Joint Aspiration and Injection (and soft tissue)
Dr. Tarif AlAkhras Prof. Mamoun Kremli
Objectives
- Joint Aspiration (Arthrocentesis) & Injection
- Indications
- Contraindications
- Method
- Soft tissue injection
- Indications
Joint Aspiration
Indications
Diagnostic Indications
- Evaluate an acutely swollen and inflamed ‘hot’ joint
- Rule out Infection (most important)
- Analyze synovial fluid
- Characterize mono- or polyarthritis
- Inflammatory
- Degenerative
- Crystalline (Gout, pseudogout)
- Characterize mono- or polyarthritis
Therapeutic Indications
- Drain large effusions / haemarthrosis
- Symptomatic relief
- Improves function
Contraindications
- ✓ Prosthetic joint
- ✓ Overlying cellulitis
- ✓ Active skin disease (e.g. psoriatic lesions at the site of injection)
- Flare in the joint post-injection when performed previously
- ✓ Bleeding diathesis
- anticoagulation, hemophilia, thrombocytopenia
- not an absolute contraindication, but be careful
- Two weeks before planned Arthroplasty
Complications
- ✓ Infection
- very rare if good sterile technique ()
- ✓ Bleeding / Haemarthrosis
- ✓ Vasovagal syncope
- ✓ Pain
- Cartilage injury
- Poor technique
What to Do with Aspirate?
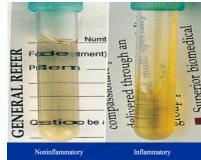
Visual Assessment
- Check yourself
- Clear colorless: normal
- Clear yellow:
- can read through: non-inflammatory
- Turbid: Inflammatory
- Pus
- Blood


Laboratory Analysis
- Send for:
- ✓ Cell count with differential
- in purple-top tube
- ✓ Gram stain / Culture and sensitivity
- in sterile container or red-top tube
- ✓ Crystals
- In red-top tube
- ✓ Glucose, Total Protein
- ✓ Cell count with differential
Joint Injection
Medications
- ✓ Steroids
- ✓ Local anesthetics +/-
- Other material:
- ✓ Hyaluronic acid ?
- Glucosamine ???
- Chondroitin ???
Indications
1. Inflammatory Arthritis
- (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthropathies)
- Up to six months improvement from a single joint injection
2. Osteoarthritis (OA)
- A weaker indication for steroid injection
Soft Tissue Injection
Treatment of Localized Inflammation
- Bursitis
- Trochanteric, subacromial, prepatellar, olecranon
- Flexor tenosynovitis (Trigger finger / thumb)
- Tenosynovitis (DeQuervain’s)
- Lateral epicondylitis (Tennis elbow)
- Medial epicondylitis (Golfer’s elbow)
- Plantar fasciitis
- Adhesive capsulitis – Frozen shoulder
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
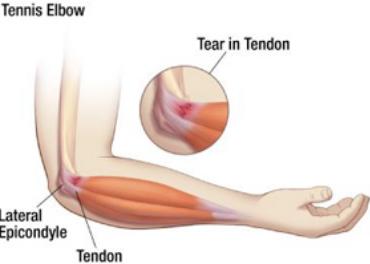
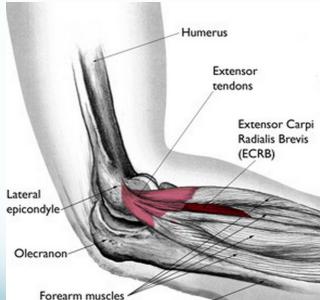
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
Have you ever heard of tennis elbow or suffered from elbow pain? Continue reading to learn about this condition and a new study that may change the way we approach treating this problem.
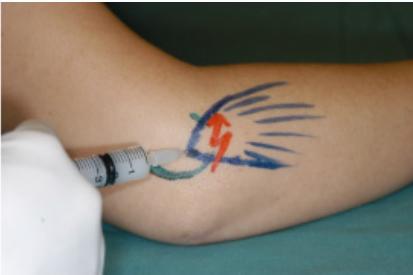
Steroid injection for tennis elbow
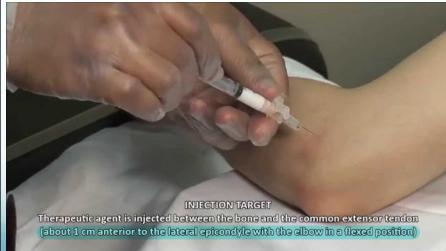
INJECTION TARGET Therapeutic agent is injected between the bone and the common extensor tendon (about 1 cm anterior to the lateral epicondyle with the elbow in a flexed position)
Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)
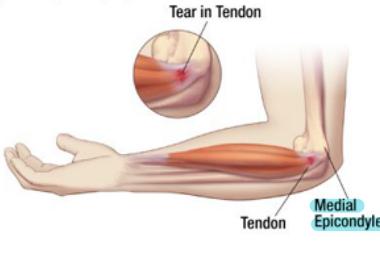
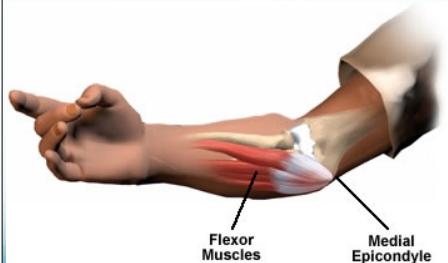
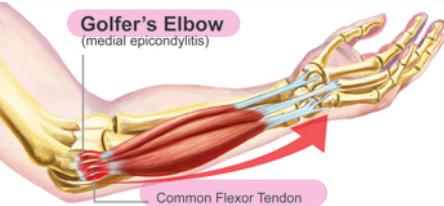
Pain occurs on the inside part of the elbow where the tendons of the forearm connect to the medial epicondyle. Pain may spread down the forearm to the wrist.