Case Study: 1-Year-Old Boy with Growth and Gastrointestinal Issues
At 1 year of age, a boy was at the 50th percentile for height and weight. At 2 years of age, he is at the 25th and 10th percentiles respectively.
Review of systems reveals fussiness, loose stools, and possibly stomach aches all beginning after the mother stopped breastfeeding and introduced table foods. Mother has consumed milk products lifelong, but her son does not drink cow milk.
The patient was a full-term infant with a birth weight of 3.6 kg. There were no complications reported with labor or delivery.
There was no history of medical problems. Family history was unremarkable. The patient was not taking any medications and had no medications and had no recent illnesses or sick contacts.
On examination, He was not in acute distress, no jaundice. Lungs and heart exam were normal. The abdomen was soft, distended, and without hepatosplenomegaly. Neurologic and skeletal exams were normal. The stool was negative for occult blood.
Questions and Answers
a- Questions for the Mother
- What’s the type of food that he received?
- Is there any similar condition in the family?
b- Important Signs to Look For During Examination
- Pale
- Aphthous stomatitis
- Clubbing
c- Important Investigations
- Serology for IgA antibody direct against tissue transglutaminase
- Jejunal biopsy (gold standard)
- CBC
d- Most Likely Diagnosis and Differential Diagnoses
- Most Likely Diagnosis: Celiac disease
- Differential Diagnoses:
- Malabsorption disease
- Lactose intolerance
e- Important Points in the Management Plan
- Strict lifelong gluten-free diet.
- Vitamins, iron, and calcium supplementation.
Case Study: 9-Year-Old Boy with Bed-wetting and Dehydration
A 9-year-old boy brought to your clinic by his mother. She noticed that he’s not feeling well for the past one week with a bed-wetting. On examination he is found to be dehydrated.
Questions and Answers
1. Relevant Questions for the Mother
- Polyuria
- Polydipsia
- Weight loss
- Vomiting
- Burning sensation on micturition
2. Examination
- Vital signs (BP, PR, RR, temperature).
3. Investigations
- Urinalysis
- Urine culture
- Blood glucose
- HA1C
- Blood gases
- Renal function test
- Liver function test
4. Differential Diagnoses
- ✓ DM (Diabetes Mellitus)
- UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)
- DI (Diabetes Insipidus)
- Child abuse
- Psychogenic polydipsia???
5. Management
- Admit
- IVF (Intravenous Fluids)
- Correction of acidosis
- Correction of hyperglycemia
- Ab if UTI (Antibiotics if UTI)
Case Study: 2-DKA(IDDM)
Questions and Answers
1 - Relevant Questions for the Mother
- Ask about Excessive drinking (polydipsia)?
- Ask about Polyuria and polyphagia?
- Ask about Weight loss?
- Ask about Smell of acetone on breath
- Ask about Vomiting, Dehydration, Abdominal pain?
- Is there any Burning sensation on micturation?
2 - Examination
- General examination and abdominal examination after taking vital signs (BP, PR, RR & TEMP)
3 - Differential Diagnoses
- DKA (IDDM)
- DI (diabetes insipidus)
- Chronic renal failure
- Psychogenic
- UTI, CHILD ABUSE
4 - Investigations
- Urine analysis and culture
- Blood glucose
- Blood ketones
- Blood gas
- HA1C
- Renal function test
- Liver function test
5 - Management
- ABC (initial bolus)
- Admission to ICU
- IV fluid (maintenance & Deficit)
- Insulin (initially IV infusion then subcutaneous)
- Electrolyte
- Antibiotic (if there is suspension of infection)
- Monitoring of blood glucose, blood gases, electrolyte.
- Education and dietary planning
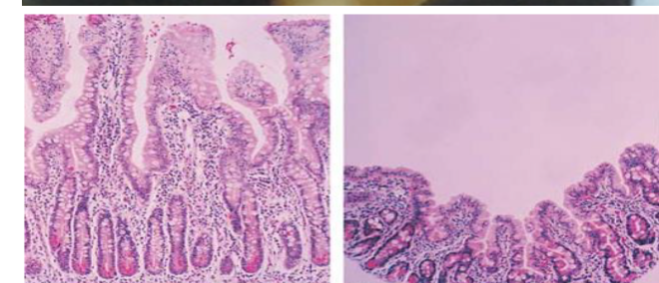
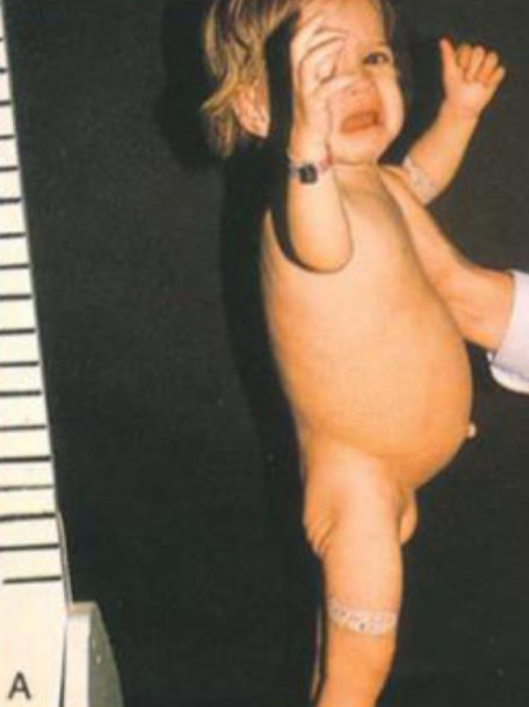 A 18 months old boy manifests poor appetite, diarrhea, and irritability.
He had been well until 9 month of age. Thereafter, he was weaned from
breast milk to regular foods. His growth curve is flattening. Patient with type 1 diabetes on insulin, experiencing frequent hypoglycemia and abdominal distension.
A 18 months old boy manifests poor appetite, diarrhea, and irritability.
He had been well until 9 month of age. Thereafter, he was weaned from
breast milk to regular foods. His growth curve is flattening. Patient with type 1 diabetes on insulin, experiencing frequent hypoglycemia and abdominal distension.
- What is your diagnosis?
- Celiac disease
- How to diagnose this condition?
Antibody titer (deamidated gliadin peptide and transglutaminase).
- Tissue transglutaminase - Ig A
- Duodenal Biopsy
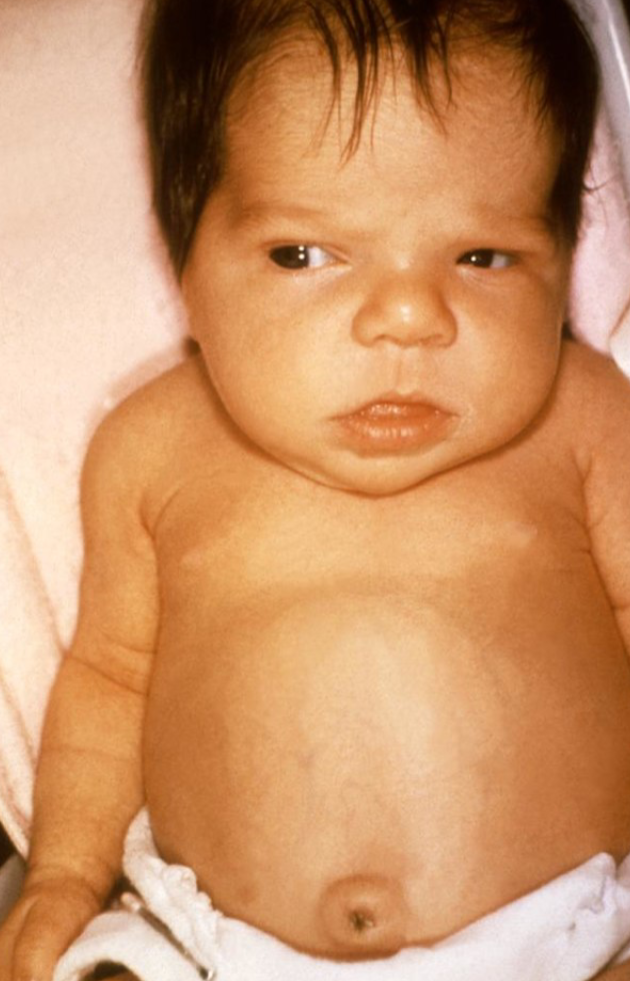
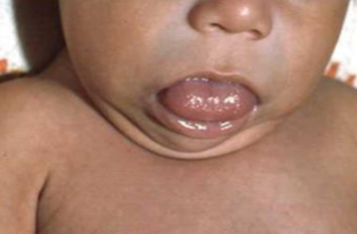 3-month-old infant with developmental delay, constipation, and umbilical hernia.
Name of the disease? Congenital hypothyroidism (cretinism) Z
3-month-old infant with developmental delay, constipation, and umbilical hernia.
Name of the disease? Congenital hypothyroidism (cretinism) Z
What are the clinical features? Developmental delay, constipation, coarse face, protruded large tongue, abdominal distension, umbilical herniation, and jaundice.
What is the treatment? Thyroxine (hormone replacement thereby)
- Q2. What are the relevant investigations?
- a. A karyotype test (size, shape, and number of chromosomes).
- b. Blood glucose and ultrasound of abdomen.
- c. Blood levels of thyroid hormone (T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
- d. Urinary test for heparan and dermatan sulfate and MPS enzyme assay.
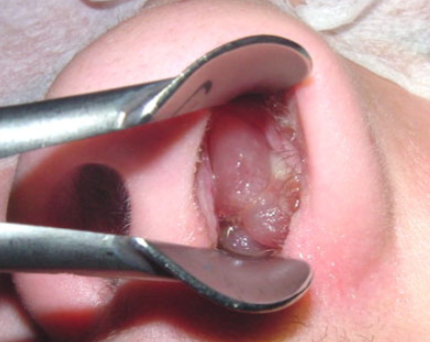
Cystic Fibrosis Z
6-year-old child with recurrent chest infection, chronic diarrhea, and failure to thrive. What are the clinical features? Recurrent chest infections, diarrhea, and failure to thrive.
What is the next diagnostic test? Sweat test for chloride. Finding: Nasal polyps
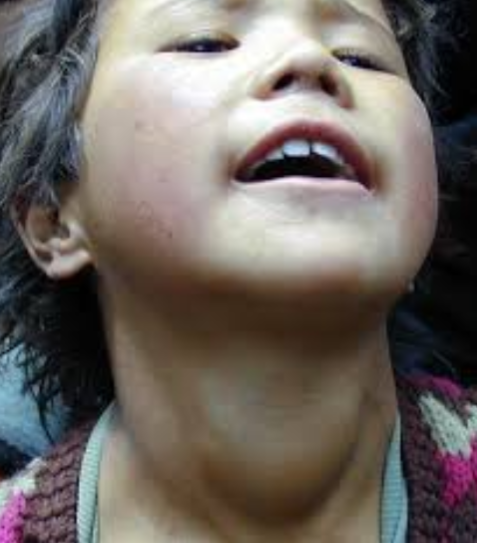
Hashimoto Thyroiditis
What is the observed abnormality? Diffuse neck swelling (goiter).
What is the likely diagnosis? Hashimoto thyroiditis.
What investigation should be done? Thyroid function test.
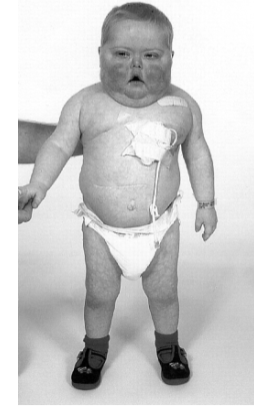
Syndrome: Cushing syndrome
- Cause? Adrenal adenoma, prolonged use of steroid
- Treatment? Surgical removal of adrenal gland or tapering off ketoconazole, metyrapone
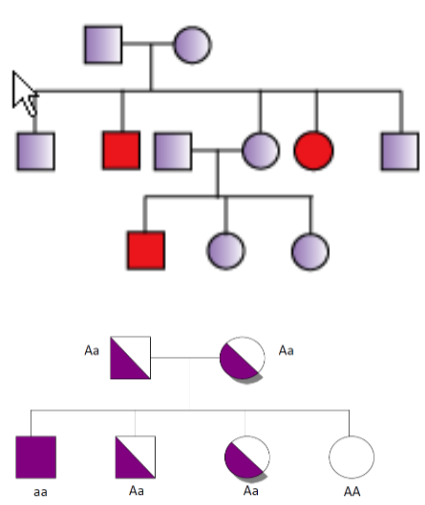
- What is the mode of Inheritance? Autosomal recessive inheritance pattern
- Give 2 Examples: Cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia
- Features seen in the family tree
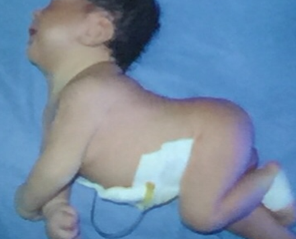
Hyperbilirubinemia after birth
- Can develop this condition
- Diagnosis: Kernicterus or bilirubin encephalopathy
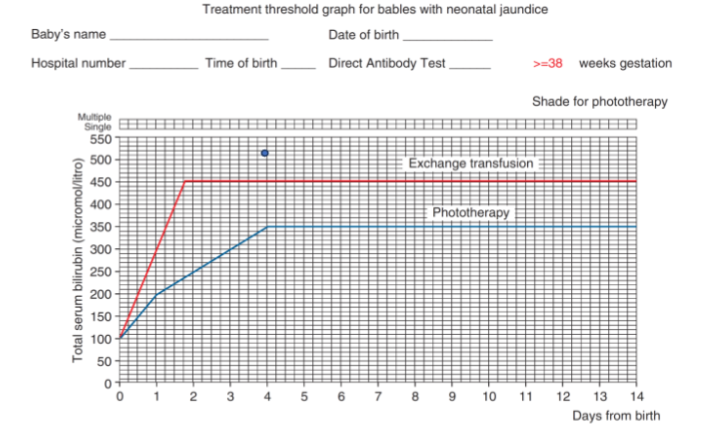
Case
A 4 days old term healthy baby with neonatal jaundice. How do you will manage this baby? Exchange transfusion, and pre- and post Phototherapy.
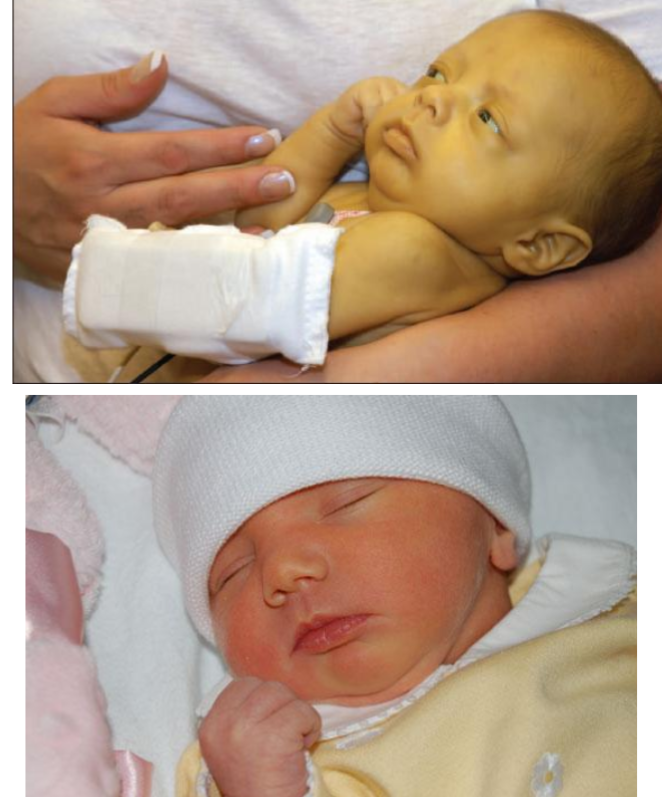
Case
Upper pic type of jaundice ? conjugated hyperbilirubinemia Lower pic type of jaundice ? Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia

Case
What is the cause of jaundice in this infant ? Neonatal hepatitis (cholistasis)
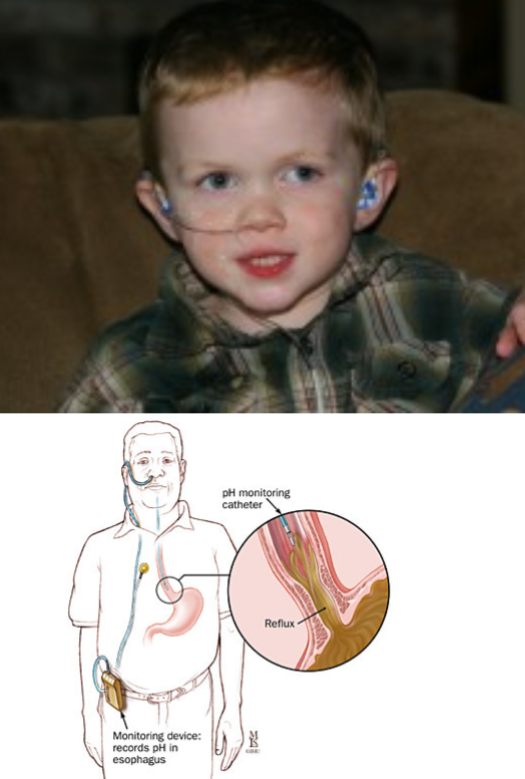
Case
What is the device ? pH probe Used for ? Diagnosis of GRED
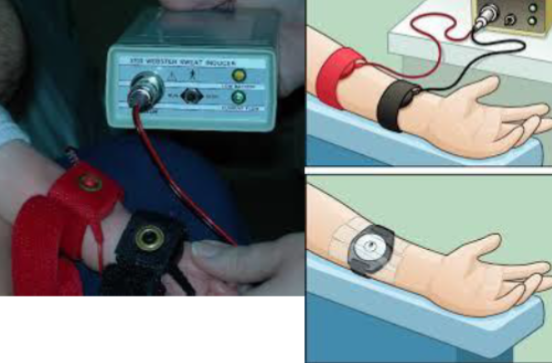
Case
What is the device ? sweat chloride test Used for diagnosis of ? cystic fibrosis