Predisposing Factors
- Increased strain on lower back (bending/lifting)
- Degeneration/weakness of annulus fibrosus
- Osteophytes of facet joints in spondylosis causing root irritation
Pathological Progression
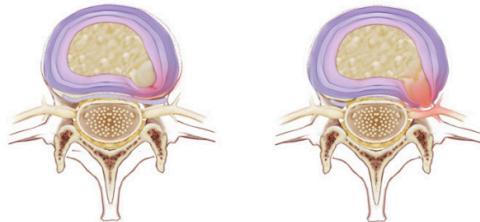
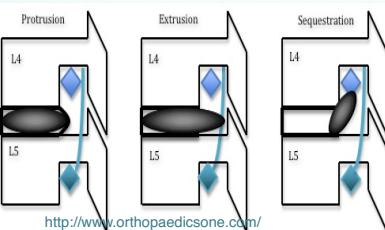
- Bulge → Back pain
- Protrusion → Sciatica
- Prolapse & Sequestration → Neurological deficits
- Numbness, paresthesia
- Weakness
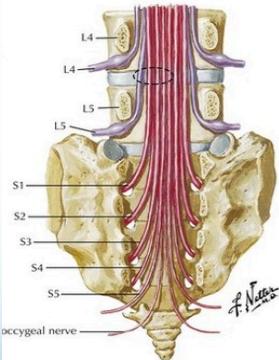
Neurological Level Correlation
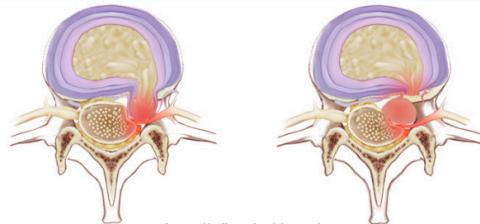
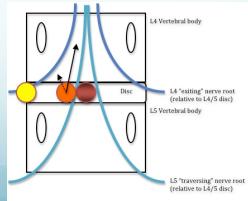
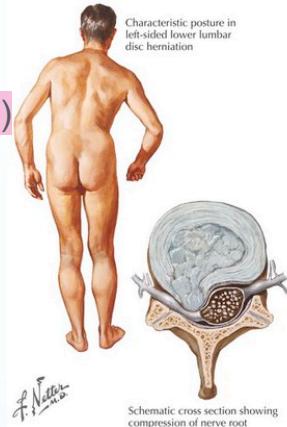
- Lateral disc L4/5 affects L5 root
- Lateral disc L5/S1 affects S1 root
- Central disc affects Sacral roots
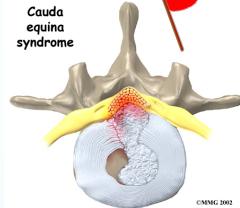
Clinical Note: Central disc herniation is a medical emergency (may cause loss of sphincteric control)


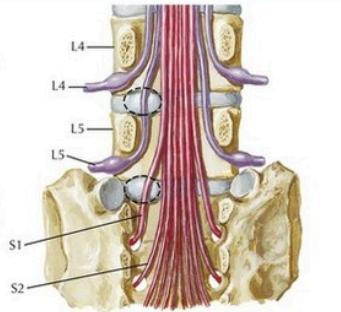
Key point: Lumbar disc protrusion does not usually affect the nerve exiting above the disc. Lateral protrusion at L4-5 affects L5 spinal nerve, not L4.
Clinical Picture
- Demographics: Male adults (35-50y) commonly affected
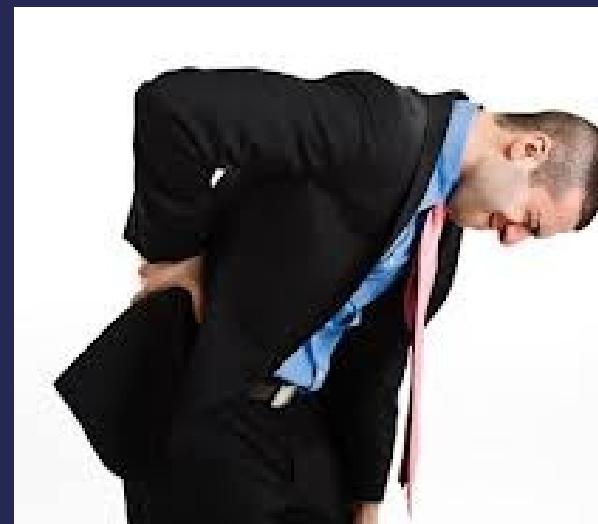
- Onset: Sudden backache while lifting or bending forwards
- Symptoms:
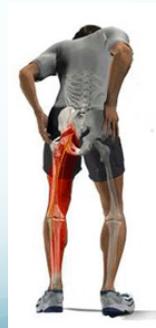
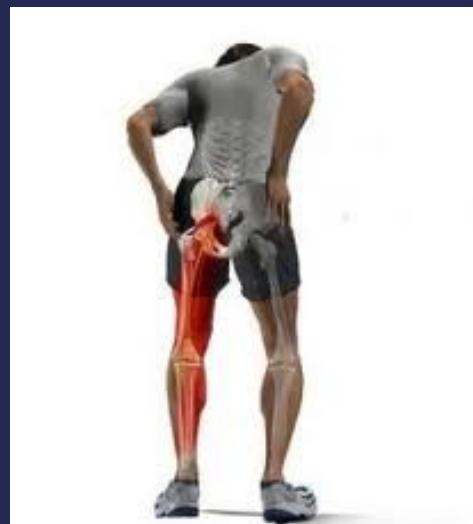
- Back pain and sciatica (increased with straining and coughing)
- Numbness and paresthesia
- Motor weakness

Physical Examination Findings
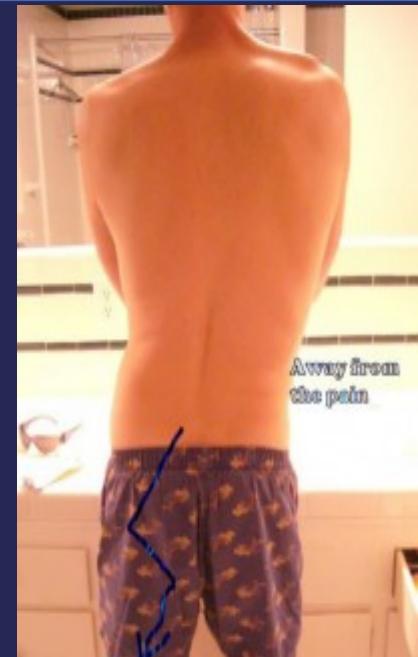
- Posture: Stands with side list (sciatic scoliosis) to avoid pain
- Tenderness: Over midline and paravertebral muscles
- Range of motion: Limitation of spinal motion, list increases with forward flexion
- Neurological assessment:
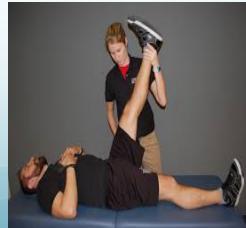
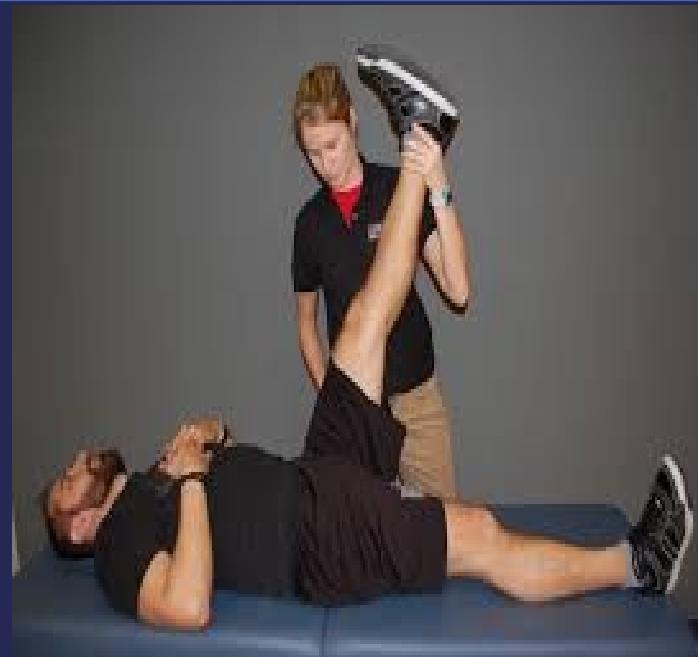
- Straight leg raising test (sciatic nerve) - assesses nerve root compression
- Cross straight leg raising
- Femoral stretch test (L3/4 disc)
Neurological Level Assessment
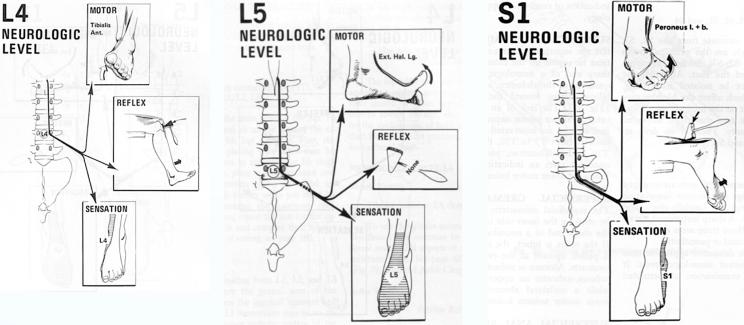
| Level | Motor Testing | Reflex | Sensation |
|---|---|---|---|
| L4 | Tibialis Anterior | Knee jerk diminished | L4 dermatome |
| L5 | Extensor Hallucis Longus | Normal | L5 dermatome |
| S1 | Peroneus Longus and Brevis | Ankle jerk diminished/absent | S1 dermatome |
Detailed Clinical Features by Herniation Level
| Level of Herniation | Pain Distribution | Numbness Area | Weakness Pattern | Atrophy | Reflex Changes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L4–5 disc; 5th lumbar nerve root | Sacroiliac joint, hip, lateral thigh and leg | Lateral leg, first 3 toes | Dorsiflexion of great toe and foot; difficulty walking on heels; foot drop may occur | Minor | Internal hamstring reflex diminished or absent |
| L5–S1 disc; 1st sacral nerve root | Sacroiliac joint, hip, posterolateral thigh and leg to heel | Back of calf, lateral heel, foot to toe | Plantar flexion of foot and great toe may be affected; difficulty walking on toes | Gastrocnemius and soleus | Ankle jerk diminished or absent |
Imaging
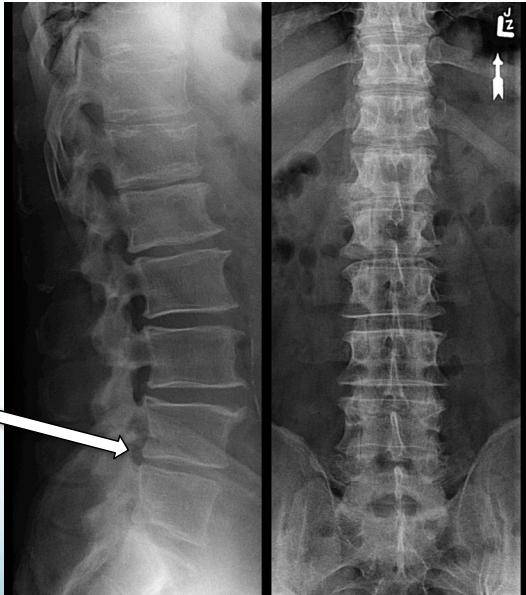
X-Ray:
- Rules out bony pathology
- Shows narrowing of disc space
- Note: Not very helpful in chronic cases, mainly to exclude other causes like tumor, fractures, or deformity
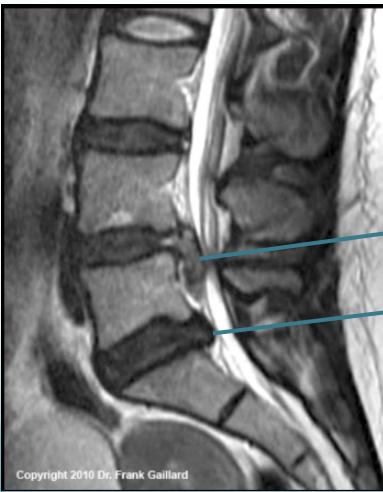
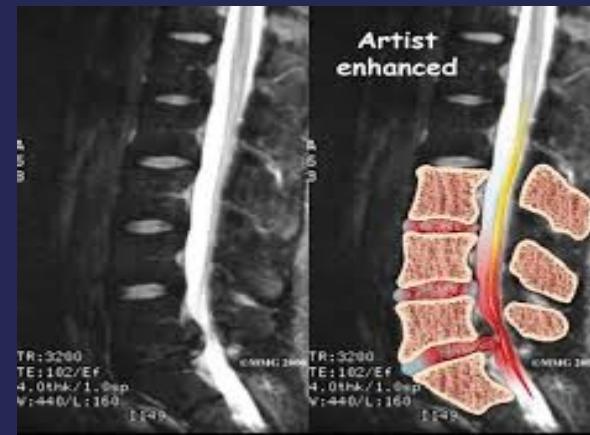
MRI:
- Gold standard for identifying disc pathology and localizing lesions
- Shows:
- Disc sequestration
- Disc bulge/protrusion
Treatment
Conservative Treatment
- Muscle relaxants
- NSAIDs
- Physiotherapy
- Traction
- Rest
Surgical Treatment
Absolute Indications:
- Cauda equina lesion (medical emergency - must be operated immediately)
Relative Indications:
- Persistent pain/frequent attacks
- Progressive neurological manifestations
COMBINE W/ ABOVE
Intervertebral Disc Lesion
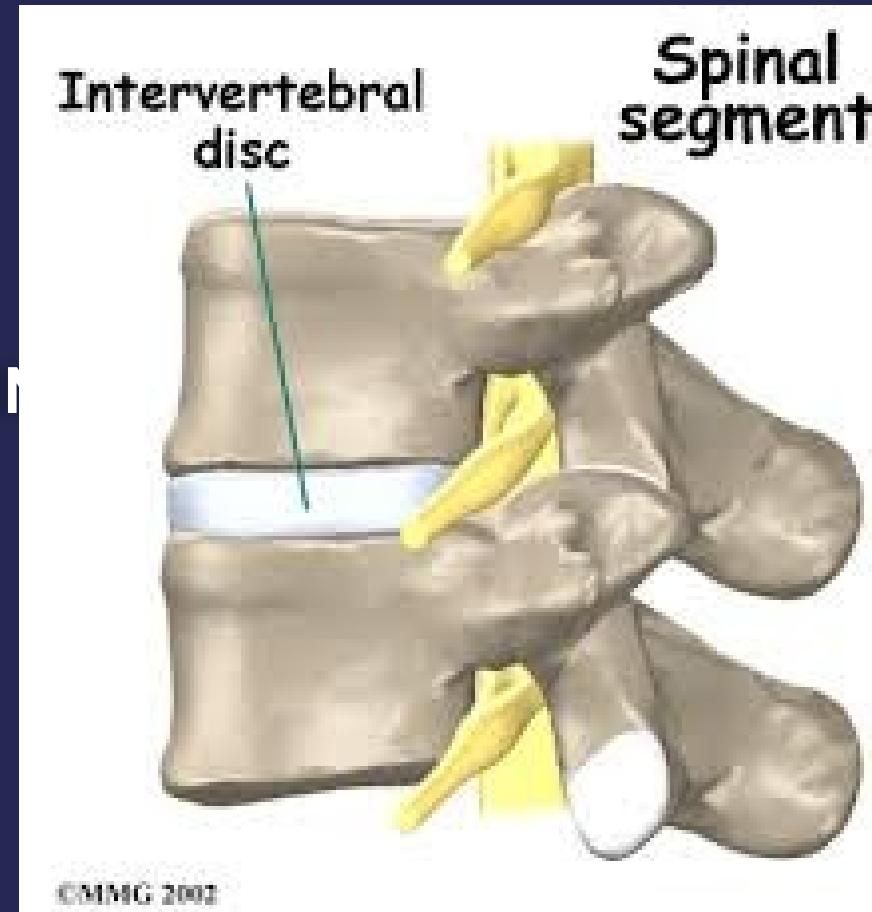
Structural Unit
The vertebral column’s functional unit involves:
Disc Anatomy
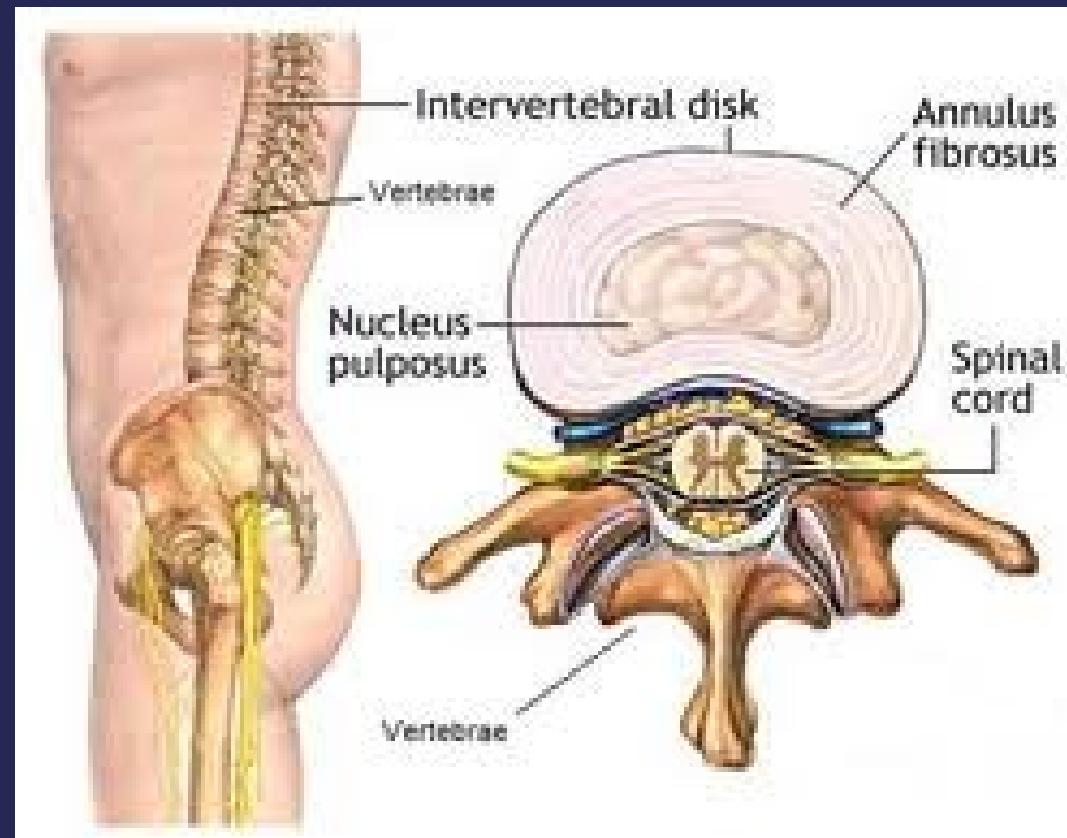
Disc is formed of:
- Nucleus pulposus
- Annulus fibrosus
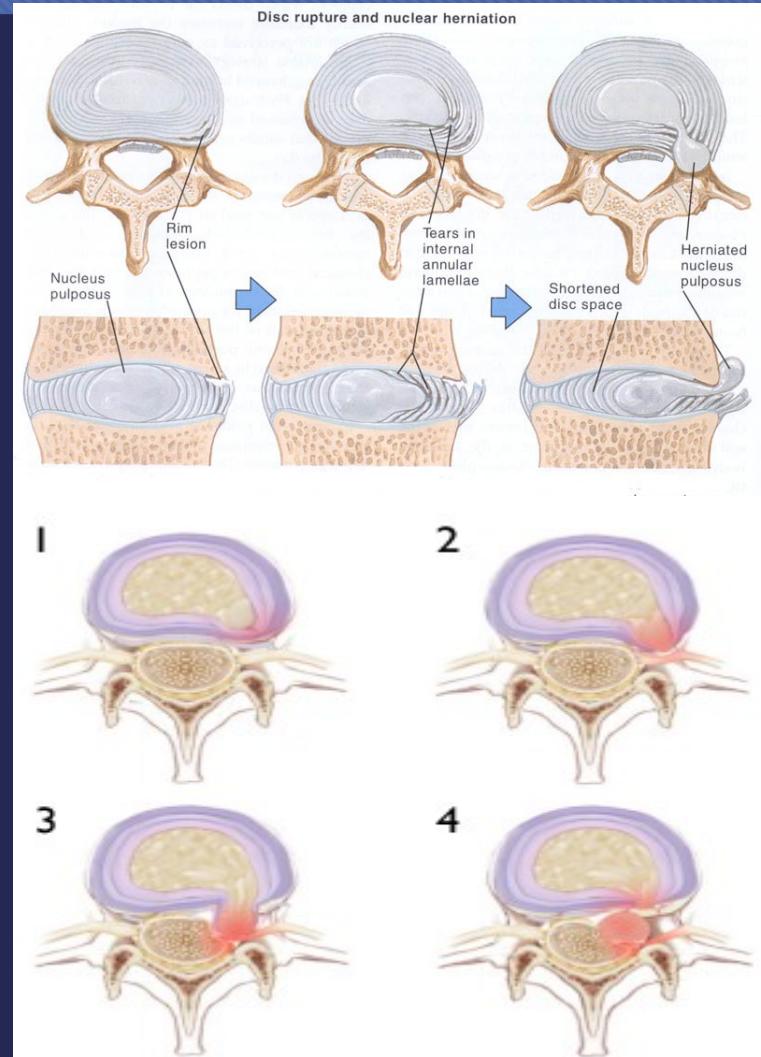
Pathology
- Bulge → back pain
- Protrusion → sciatica
- Prolapse & sequestration → numbness, paresthesia, weakness
Clinical Picture
Demographics
- Young adults commonly affected
- Children and elderly not immune
History and Symptoms
- Back pain and sciatica (increased with straining and coughing)
- Numbness and paresthesia
- Motor weakness

Examination Findings
- Spinal list
- Tenderness over midline and paravertebral muscles
- Straight leg raising test
- Cross straight leg raising
- Femoral stretch test
- Full neurological assessment
- Cauda equina lesion: sphincter problems, saddle area sensory loss
Neurological Levels by Disc Herniation
| Level of Herniation | Pain Distribution | Numbness Pattern | Weakness | Atrophy | Reflex Changes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L4-L5 disc (L5 root) | Over sacroiliac joint, hip, lateral thigh and leg | Lateral leg and first 3 toes (L5 dermatome) | Dorsiflexion of great toe and foot | Minor | Internal hamstring reflex diminished/absent |
| L5-S1 disc (S1 root) | Over sacroiliac joint, hip, posterolateral thigh and leg to heel | Back of calf, heel, foot to toe (S1 dermatome) | Plantar flexion of foot and great toe | Gastrocnemius and soleus muscles | Ankle jerk reflex changes |
Neurological Level Assessment
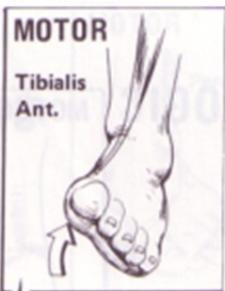
L4 Nerve Root
- Motor: Tibialis anterior
- Reflex: Patellar reflex
- Sensation: L4 dermatome

L5 Nerve Root
- Motor: Extensor hallucis longus
- Reflex: None specific
- Sensation: L5 dermatome

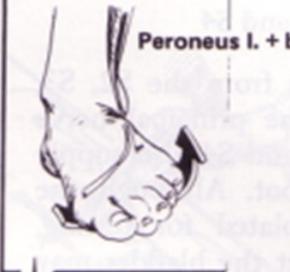
S1 Nerve Root
- Motor: Peroneus longus and brevis
- Reflex: Achilles reflex
- Sensation: S1 dermatome
Imaging
- X-ray:
- To rule out other bony pathology
- May show disc space narrowing
- MRI:
- Gold standard for disc identification and lesion localization
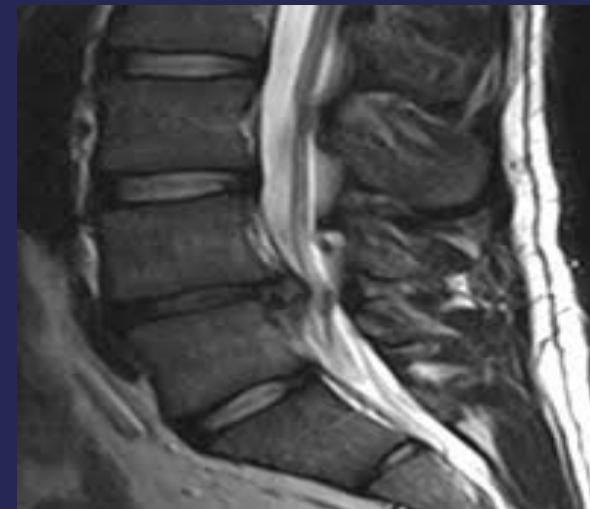
Treatment
Conservative Management
- Rest
- NSAIDs
- Muscle relaxants
- Physiotherapy
Surgical Management
Absolute Indications
- Cauda equina lesion
Relative Indications
- Persistent pain
- Progressive neurological manifestations
- Frequent attacks
