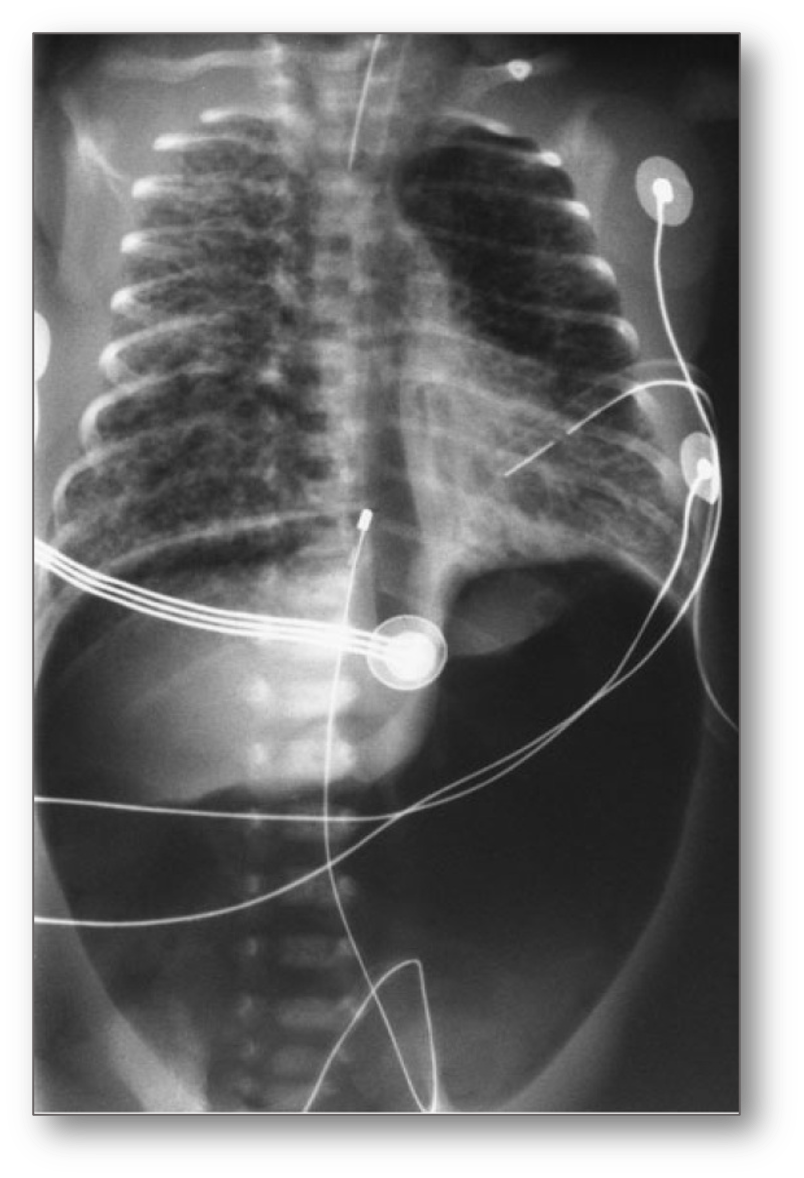
Pulmonary Air Leaks
Occurs in infants with underlying lung disease. It refers to a collection of gas outside the pulmonary compartment. Asymptomatic pneumothorax is more common than symptomatic pneumothorax.
Transpulmonary pressures that exceed the strength of the terminal airways and alveoli can damage the respiratory epithelium. The air enters the interstitium, causing pulmonary interstitial emphysema, then dissection of air toward the visceral pleura and/or the hilum through the peribronchial and perivascular spaces.
sudden desaturation after stabilized birth
Rupture of the Pleural Surface Allows the Air to Decompress:
- Into the pleural space > Pneumothorax
- Into the mediastinum > Pneumomediastinum
- Into the pericardium > Pneumopericardium
- Into the fascial and neck skin > Subcutaneous emphysema
- Into the retroperitoneum and peritoneum > Pneumoperitoneum
- Into the scrotum or labial folds > Pneumoscrotum
- Into the pulmonary veins > Air embolism (Pneumocardium)
Risk Factors in Premature Infants
- Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)
- Mechanical ventilation(Pneumothorax, displacement of tube, obstruction; mucous, equipment failure)
- Meconium aspiration
- Neonatal sepsis
Surfactant therapy for RDS has markedly decreased the incidence of pneumothorax.
Risk Factors in Term Infants
- Aspiration of meconium, blood, or amniotic fluid
- Pneumonia
- Congenital lung malformations (congenital lobar emphysema)
- Mechanical ventilation
Pneumothorax Treatment
In asymptomatic patients, a short course of oxygen is given (8-12 hours) to help absorb the air in the pleural cavity. Repeated chest X-ray is done to follow up improvement.
In symptomatic patients:
- A 22-gauge angiocatheter is placed perpendicularly to the chest wall in the 2nd intercostal space in the midclavicular line or in the 5th intercostal space in the midaxillary line.
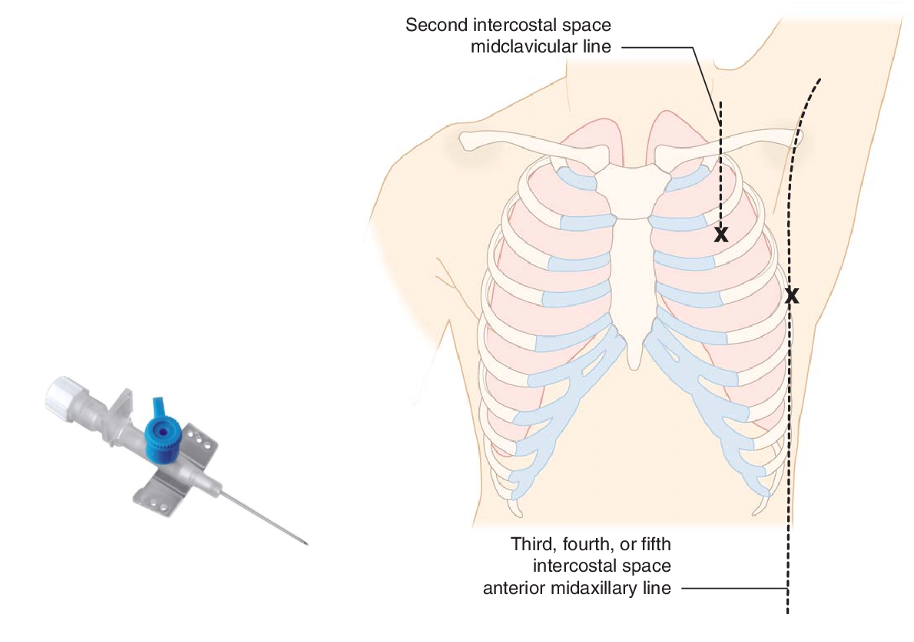
Tension right pneumothorax In Case of Large Pneumothorax
The mediastinum and heart may be pushed to the other side, absent of breath sounds on the ipsilateral side, shifting of cardiac impulse to the contralateral side.
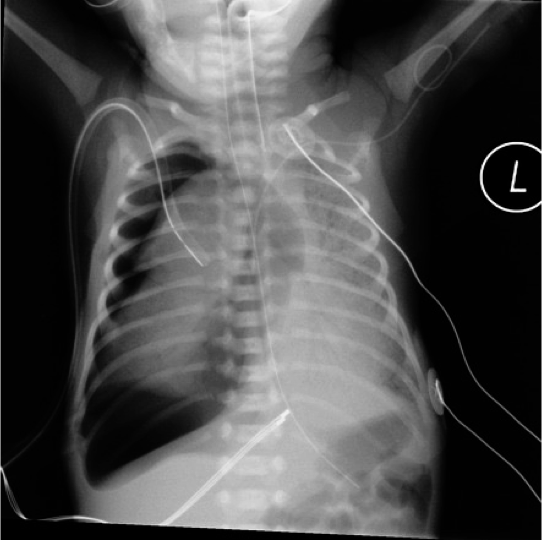
Newborn with Mild Respiratory Distress
Had pneumomediastinum elevating the thymus “spinnaker sail” sign.
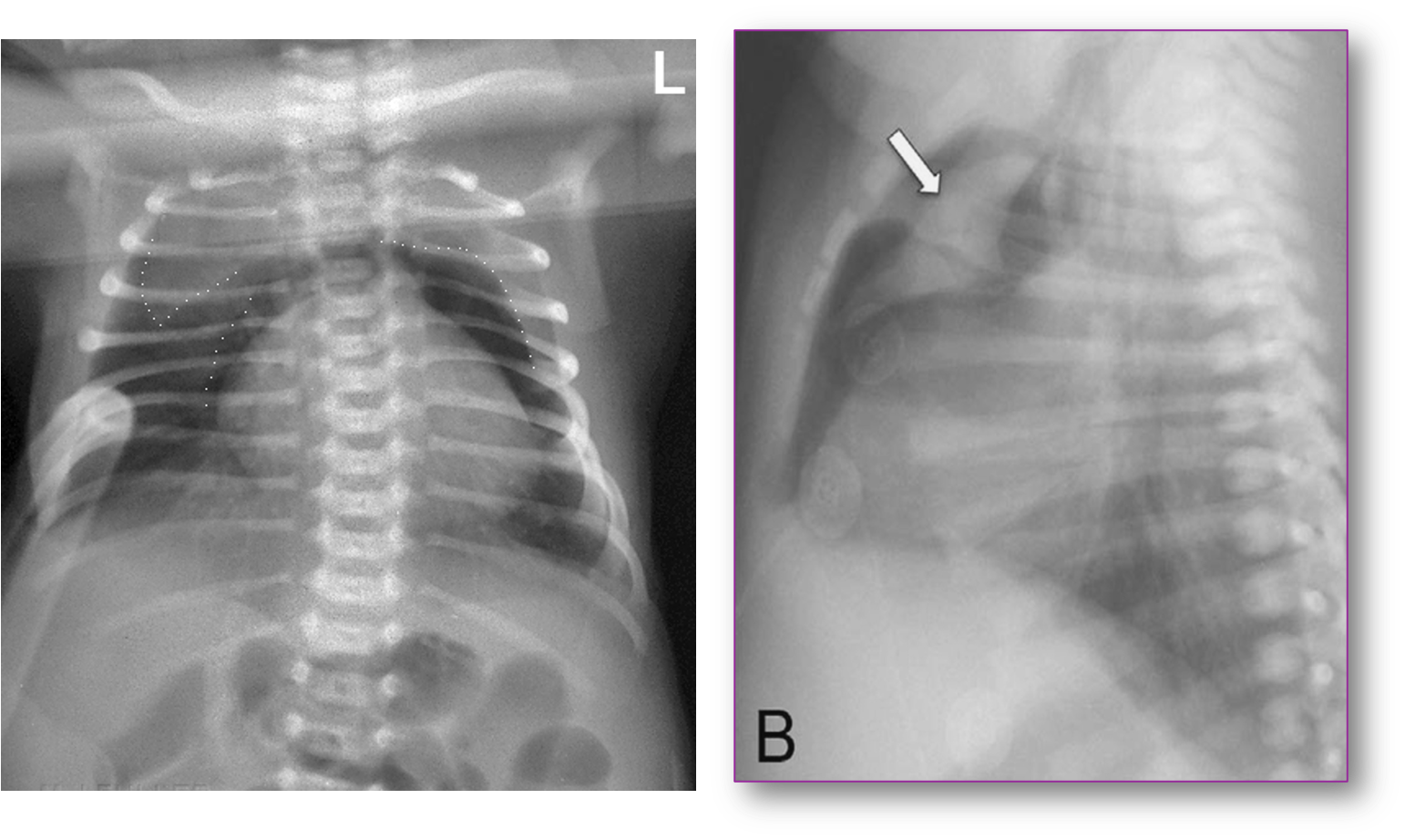
Pneumopericardium
With air completely surrounding the heart, demarcating the pericardial sac.
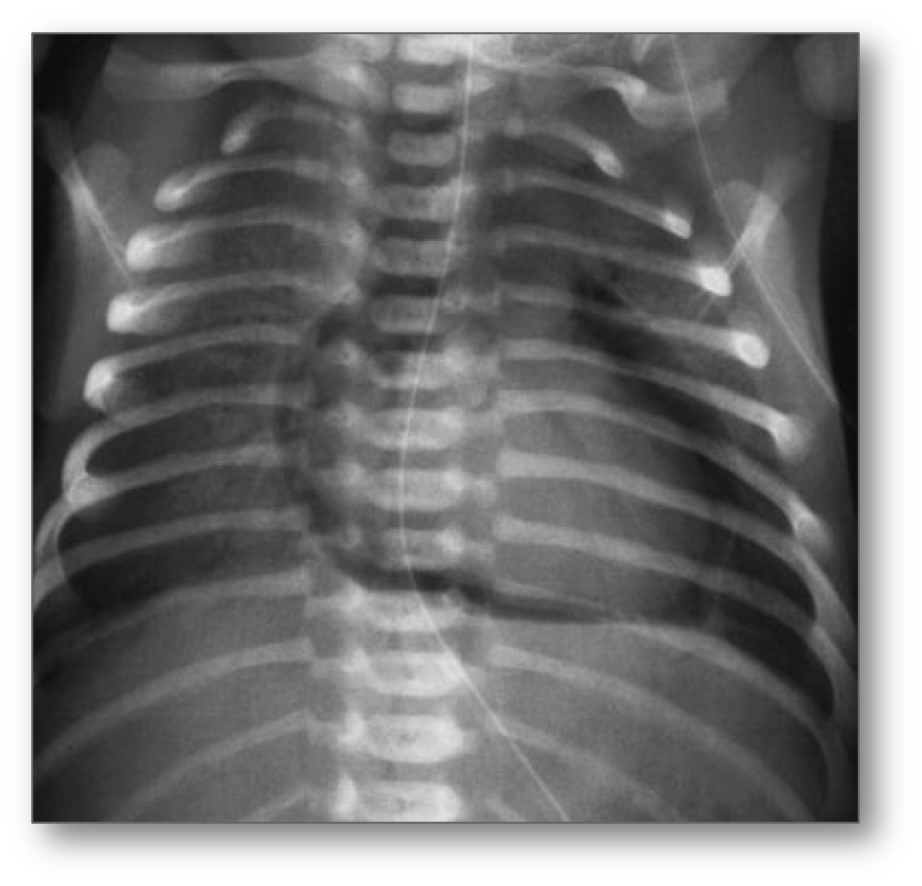
Pneumoperitoneum