Rheumatic Fever
gram-positive coccus that frequently colonizes the skin and oropharynx. It has :
Structural components M protein: The presence of the M protein is the most important virulence factor for group A streptococcal infection in humans
Enzymes Streptokinases which facilitate the Rapid spread of streptococci through tissues - resulting in short incubation peroid. attach to the epithelial cells of the upper respiratory tract and produce a battery of enzymes allowing them to damage and invade human tissues. After an incubation period of 2-4 days, the invading organisms elicit an acute inflammatory response with 3-5 days of sore throat, fever, malaise, headache, and an elevated leukocyte count
Toxins: Eythrogenic Toxins causes rash of scarlet fever & associated with a toxic shock-like syndrome
Streptolysins: Streptolysin O lyse red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
- group A beta-hemolytic Streptococcus attach to the epithelial cells of the upper respiratory tract and produce a battery of enzymes allowing them to damage and invade human tissues.
- After an incubation period of 2-4 days, the invading organisms elicit an acute inflammatory response with 3-5 days of sore throat, fever, malaise, headache, and an elevated leukocyte count
Diseases caused by strept. pyogenes - Cause
**A) Supppurative infections Pus forming
- ●Pharyngitis & acute follicular tonsilitis
- ●Otitis media
- ●Bronchopneumonia
- ●Bacteremia and septicemia
- ●Meningitis
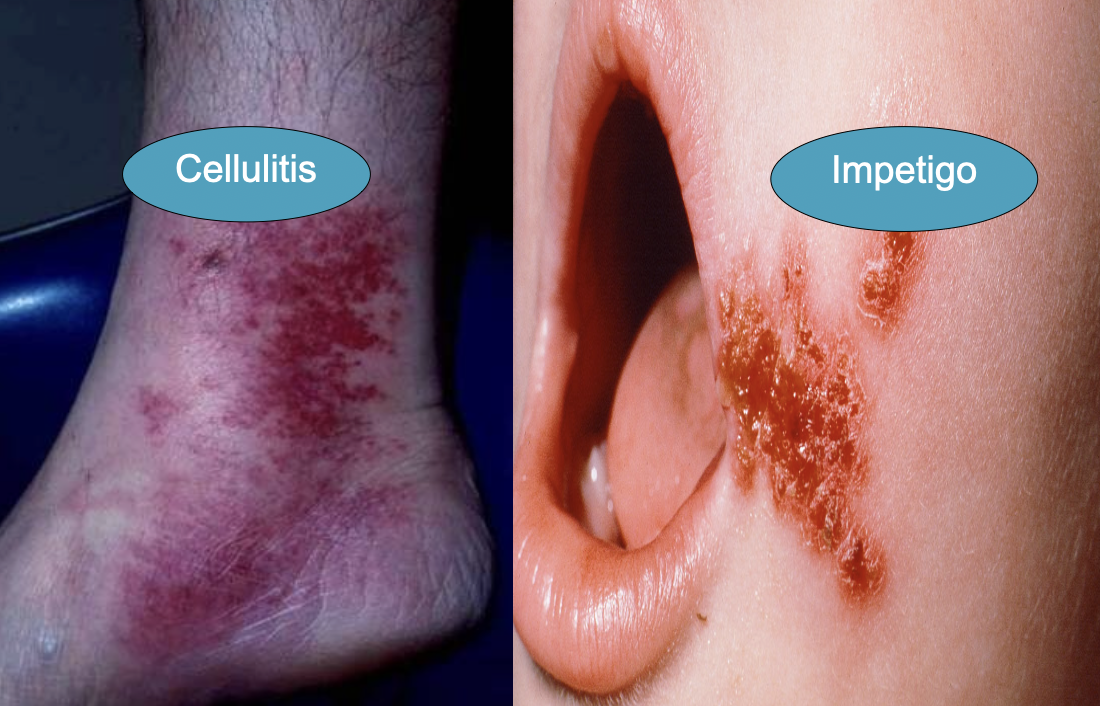
- ●Skin infection, Impetigo, Pyoderma, erysipelas and cellulitis
B) Toxogenic diseases
-
toxic shock like syndrome - similar in pathogenesis and manifestation to staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome .
-
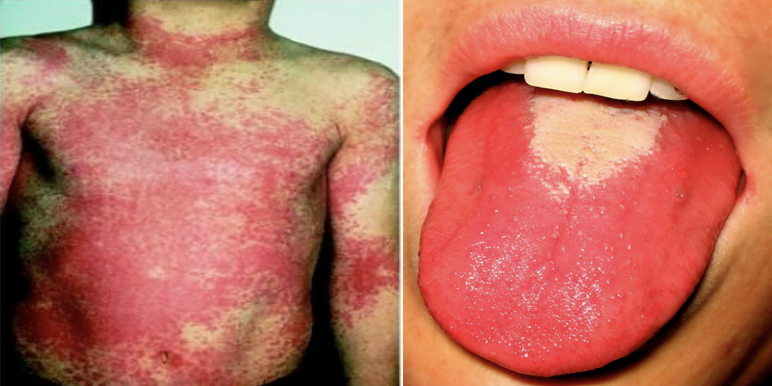
Scarlet fever (erythrogenic toxin) Usually affects children ,characterized by fever, skin rash & stomatitis (Strawberry tongue) . - The skin rash is due to direct effect of the erythrogenic toxin on the skin .
C) Post streptococcal sequelae
- Non suppurative complication which follow strept. pyogenes infection by 1-3 weeks
- Affect mainly in children between 5 – 15 years
- Occur following pharyngitis or skin infection (nephrogenic strains)
- No bacteria present in pharynx at time of occurance of the complications
These complication includes
- Rheumatic fever.
- Glomerulonephriti Why? Due to incomplete eradication, antibodies will form and attack M protein structures in the body, or similar structures - susceptible in children due to weak immunity?
Pathogenesis
-
similarity and cross reactivity (molecular mimicry): M protein of Strept pyogenes is similar with heart myosin glycoprtein so antibodies against M protein will cross react with heart myosin glycoprtein joint proteins, basal ganglia etc….. (autoimmunity)
-
Immune comples disease (type III hypersensitivity): Due to prolonged antigenemia in vivo, antigen antibody complexes will be formed into the circulation and precipitate on basement membrane of renal glomeruli then damage of renal glomeruli occur by type III hypersensitivity