Open Injury Types
Skull Fractures
A skull fracture is any break in the cranial bone, also known as the skull.
Symptoms that can indicate a fracture include:
- Swelling and tenderness around the area of impact
- Facial bruising
- Bleeding from the nostrils or ears
- Severe pain at the trauma site
Causes:
A skull fracture occurs when a force that’s strong enough to break the bone hits the skull.
Probability of Skull Fracture Depends on:
- Object Impacted or Impacting Head (weight , shape , consistency)
- Thickness of Hair
- Thickness of Scalp
- Thickness of Skull
- Age of Victim (elasticity, brittleness of bone)
Types of Skull Fractures
- Linear
- Depressed
- Diastatic
- Basilar
Linear Fracture
Are breaks in the bone that transverse the full thickness of the skull from the outer to inner table.

Depressed Fracture
Is a type of fracture usually resulting from blunt force trauma, such as getting struck with a hammer, rock or getting kicked in the head.

Diastatic Fracture
Occur when the fracture line transverses one or more sutures of the skull causing a widening of the suture.

Basilar Fracture
Are linear fractures that occur in the floor of the cranial vault (skull base), which require more force to cause than other areas of the neurocranium
Scalp Wound
An open wound is an injury involving an external or internal break in body tissue, usually involving the skin.
Types of open wounds:
- Abrasion
- Bruises
- Lacerations (Contused)
- Incised Wound
- Puncture
Abrasion
Occurs when the skin rubs or scrapes against a rough or hard surface. Road rash is an example of an abrasion. By degree:
- A first-degree abrasion involves only epidermal injury.
- A second-degree abrasion involves the epidermis as well as the dermis and may bleed slightly.
- A third-degree abrasion involves damage to the subcutaneous layer and the skin and is often called an avulsion.
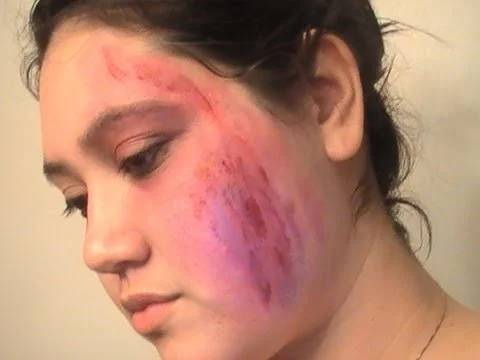
Bruises
Is a condition in which small blood vessels under the skin rupture, causing blood to leak into the underlying skin tissue.
Severity: Bruise Harm Score
| Harm score | Severity level | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Light bruise | No damage |
| 1 | Mild bruise | Little damage |
| 2 | Moderate bruise | Some damage |
| 3 | Serious bruise | Dangerous |
| 4 | Extremely serious bruise | Dangerous |
| 5 | Critical bruise | Risk of death |
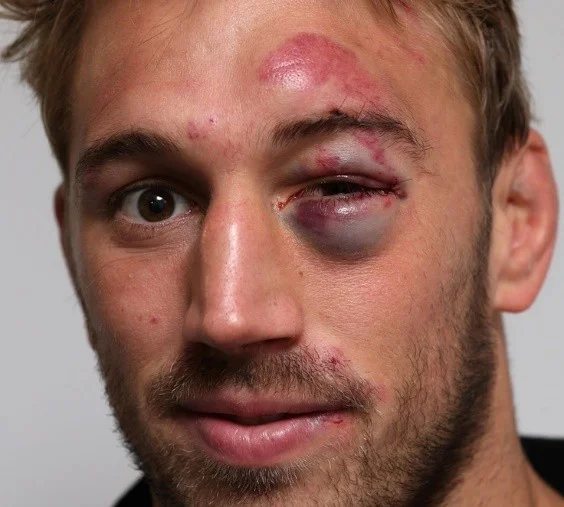
Black Eye
A black eye often results from injury to the face or the head, and is caused when blood and other fluids collect in the space around the eye
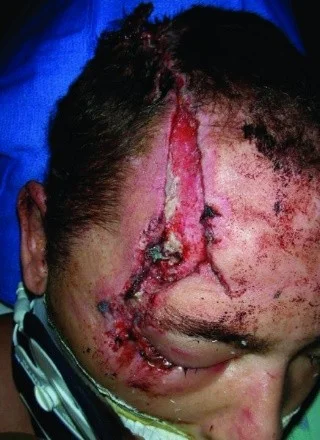
Lacerations
Is a wound that occurs when skin, tissue, and/or muscle is torn or cut open. Lacerations may be deep or shallow, long or short, and wide or narrow.
Incised Wound
Incised wounds are wounds caused by a clean, sharp object such as a knife, glass, or razor.

Characteristics of blunt force lacerations vs sharp force incised wounds:

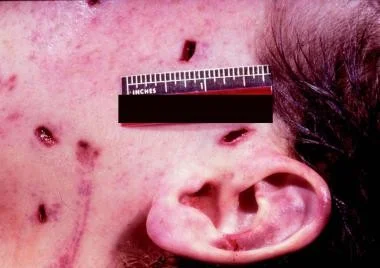
Puncture
Puncture wounds are not the same as cuts. A puncture wound has a small entry hole caused by a pointed object, such as a nail that you have stepped on.
Firearm Wounds
Also known as, ballistic trauma is a form of physical trauma sustained from the discharge of arms or munitions.
Classification:
- Low-velocity projectile: as 1,200 ft/s (370 m/s) or less.
- Medium: 200 ft/s (370 m/s) to 2,500 ft/s (760 m/s).
- High: as greater than 2,500 ft/s (760 m/s).
- Bullets from handguns are generally less than 1,000 ft/s
- Bullets from rifles exceed 2,500 ft/s (760 m/s)
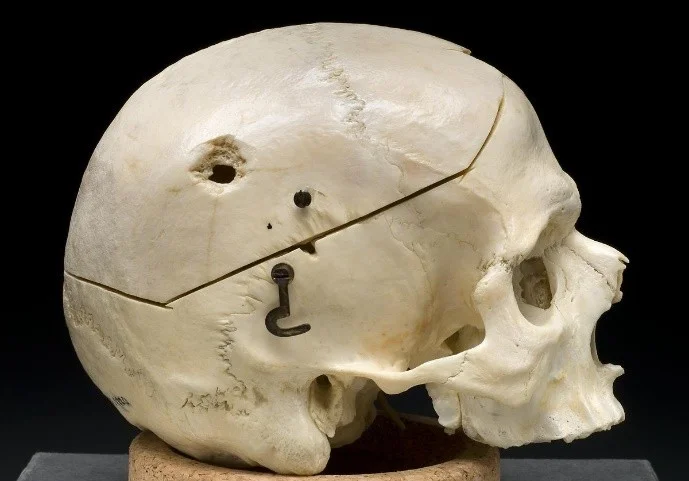
Head Injury Caused By Gunshot Gunshot wound to the head when caused by a bullet that is travelling at high velocity and force results in two types of injuries of the skull bone. The strike of smaller bullet over the skull causes penetrating cone shape inlet of the bone and larger bullet causes bullet entry surrounded by fracture of skull bone.
![]()
The brain damage depends on following factors
- The distance bullet travels through brain tissue
- The direction of passage of bullet
- The distance of the shooting range
- Projectile path prior to bullet strike to skull bone and
- Type of bullet fired.
The injuries caused by the gunshot wound to head include following injuries
- Skull fracture like bullet aperture or shattered bone
- Injury of brain tissue
- Injury of blood vessel resulting in internal bleeding
- Tears brain sinuses and brain tissue surrounding sinuses
- Injuries of cranial nerves resulting in facial palsy and hearing loss
- Injury of vital centers like breathing center, blood pressure center, heart monitoring center and various brain coordinating centers.
Symptom and Signs of Gunshot Wound to the Head
- Brain Swelling
- Brain Hemorrhage- Bleeding within brain or between skull and brain
- Cerebral Ischemia- lack of blood supply to brain and
- Increased Intracranial Pressure- Increased pressure within skull resulting in displacement or compression of brain inside the skull.