Placenta Previa
Definition
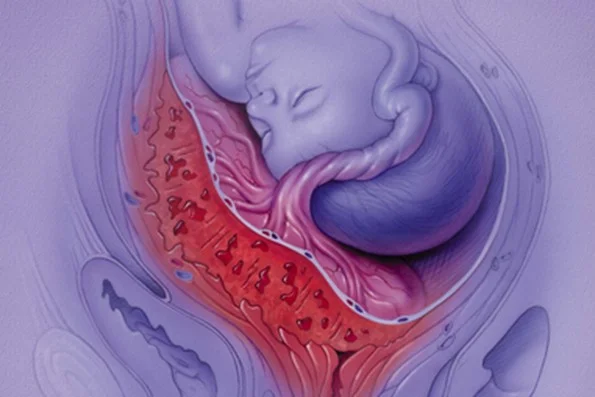
A presence of the placenta in the lower uterine segment, which can lead to partial or not full obstruction of the internal os.
The bleeding is from the maternal not fetal circulation and is more likely to compromise the mother than the fetus.
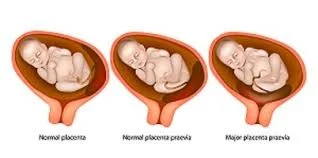
Types of Placenta Previa
-
Minor Placenta Previa: Placenta sited in the lower segment but does not cover the cervix
-
Major Placenta Previa: Placenta covers the cervical os
Prevention
Avoidance of non-clinically indicated cesarean section.
Risk Factors
- Multiple Gestation
- Previous Cesarean Section
- Uterine Structural Anomaly
- Assisted Conception
- Increased Parity
- Previous Placenta Previa
- Previous Dilatation & Curettage
- Maternal Age > 35 Years, Multiparity, Short Intervals Between Pregnancies
- History of Uterine Surgery, e.g., Myomectomy
Warning Signs
- Low-Lying Placenta at 20-Week Anomaly Scan
- Maternal Collapse (Shock Signs)
- Painless Vaginal Bleeding
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
- Presenting Complaint:
- Painless Vaginal Bleeding
- But May Have Irregular Abdominal Pain (Associated with Uterine Contractions)
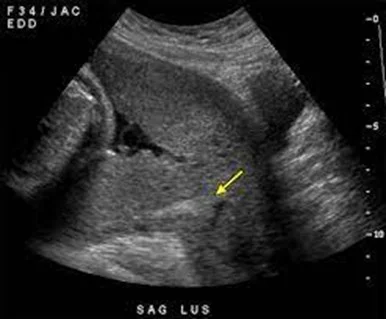
- Diagnosis:
- Ultrasound (Preferably Transvaginal) as patients will have been highlighted as having a low-lying placenta at their anomaly scan.
Management
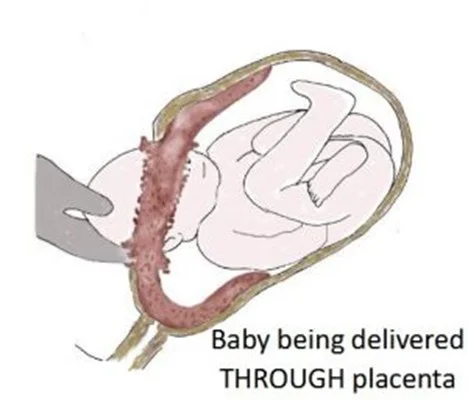
Minor: Reach term then vaginal delivery. Major:
If no bleeding:
- Admission at 34 weeks or send home?
If there is bleeding:
-
Should be admitted to hospital (length of stay depends on GA, amount of bleeding).
- If Severe Bleeding, Resuscitation + Immediate Delivery
- Delivery (between 37-38 weeks)
- Prepare Blood
- Give Corticosteroid
- Give Anti-D (if needed)
Complications
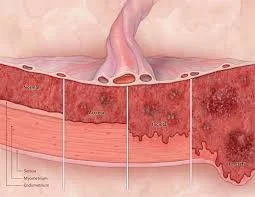
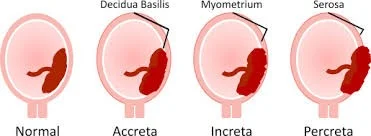
- Placenta Accreta
- Antepartum Hemorrhage
- Postpartum Hemorrhage
- Fetal Distress
- Preterm Labor and Delivery
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism