ESOTROPIA
Definition
- Convergent misalignment of the visual axis
- Concomitant
- Infantile esotropia
- Accommodative esotropia
- Incomitant
- 6th nerve palsy
Epidemiology
- Occurs in 2% of American children 1-3 years old;
- No gender difference;
- Most common strabismus of childhood (60%); Z
- Amblyopia is commonly associated with esotropia. ±
Infantile (or congenital) esotropia
-
- Equal sex *distribution;
- Present by 6 months of age;
- Family history of strabismus is common;
- Incidence is higher in patients with a history of prematurity, cerebral palsy, hydrocephalus, and other neurological disorders;
- Maternal cigarette smoking and low birthrate have also been linked to the development of esotropia1.
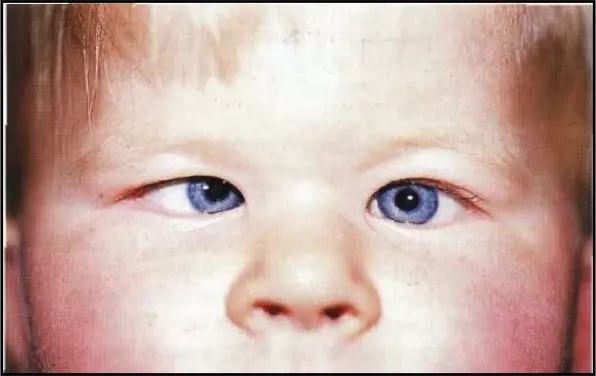
Physical examination:
- Present by 6 months of age;
- Large angle of esodeviation (usually ≥ 30 prism diopters
- Cycloplegic refractions similar to those of normal children of the same age (low hyperopia).
- Often cross-fixation with equal visual acuity in each eye;
- Apparent abduction deficit (pseudoparesis)
Treatment:
Nonsurgical:
- Correct amblyopia before surgery (patching, atropine eye drops)
- Cross-fixation suggests equal visual acuity of both eyes
- Glasses (rarely necessary)
Surgical: mainly
- Surgical alignment earlier than age 2 is associated with better sensory binocular fusion
Look at the corneal light reflex!
 eso lateral
normal central
right str
eso lateral
normal central
right str
Accommodative esotropia
- Convergent deviation of the eyes associated with activation of the accommodation reflex;
- Onset usually between ages 2 and 3
- Often, positive family history;
- May be intermittent at onset;
- Associated with amblyopia (generally from anisometropia);
- May be precipitated by trauma or illness;
- High hyperopia (range +3.00 to +10.00; average: +4.00D). Z
due to high accomidation, only solution is glasses -
OSPE - accomidated ESO - treatment with glasses
- May be partial or total
Treatment:
- Full hyperopic correction
- Treat amblyopia (patching, atropine eye drops)
- If residual strabismus > 10 prism diopters: SURGERY

Look at the corneal light reflex!

R- +10 +9
6th nerve palsy
- Incomitant esotropia (esotropia varies in different fields of gaze);
Congenital 6th nerve palsy is uncommon: - Usually resolves spontaneously within 6 weeks; - Thought to be caused by increased ICP associated with the birth process;
-
Trauma and neoplastic disorders are the most common cause;
-
Neurologic evaluation and CT or MRI recommended;
-
Surgery is indicated when spontaneous resolution does not take place after 6 months or more of follow-up and after exclusion of intracranial lesions.

SYMPTOMS
- Esotropia
- Horizontal diplopia: 1. Uniocular 2. Painless 3. Increase on looking towards the lateral side.


Signs
-
- Limitation of abduction
-
- Esotropia in primary position
-
- Uncrossed horizontal diplopia: increased towards the paralyzed side.
-
- Slight face turn towards the side of diplopia