SURGE
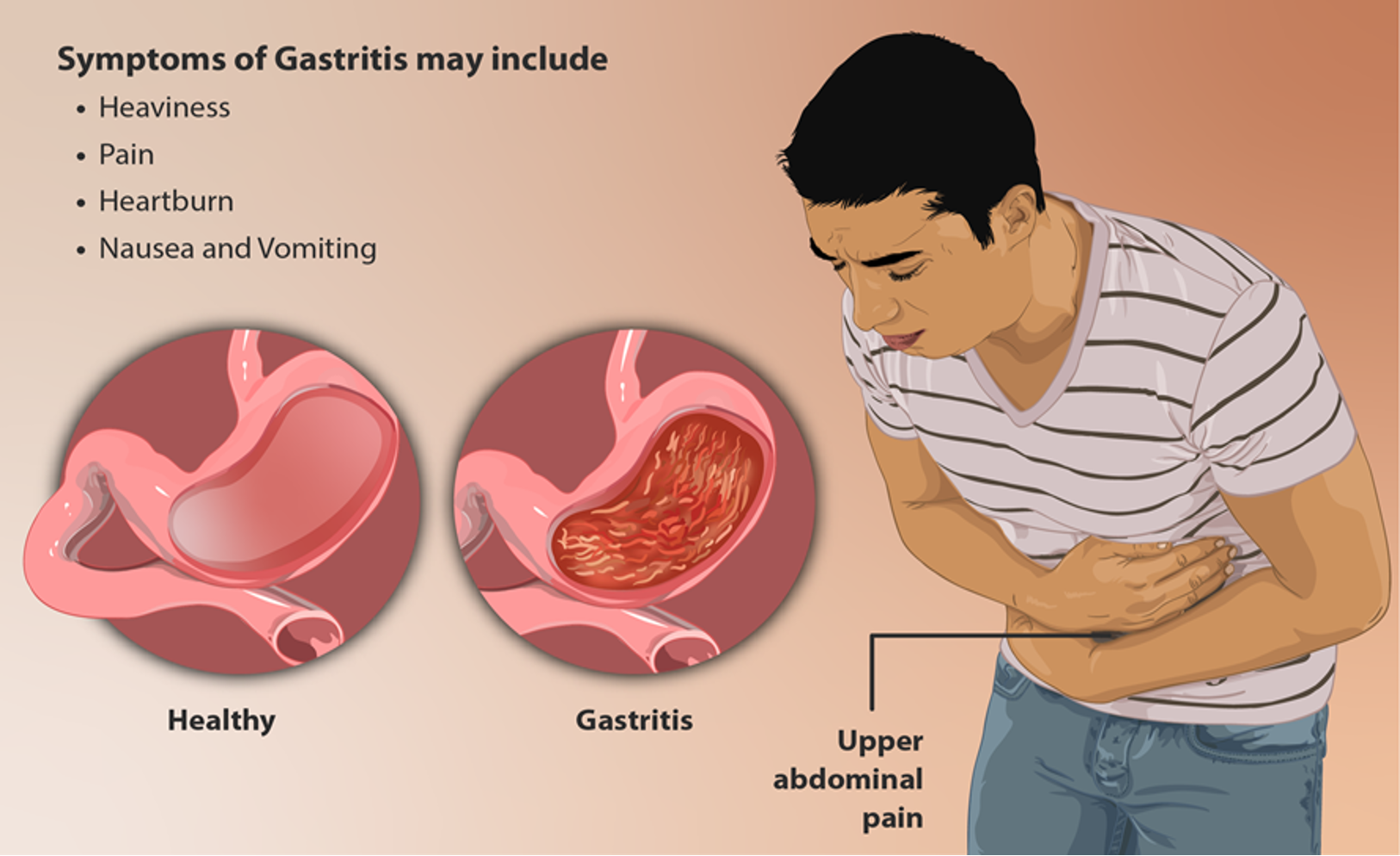
Irritation of gastric mucosa, causes episodes of discomfort (usually after eating), sometimes associated with nausea and/or vomiting
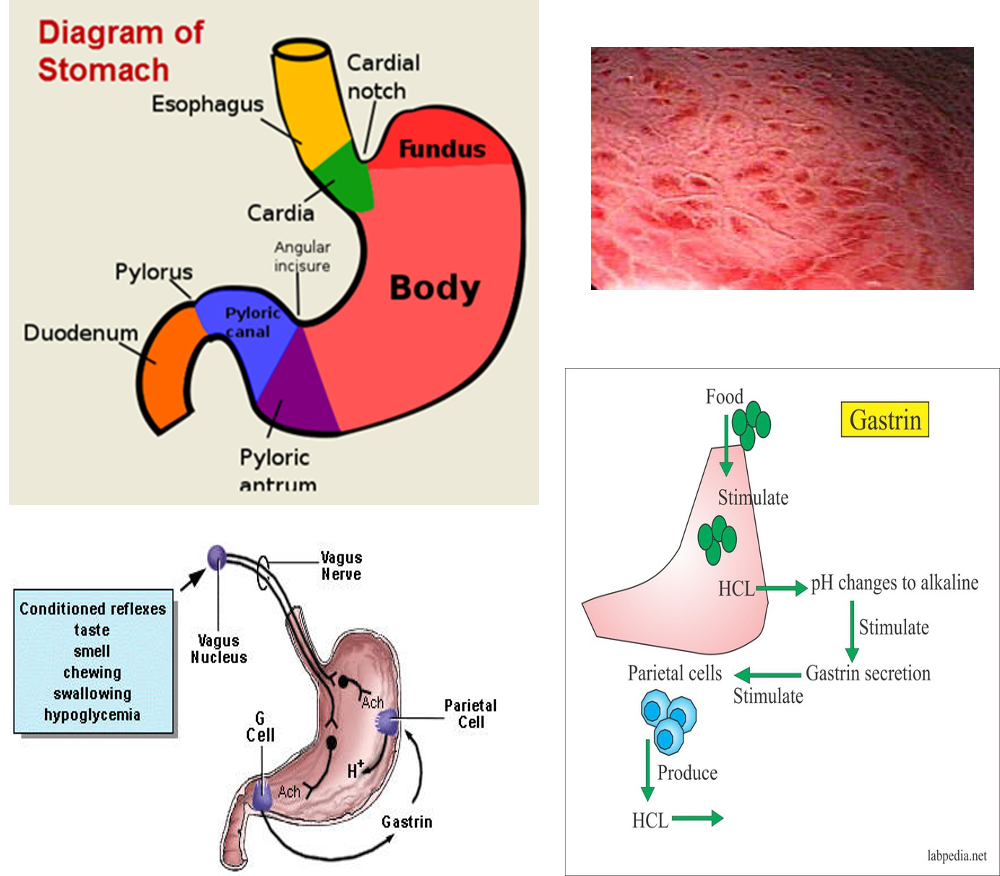
Acute vs chronic
Acute Gastritis
Causes
- Medications: aspirin or other NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), poisons (including strong alcohol)
- Infections: bacterium helicobacter pylori.
Usually, the inflammation settles quickly when the irritant is removed.
Symptoms:
- Upper abdominal pain (Epigastric) or discomfort
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bloating
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Pernicious anemia
Chronic Gastritis
Types:
- Type A or autoimmune gastritis.
- Type B or antral gastritis.
- Rarer forms, e.g., eosinophilic gastritis, granulomatous gastritis.
Type A Gastritis : It is characterized by the presence of antibody to parietal cells. The antrum is spared, and gastrin secretion is frequently elevated.
It is this form that may progress to pernicious anemia.
It is common in the elderly people and may be associated with other organ specific autoimmunity, e.g., Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
The gastritis itself is usually asymptomatic, but there is a fourfold increase in the risk of gastric cancer.
2. Type B Gastritis Helicobacter pylori, Antral gastritis : A symptomatic and do not require any treatment but patients with dyspepsia may benefit from H. pylori eradication.
3. Granulomatous Gastritis: It is associated with tuberculous infection, sarcoid or Crohn’s disease characterized by antral and duodenal involvement with mucosal inflammation and ulceration that may lead to gastric outlet obstruction.
4. Eosinophilic gastritis:
It is a rare condition in which eosinophils infiltrate the distal stomach and the proximal small bowel, resulting in enlargement of antral folds, ←Prednisone

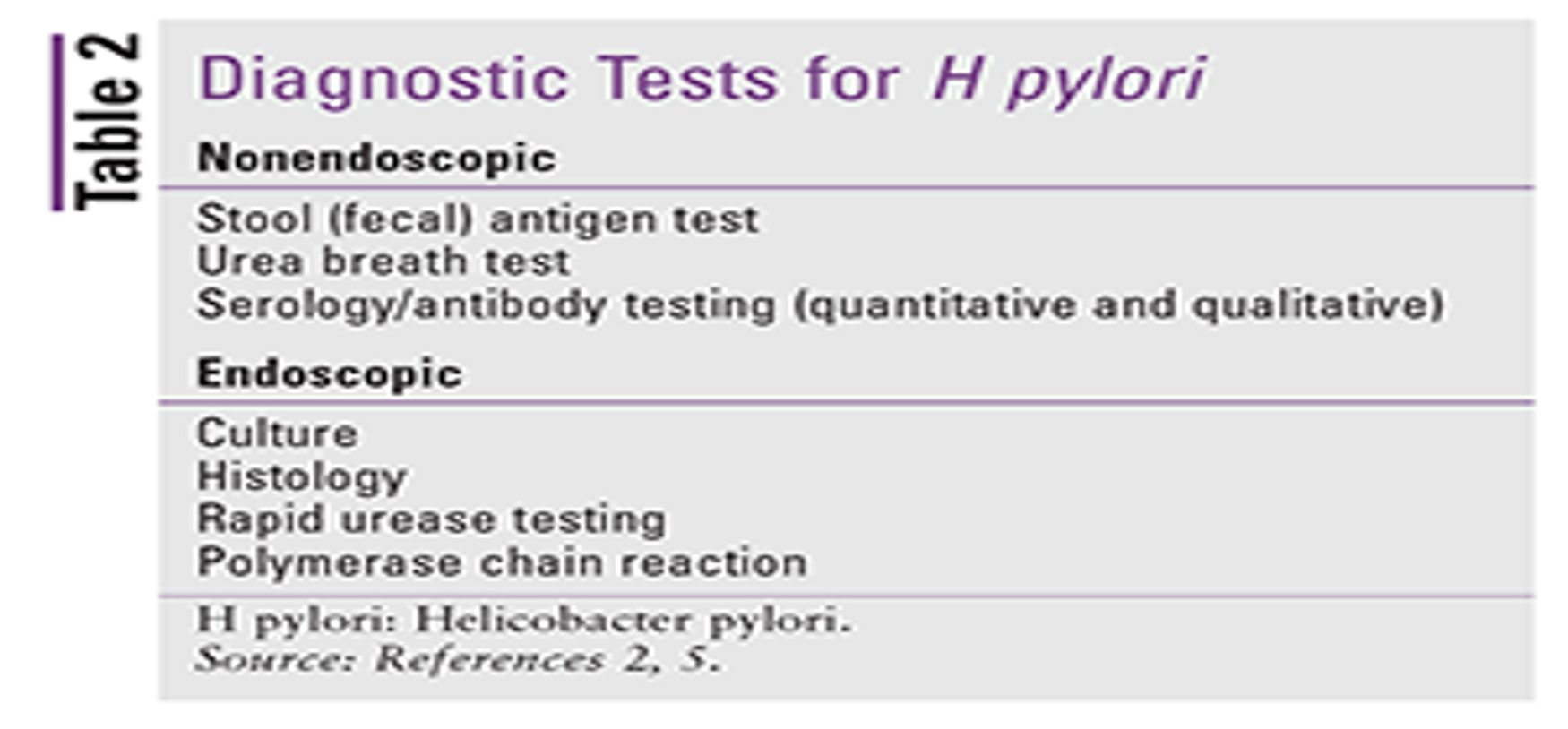
Diagnosis:
- History, & examination
- Labs: CBC, H-pylori
- Radiology: AXR- USS- CT scan
- OGD, and biopsy
Treatment:
- Underlying cause (Medications- Vitamin def. - lifestyle)
- Medications: To reduce gastric acid
- H2 antagonists (Zantac©)
- Proton pump inhibitor (Nexium©)
- Anti-emetic medications may be needed
- Treatment of H. Pylori
Therapeutics
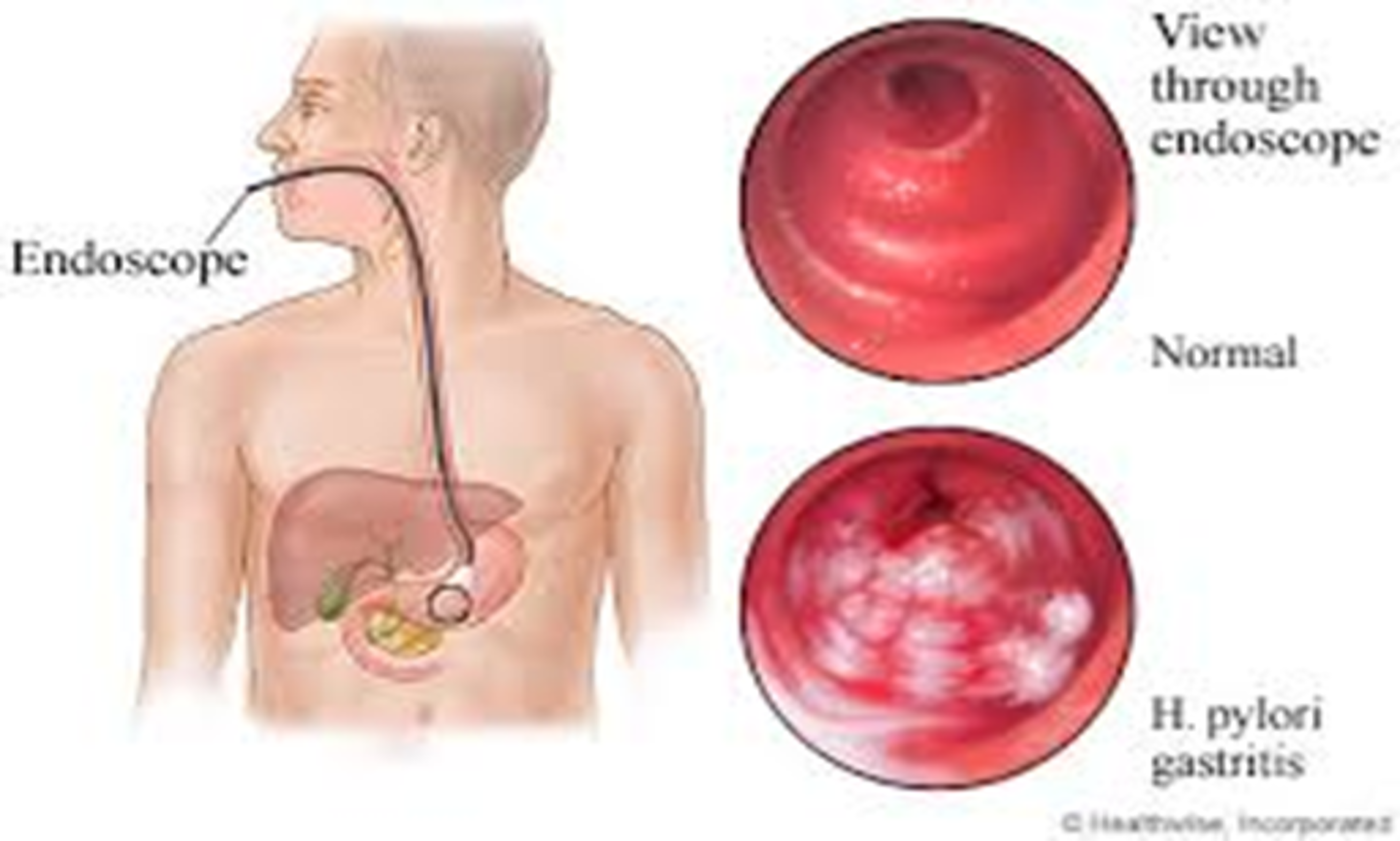
GASTRITIS
Definition: It is inflammation of the gastric mucosa. It might be acute or chronic. Causes:
- a. Helicobacter Pylori Gastritis (commonest cause)
- b. Erosive and hemorrhagic gastritis (NSAIDs)
- c. Autoimmune Gastritis
- d. Viral infection (CMV & herpes simplex)
- e. Crohn’ s disease