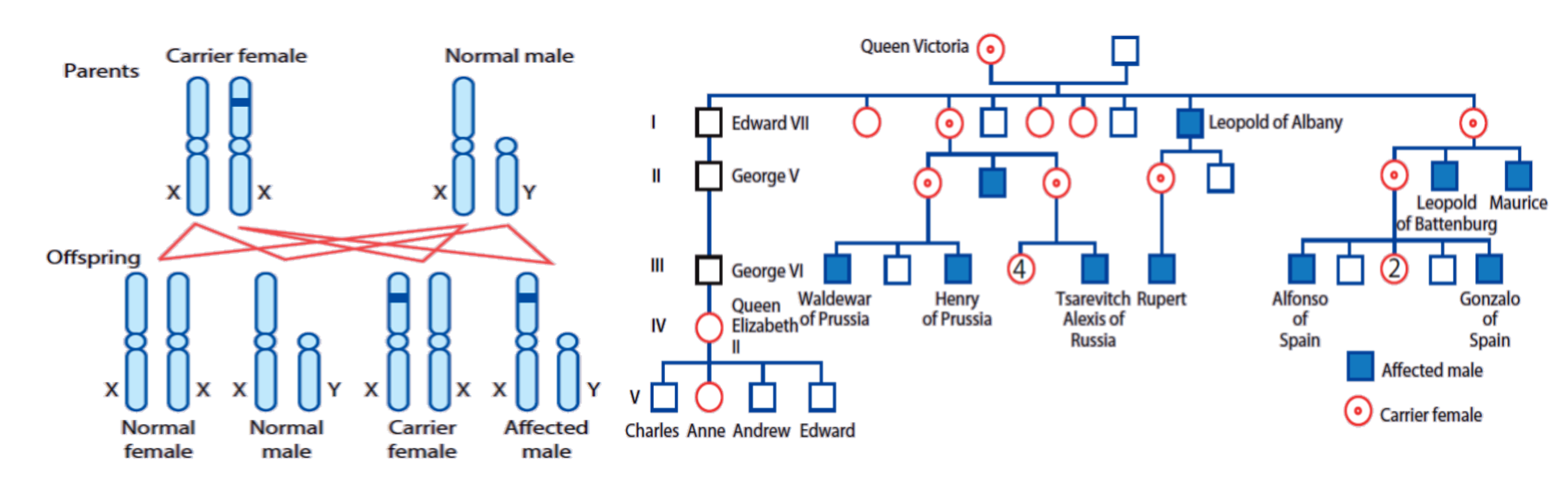
- Males are affected.
- Female carriers are usually healthy; occasionally, a female carrier shows features of the disease.
- Each son of a female carrier has a 1 in 2 (50%) risk of being affected.
- Each daughter of a female carrier has a 1 in 2 (50%) risk of being a carrier.
- Daughters of affected males will all be carriers.
- Sons of affected males will not be affected because a man passes a Y chromosome to his sons.
- Family history may be negative – many arise from new mutations or gonadal mosaicism.
- Identifying female carriers is important to provide genetic counselling.
Examples of X-linked recessive disorders:
- Hemophilia A and B
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
- Color blindness
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Fragile X syndrome