Prof. Mamoun Kremli Dr. Tarif Alakhras
Overview
This section covers:
- Types of clubfoot
- Causes and etiology
- Management approaches
- Case examples
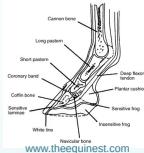
Definition and Nomenclature
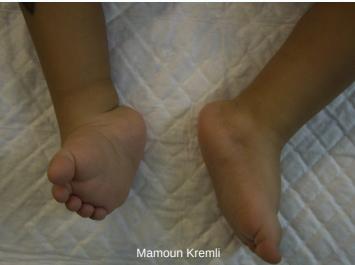
Clubfoot (Talipes Equinovarus)
- Clubfoot: Foot shaped like a club
- Talipes: Latin derivation (talus = ankle + pes = foot)
- Equino: From equine (horse) - ankle plantarflexed like a horse’s foot
- Varus: Deformity directed toward the midline
Congenital Talipes Equinovarus (CTEV)
- Ankle and foot directed downward and inward


Clinical Types
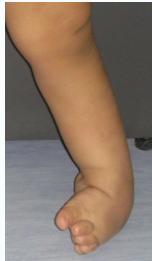
Main Variations
-
Talipes Equinovarus (most common):
- Foot and ankle turn downward (equinus) and inward (varus)
-
Talipes Calcaneovalgus:
- Foot and ankle turn upward (calcaneus) and outward (valgus)
- Often associated with DDH
Etiology and Classification
Types of Clubfeet
Idiopathic (Unknown Etiology)
- Positional clubfoot
- Congenital Talipes Equinovarus (CTEV)
Acquired (Secondary to)
- CNS diseases: Spina bifida, Poliomyelitis
- Arthrogryposis
- Absent bones: Fibula or tibia
Detailed Classification
Positional TEV
- Etiology: Held in deformed position in utero
- Characteristics: Flexible on examination (correctable)
- Management: Needs manipulation - often corrects spontaneously
Congenital TEV (CTEV)
- Etiology: Multifactorial inheritance with environmental factors
- Characteristics: Fixed deformity, not flexible (not easily correctable)
- Management: Requires active treatment
Epidemiology
Congenital Talipes Equino Varus typically occurs in an otherwise normal child
CTEV Statistics
- Incidence: 1/1000 live births
- Family history: 30× more frequent in offspring
- Gender distribution: 65% of cases in males
- Laterality: Bilateral in 30-40% of cases
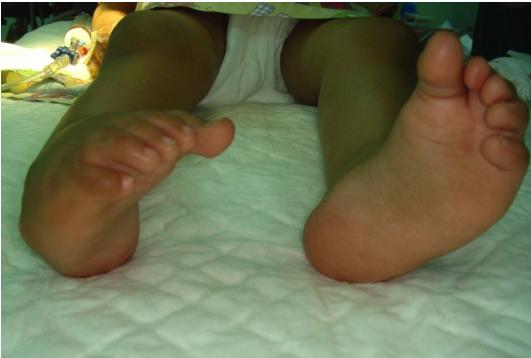
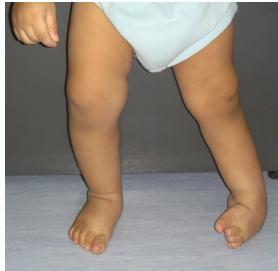
Pathological Deformities in CTEV
Hindfoot Deformities
- Equinus: Plantar flexion of the ankle
- Varus: Medially tilted subtalar joint
- Empty heel pad: Loss of normal heel pad fullness
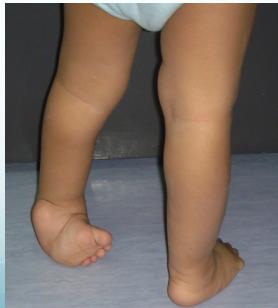
Forefoot Deformities
- Adduction: Of midtarsal joint
- Transverse medial crease: Skin crease formation
- Supination: Forefoot supination
- Cavus: High arch deformity
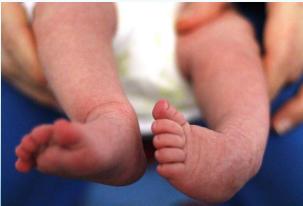
Additional Features
- Wasted calf: Calf muscle atrophy
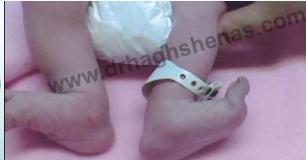
Management of CTEV
The Ponseti Technique
The gold standard for CTEV management
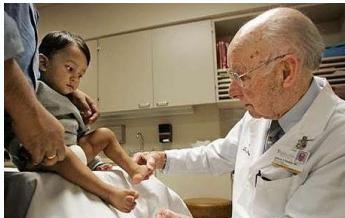
Treatment Protocol
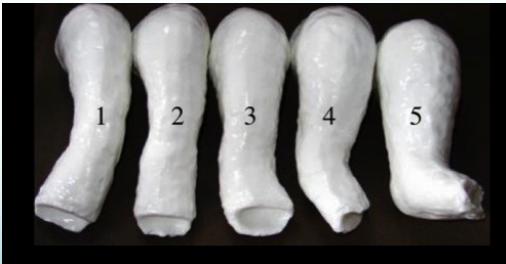
Phase 1: Serial Manipulation and Casting
- Serial manipulation and cast changes (every week for 4-6 weeks)
- Progressive correction of deformities

Phase 2: Tenotomy of Achilles Tendon
- Complete cut of the Achilles tendon
- Terminology:
- Teno: tendon
- Otomy: cutting
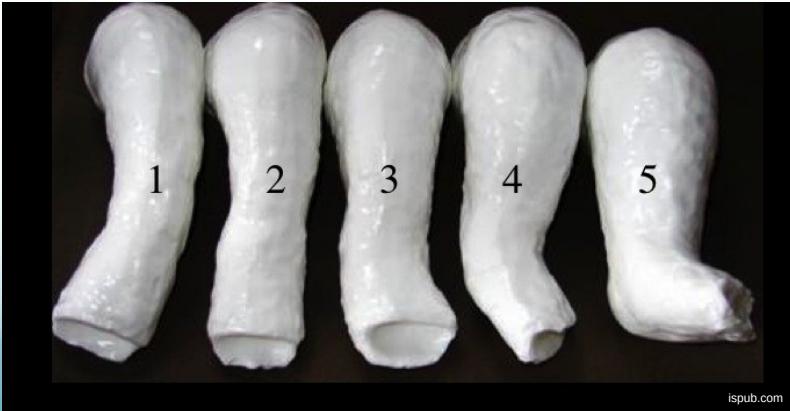
Treatment Timeline: 4-6 Weeks

Progressive Stages
- Stage 1: Initial casting and manipulation
- Stage 2: Correction of cavus and adduction
- Stage 3: Correction of varus deformity
- Stage 4: Correction of equinus
- Stage 5: Final correction before tenotomy
Phase 3: Post-Tenotomy Care
- Cast application for 6 additional weeks after tenotomy
- Special splinting (Dennis-Brown shoes):
- Initial phase: Worn most of the time
- Maintenance phase: Night-only wear for 4 years
- Long-term follow-up required with possible need for additional splints or surgery
Surgical Management for Resistant Cases
In severe or resistant cases, surgical intervention may be required:
- Tendon lengthening of tight structures
- Joint correction procedures
- Bone correction procedures
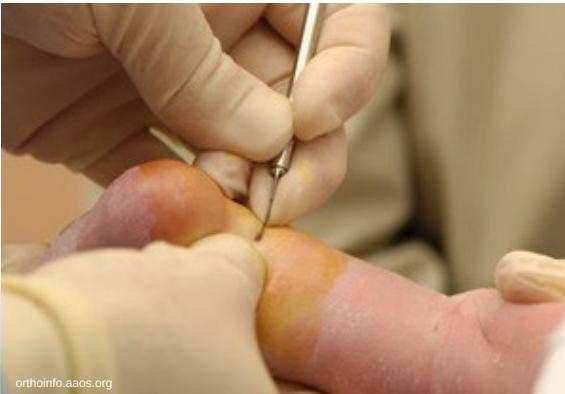
Detailed Tenotomy Procedure
Technique Overview
- Complete cut of the Achilles tendon
- Performed with knife under local anesthesia
- Minimally invasive outpatient procedure
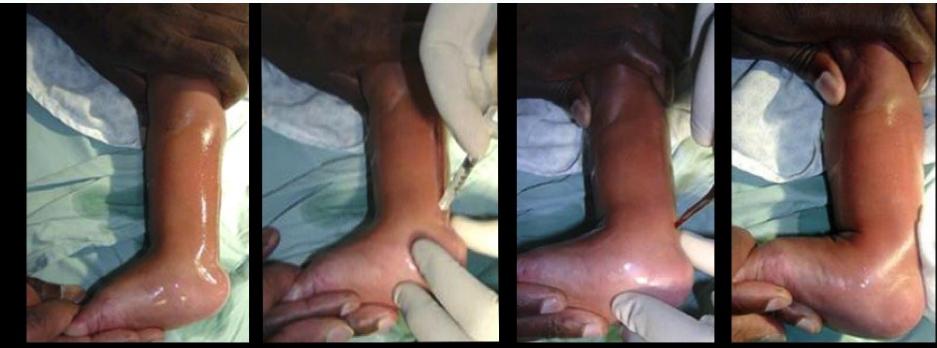
Procedure Steps
- Preparation: Local anesthesia administered
- Tenotomy: Complete surgical division of Achilles tendon
- Result: Full correction achieved
Ponseti method
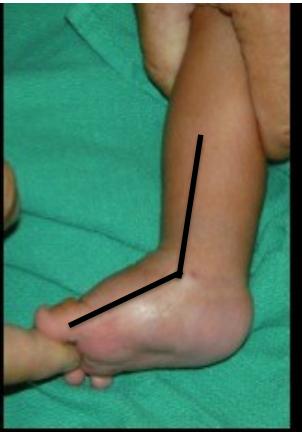
Before Tenotomy
- After casting completion
- Still tight Achilles tendon
- Cannot dorsiflex ankle
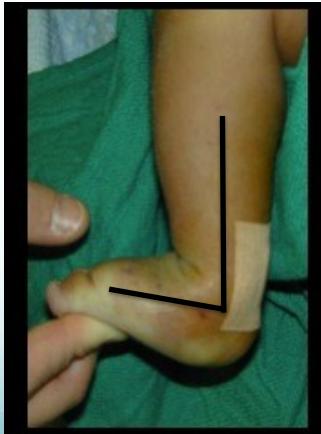
After Tenotomy
- Tightness released
- Can dorsiflex ankle fully
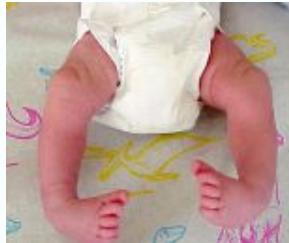
Case Examples
Progressive Treatment Documentation
Case 1: Initial Presentation
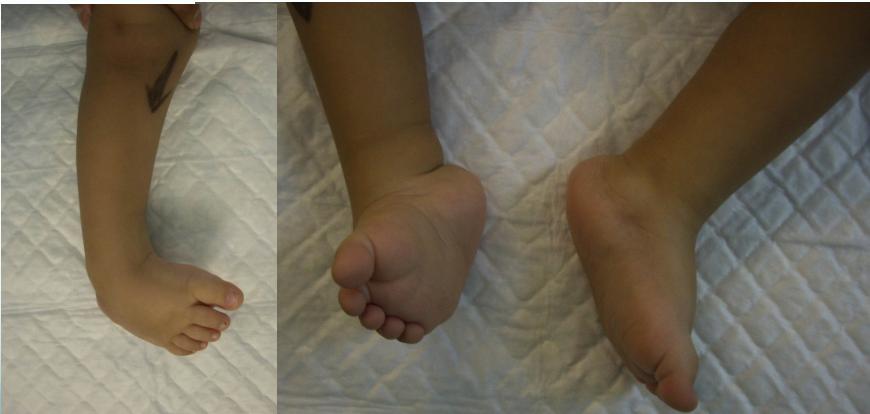
Case 2: Early Treatment Phase
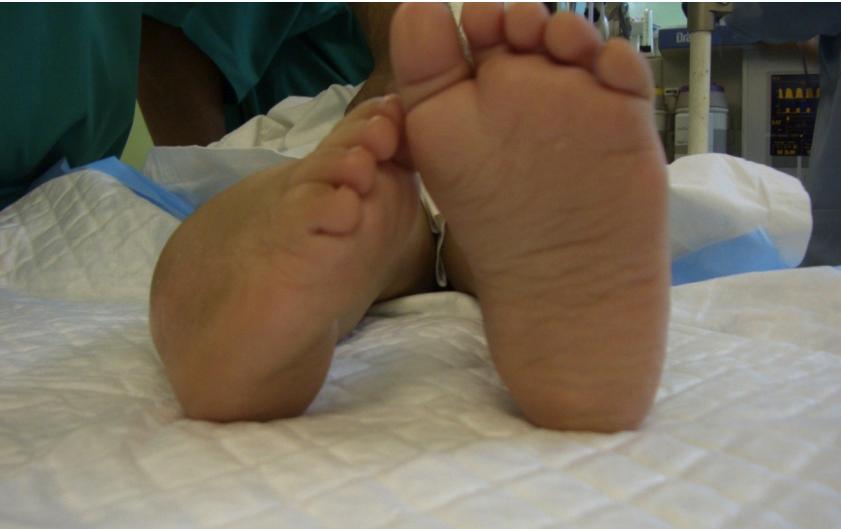
Case 3: Mid-Treatment Progress
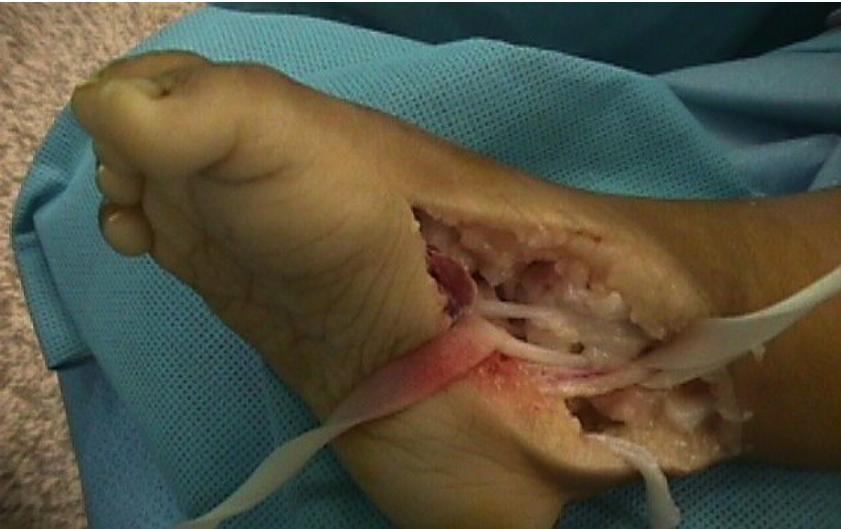
Case 4: Advanced Correction
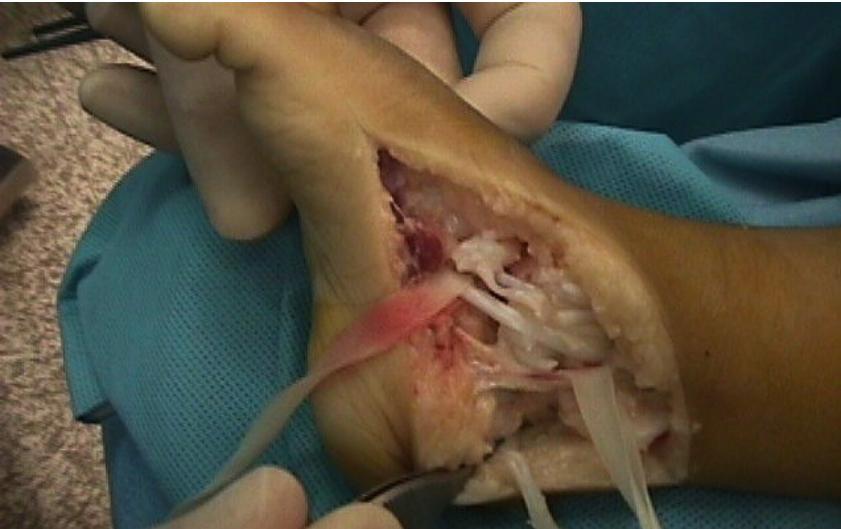
Case 5: Near-Complete Correction
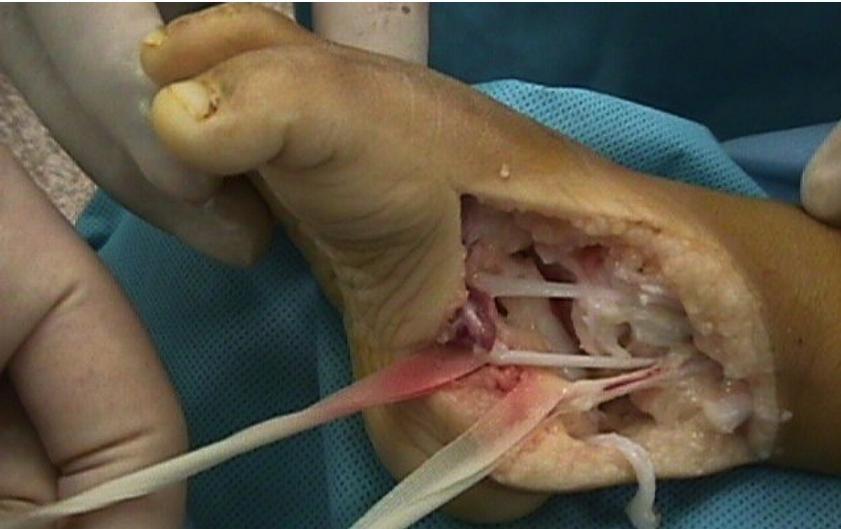
Case 6: Pre-Tenotomy
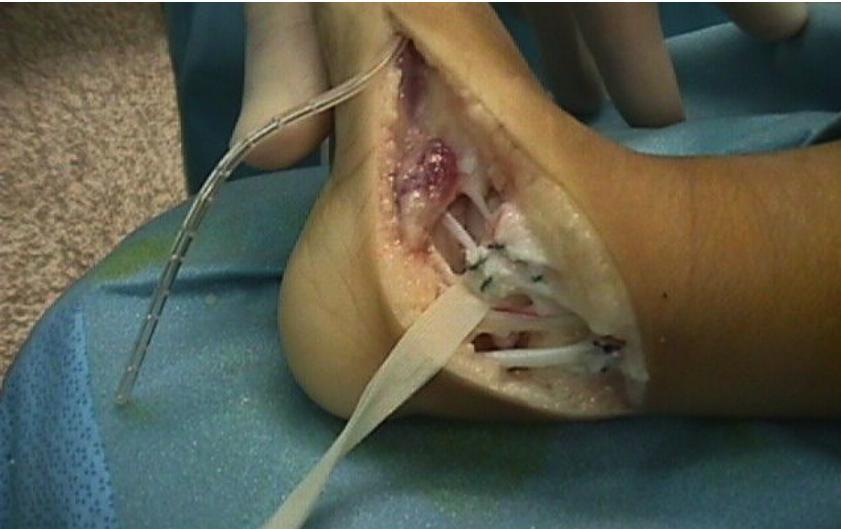
Case 7: Complete Treatment Series
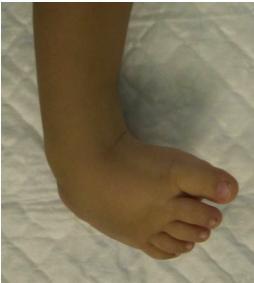
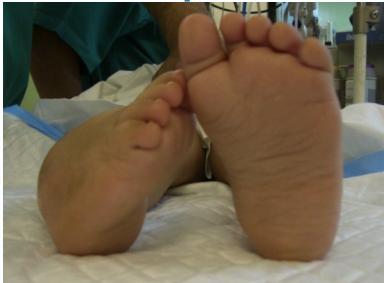
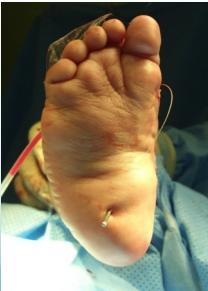
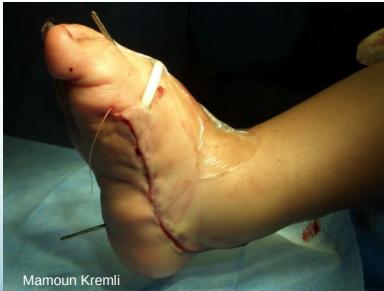
All cases presented by Prof. Mamoun Kremli
CTEV Summary
Key Points
- Definition and types of clubfoot conditions
- Treatment approaches:
- Positional: Manipulation alone
- CTEV: Serial casting + tenotomy (Ponseti method)