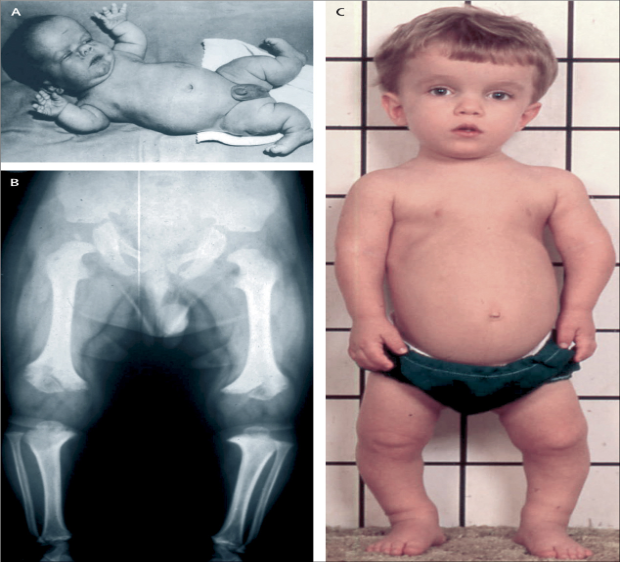
Achondroplasia
- Mutation in the gene for fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) on chromosome 4
- Inheritance is autosomal dominant, but about 50% are new mutations
- Most common type of short limb disproportionate dwarfism
Clinical Features
- Short stature
- Marked shortening of the limbs
- Rhizomelic Shorting (Short proximal long bones)
- A large head, frontal bossing
- Depression of the nasal bridge
- The hands are short and broad
- A marked lumbar lordosis develops
- Hydrocephalus sometimes occurs
Management
- Growth hormone is currently being used to augment the height of patients with achondroplasia
- Limb lengthening