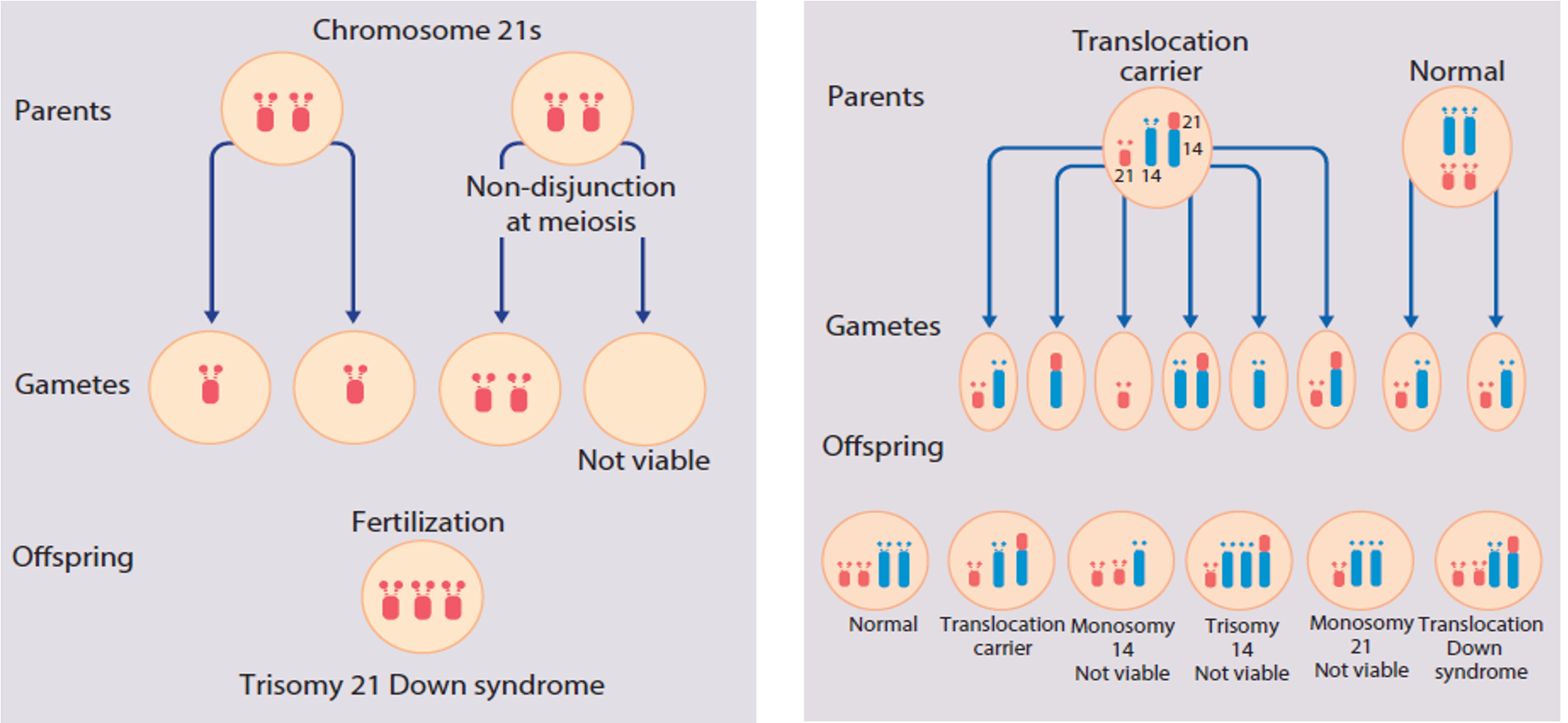
Inheritance of Down Syndrome
Chromosomal Abnormalities
-
Meiotic Nondisjunction (94%):
- Most cases result from an error at meiosis
- The chromosome 21 pair fails to separate, so that one gamete has two chromosome 21s and one has none
- Fertilization of the gamete with two chromosome 21s gives rise to a zygote with trisomy 21
- The incidence of trisomy 21 due to nondisjunction is related to maternal age
-
Translocation (5%): When the extra chromosome 21 is joined onto another chromosome (usually chromosome 14, but occasionally chromosome 15, 22, or 21), this is known as a Robertsonian translocation.
-
Mosaicism (1%): In mosaicism, some of the cells are normal and some have trisomy 21.
Risk of Recurrence
- Trisomy 21 Recurrence Risk: If nondisjunctional, add 1% to maternal age-related risk, which ranges from 1–4%. Most likely, 96–99% will not have a child with Down syndrome.
- Robertsonian Translocation: If the mother is a carrier of 14q:21q translocation, the risk is 15% with amniocentesis and 10% for a liveborn child with Down Syndrome. If the mother is 21q:21q translocation, the risk of recurrence is 100%.