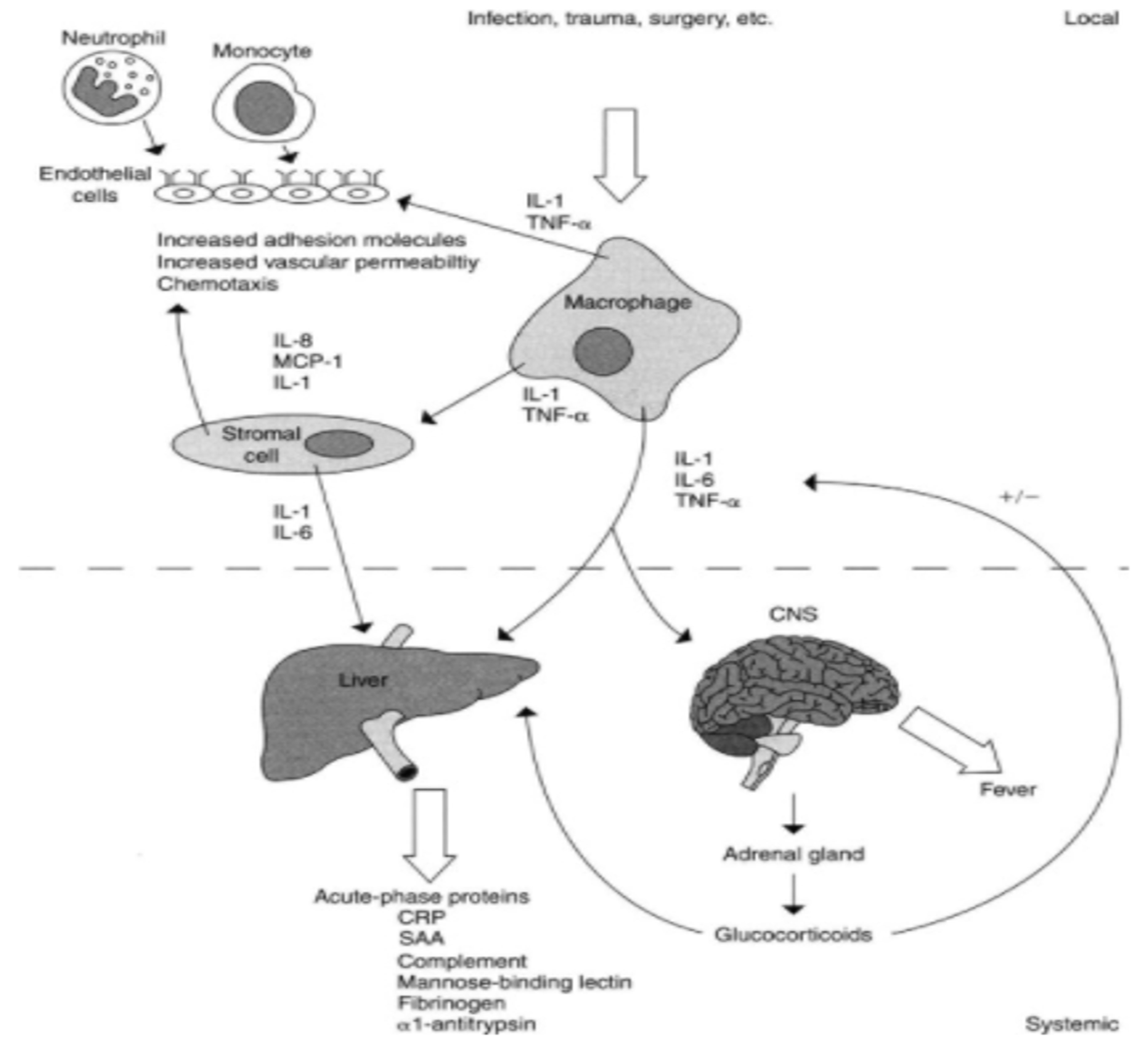
Acute-phase proteins:
Amino acids utilized by the liver as a substrate for gluconeogenesis, also used in the liver as substrate for the ‘acute-phase protein response’.
This response involves increased production of proteins (positive acute-phase proteins) and decreased production of another (negative acute-phase proteins)
Positive acute-phase proteins (≠ after injury)
- C-reactive protein
- Haptoglobins
- Ferritin
- Fibrinogen (COVID)
- α1-Antitrypsin
- α2-Macroglobulin
- Plasminogen
Negative acute-phase proteins (Ø after injury)
- Albumin
- Transferrin
The acute-phase response is mediated by pro-inflammatory cytokines (notably IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-α) Its function is in host defence and the promotion of healing.
The mechanisms mediating muscle catabolism are inflammatory mediators and hormones (e.g. cortisol) released as part of the metabolic response to injury