Common Skin Malignancies CS-OSPE
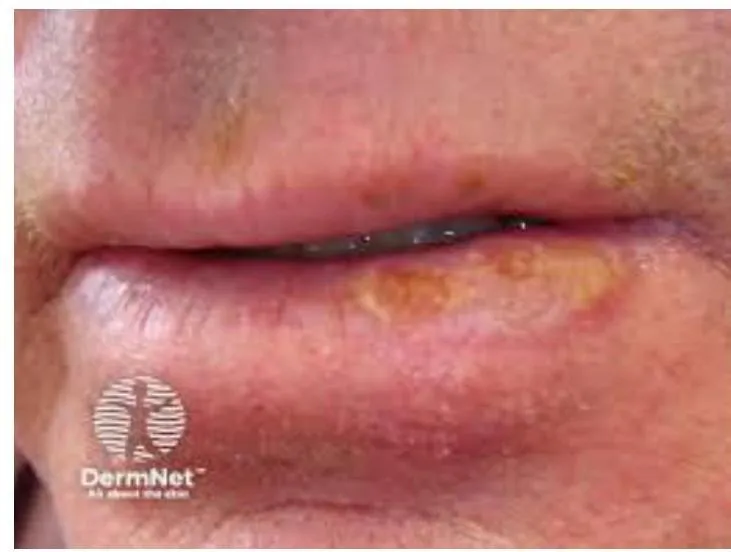
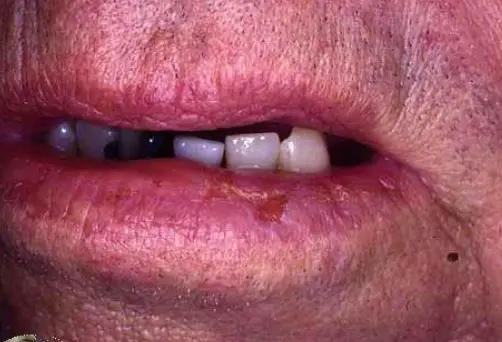
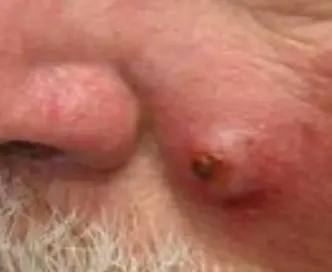
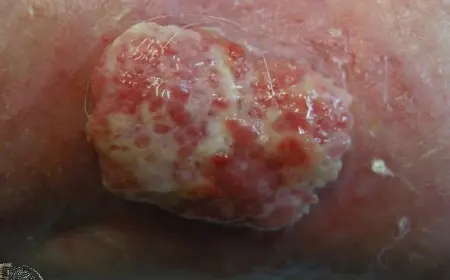
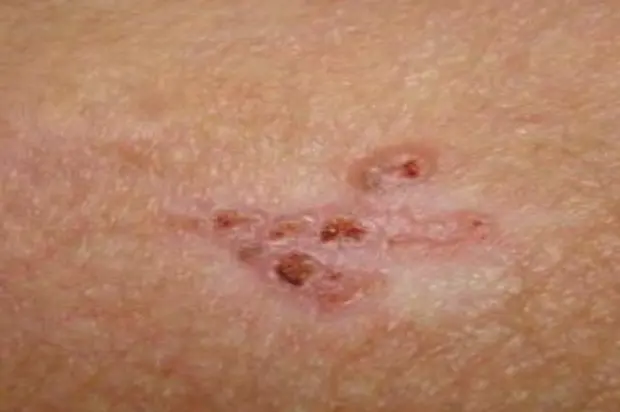
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What is the diagnosis?
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
What is the clinical presentation?
- Tender, scaly or crusted lumps.
What are the treatment options?
- Excision: with 4-5mm margins (“gold standard”), cure rate 90-95%.
- Electrodesiccation and curettage.
- Mohs Micrographic Surgery: specialized technique for removing high risk NMSC.
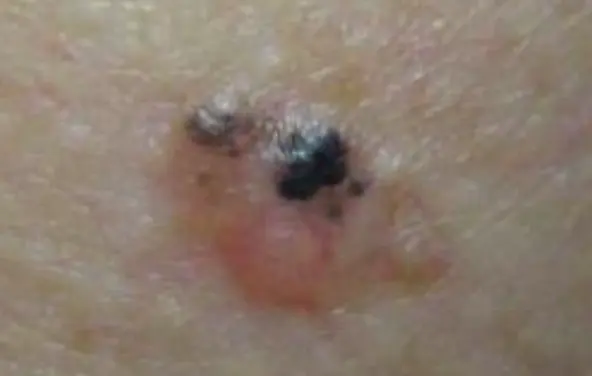
Melanoma
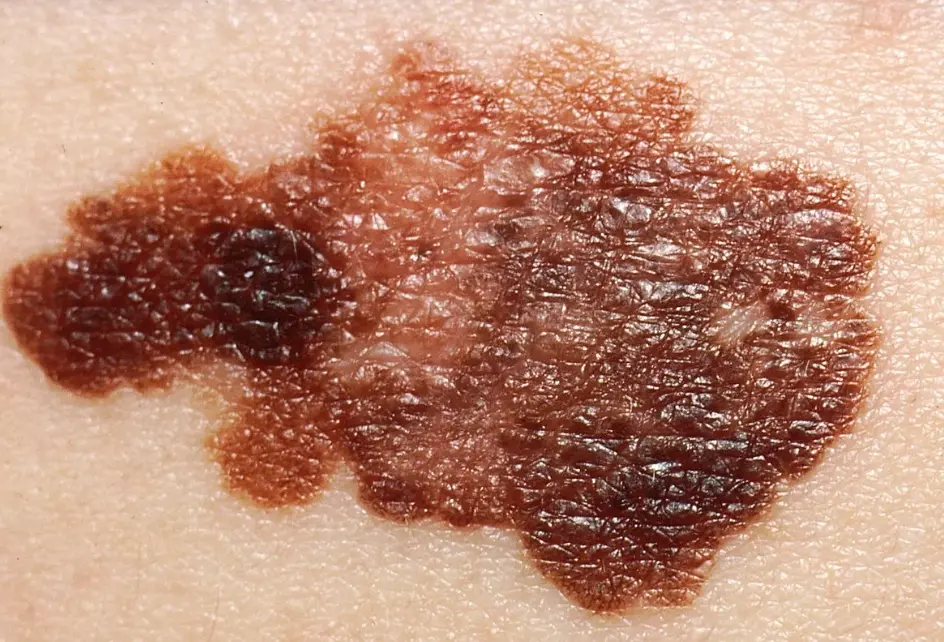
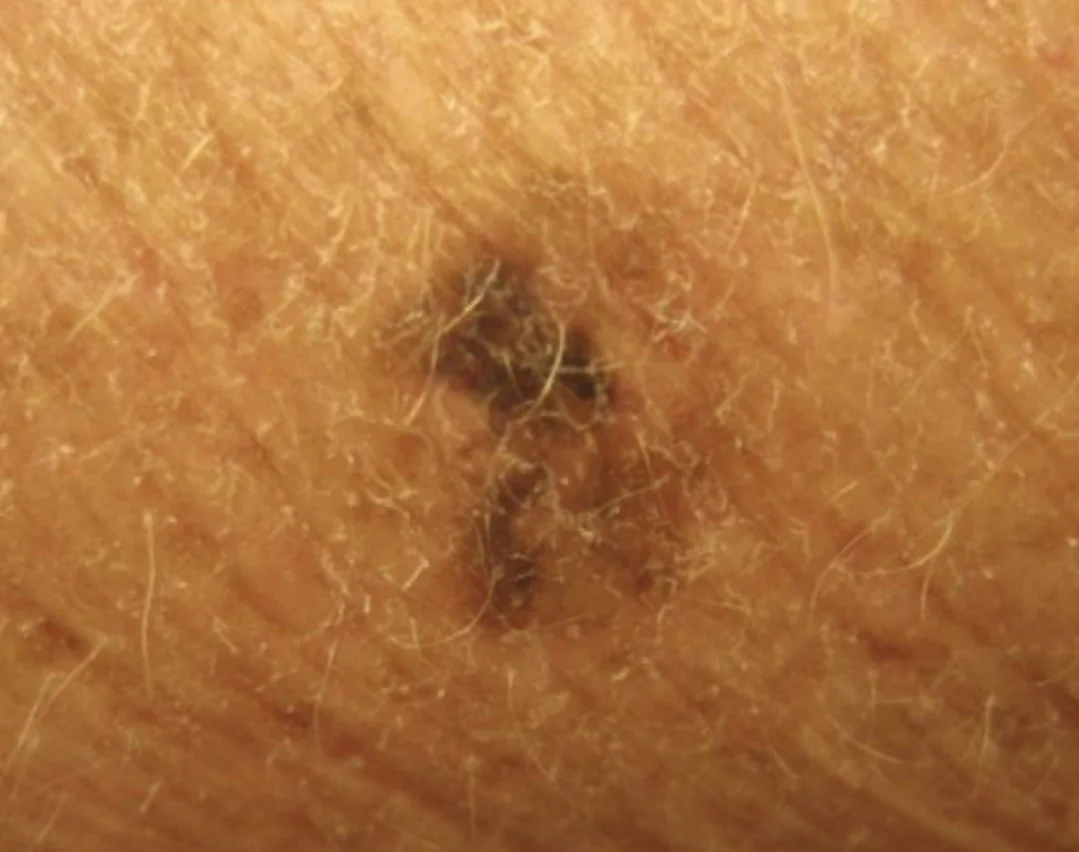
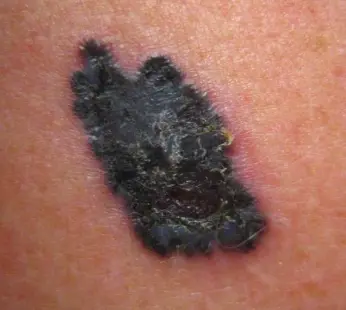
Diagnosis: Melanoma Description/Characteristics:
- sharply marginated pigmented papule
- The 2-centimeter pigmented lesion appeared one year ago on the cheek of a Caucasian 65-year-old retired oil engineer.
- ABCDEs standards applied:
- A → Asymmetrical
- B → Irregular Border
- C → Vary in color, there is area with more pigmentation
- D → Increase
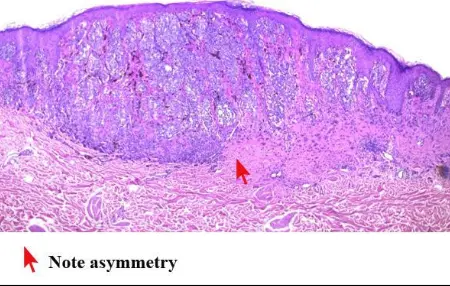
- E → Evolution of the old one Histological sign: Asymmetry, pigmented, ulcerative epidermis
Management/Next Steps:
- Biopsy/Treatment: Excisional biopsy, followed by Excision
- Additional Treatment: Chemotherapy
- Further Examination: Check Cervical lymph nodes, Regional lymph nodes
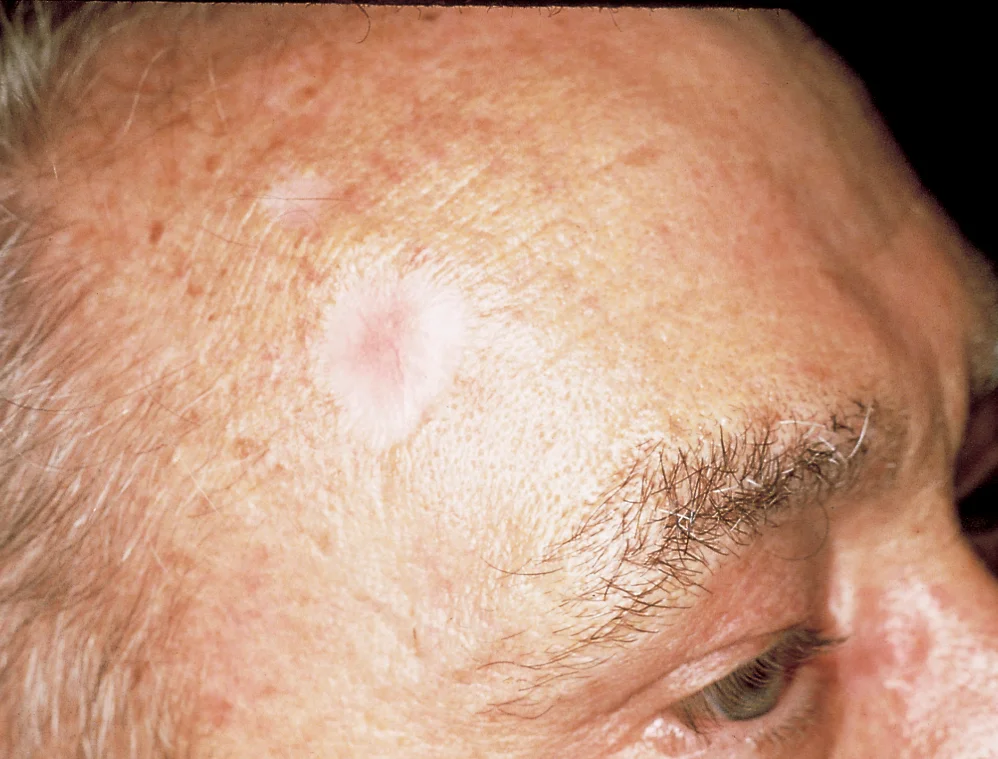
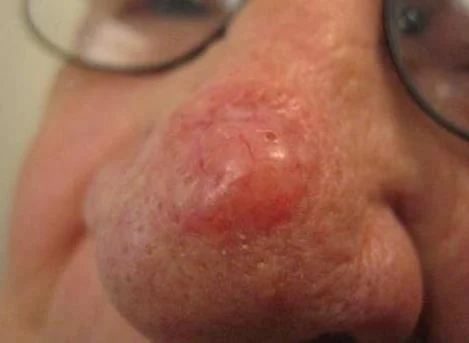 Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma.
Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma.
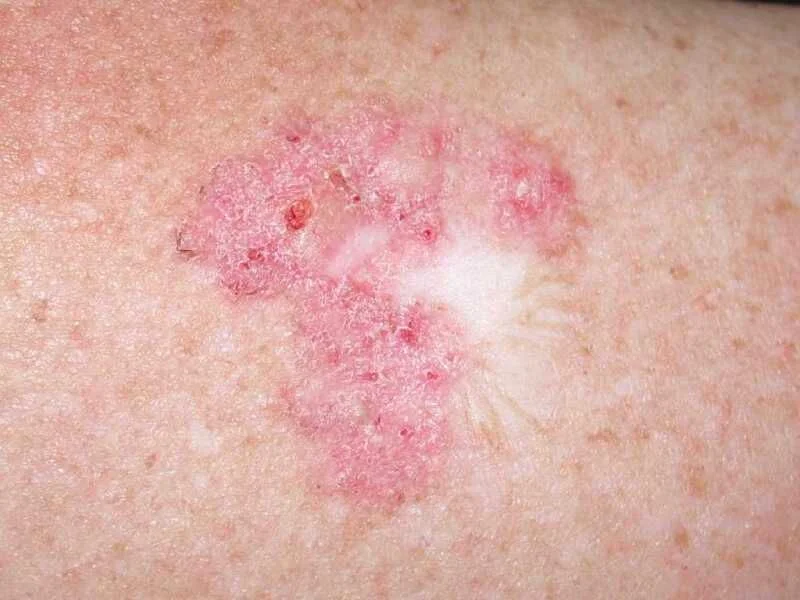
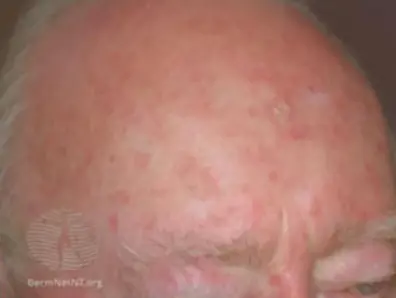
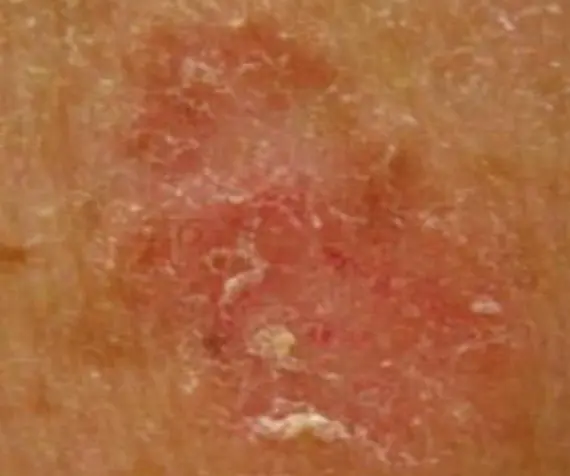 Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma.; Red scaly plaque.
Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma.; Red scaly plaque.
 Morpheaform Basal Cell Carcinoma.; Scar-like plaque. Whitish dermal plaque with atrophy.
Morpheaform Basal Cell Carcinoma.; Scar-like plaque. Whitish dermal plaque with atrophy.
 Pigmented Basal Cell Carcinoma.; Dark brown plaque.
Pigmented Basal Cell Carcinoma.; Dark brown plaque.
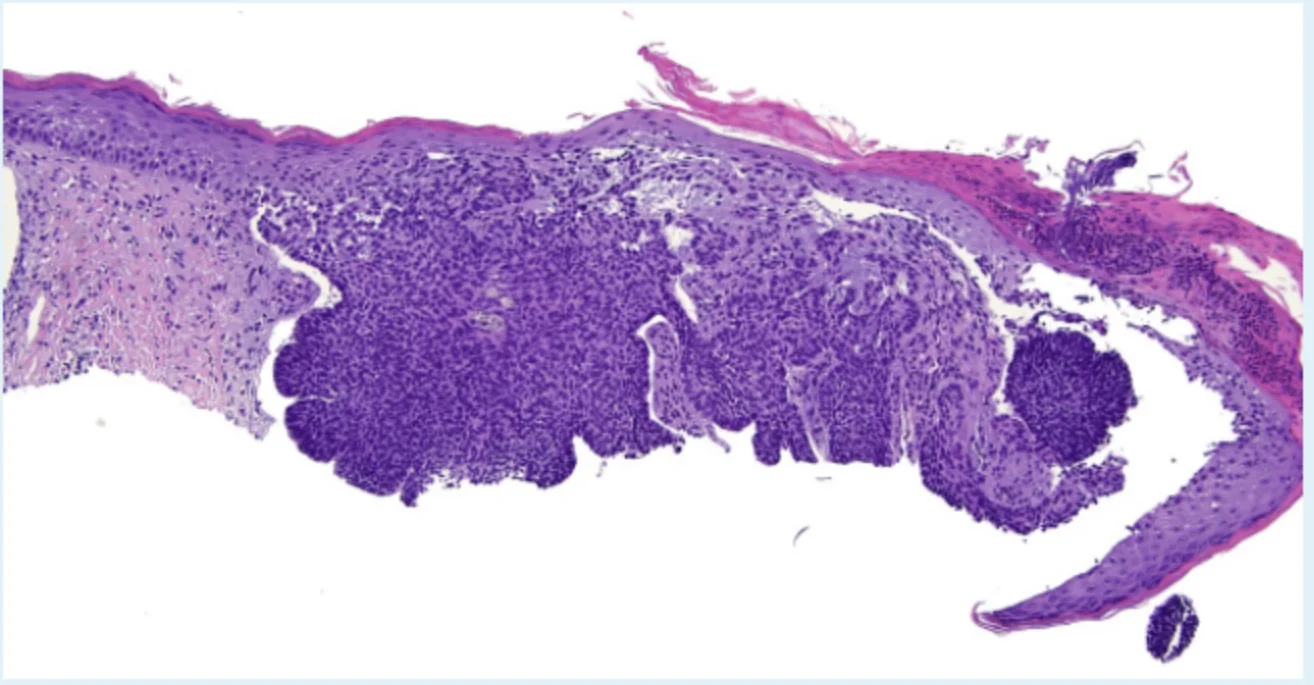
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Diagnosis: Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) Variants/Description:
- Morpheform BCC (often presents as Whitish Plaque)
- Superficial basal cell carcinoma
- Most invasive variant: Morpheaform
Clinical Presentation:
- He developed this nodule over 18 months. (If considering a cancer, it would be BCC).
Histopathology:
- Sign: Basal Cell in epidermis
Management/Next Steps:
- Biopsy:
- Excisional Biopsy (for nodule/general BCC)
- Shave biopsy using dermablade (for premalignant skin lesions/superficial BCC)
- Treatment:
- Electrodesiccation and Curettage (or Electrodessication | Cuttage)
- Cryotherapy
- Excision with 4-5mm margins