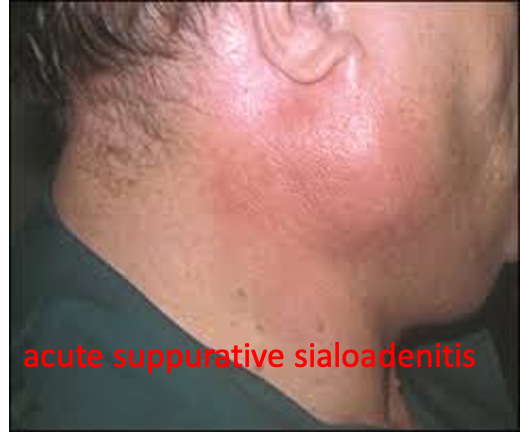
Acute Bacterial Sialoadenitis
- Also known as acute suppurative sialoadenitis.
Definition
- Acute suppurative inflammation of salivary glands.
Causative Organism
- The most common is Staph. Aureus.
- Less commonly strept, pneumococci, etc.
Predisposing Factors
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Common post-operative due to a combination of dehydration and poor oral hygiene (due to fasting + anesthetic medication).
Precipitating Factors
- Obstruction of the salivary duct by stone or food particles.
Route of Entry
- Direct: along the duct from the mouth.
- Blood-borne.
Symptoms
- General: Fever, anorexia, headache, and malaise.
- Local
- Pain:
- In the side of the face, marked as the gland lies within tough fascia increase with eating.
- Disturbance of function: pain increases with the ingestion of lemon or acidic juice (lemon test).
Signs
Before Suppuration
- General:
- Mild toxemia (fever + tachycardia).
- Local:
- Gland: diffusely enlarged, firm, tender, raising the lobule of the ear.
- Skin: congested red, hot tender.
- Duct: inflamed opening is red, raised, edematous and a stone may be felt inside it by bimanual examination.
After Suppuration
- General
- Marked toxemia: marked fever + increased tachycardia.
- Local
- Gland: fluctuation is very late (tough fascia).
- Skin: Pitting edema + Marked tenderness.
- Duct: pus exudates from the duct orifice after pressure on the gland.
- Stones may or may not be felt on bimanual examination.
Complications
- Chronicity.
- Abscess.
- Stone.
- Fistula.
- Spread of infection (ear, mastoid region, and retropharyngeal space).
Investigation
- CBC shows leukocytosis.
- ESR, CRP increased.
- Culture and sensitivity of purulent discharge.
- Radiology for stone.
Treatment
Prophylactic
- Avoid predisposing factors.
Curative
- Initially antibiotics, analgesics, antipyretics + hot fomentation.
- Indications of surgery:
- Failure to respond to conservative treatment within 48 hours.
- Evidence of abscess formation.