CCTD History
CCTD 1 Hx Abdominal
Introduction, Permission, Assure privacy, chap.
- Demographics (Name, Age, Gender, Nationality, Martial, Residency)
- Chief of complaint (Cause of hospitalization)
- HOPI + B Symptoms + Episodes
- Systemic. Review
- Past Hx
HOPI
Site
Pain wide range - (quadrants)
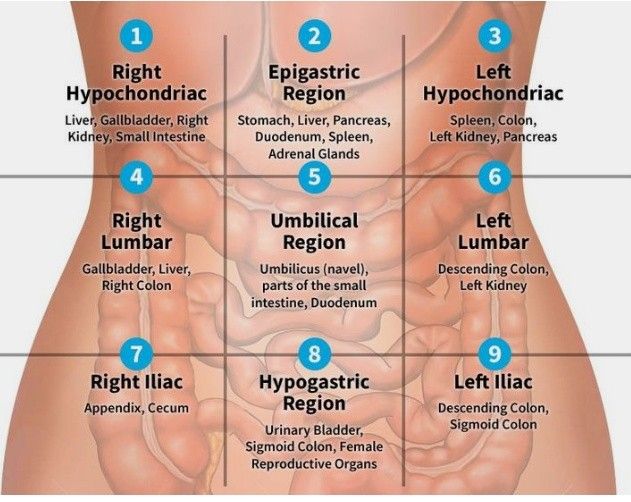
-
Right Hypochondriac
-
Right Lumbar
-
Right Iliac
- Appendicitis, Uriteric colic, pyelonephritis, cecum; IBD)
-
Epigastric
- Peancreatitis, GERD, Peptic Ulcer, Cancer, Deuodenal Ulcer, esophagitis, Left lobe of liver, Myocardial infacrtion)z
-
Umbilical region
-
Hypogastric region
-
Left Lumbar
-
Left iliac
- Divertucilitis
- Sigmoid -
- Ulcer
Onset
Acute
- Peritonitis follower by perforation (dialysis)
- Appendicitis
Chronic
- Hepatitis
- IBD
Both
- Intestinal Obstruction
Character
**Sharp/Stabbing/
Constrictive
Burning
- GERD
- Peptic Ulcer Disease
Throbbing
- Acute severe inflammation (infections)
- Abcess
Dull / Aching
- Acute cholecystitis (Inflammatory process)
Colicky Pain (Tubular structures - smooth muscle contractures)
- Stones (gallbladder, kidney, intestinal…)
- Uterine contractions
Heaviness?
Radiation
- Pancreatitis - RAD to the back
- Spleen - Left shoulder
- Cholecystitis - RAD Right shoulder (phrenic nerve)
- Appendicitis - Peri-umbilicus shifting to the right illiac fossa ???
Associated
Fever, melena, hematemesis + B symptoms + Systemic
Episodes
timing, Duration, episodes of free disease.
Factors
-
relieving factor,
-
Exacberating factors
Peptic ulcer GERD - R Milk peritonitis - any movement pain - stand still IBD IBS - Stress factor
Severity
1-10 Grading with Limitations - cant walk, work, or think
CCTD 2 Hx Biliary Colic
type of pain - it comes in goes
- Renal colic
- biliary colic
- urinary colic
Cholecystitis constant Dull aching pain - radiation to shoulder due RT dome diaphragm supplied by phrenic nerve
Introduction, Permission, Assure privacy, chap.
- Demographics (Name, Age, Gender, Nationality, Martial, Residency)
- Chief of complaint (Cause of hospitalization)
- HOPI + B Symptoms + Episodes
- Systemic. Review
- Past Hx
Demographics
35 years old male
-
40 age & Females most commonly due estrogen
Chief of complaint
complain pain 5D in right upper quadrant - associated with jaundice
HOPI
Site + Radiation RUQ - rad to shoulder - Chole Epigastric - RAD Back - pancreatitis
Onset Sudden? Chronic?
Character Coloiky, Constant dull aching pain Biliary colic if theres impaction of stone???
Association Fever, maliase , nausea, vomiting, urine, stool
(obstructive jaundice in case pale stool) (Urine dark due liver is normal water soluble goes serum body fluids) (Pre-hepatic insoluble bilirubin - Normal urine & Stool Dark) (steatarohea due ??)
jaundice if someone noticed it do you have itching or dark urine
Timing After eating food
Exacerbating relieving Eating especially in Fatty food will increase pain - due bilestone contraction Leading forward? Not eating? Analgesics?
Severity 8-9?
Past Hx
Past Medical: recurrence, DM, HTN Past Surgical; cholecystectomy, previous stone removal Drug abuse: Alcohol, Travel (malaria),
Systemic Review
…
Jaundice
Prehepatic: hemolysis, Malaria
- normal hepatic function - high indirect bilirubin
- urine & stool normal
Hepatic: Liver cirrhosis, Viral Hepatitis,
- Fever + malaise, Organomegaly
- ALT & AST ratio is higher
- Total bilirubin raised
- ALP is normal?
Post-Hepatic: Obstruction (Stones, head pancreas, carcinomas, strictures, inflammatory conditions; cholangitis, ((((((perampilliary tumour around the ampulla of vater - oppening both cbd????) ))) ((2cm pearmapillary tumour - maybe cancerinoma of ampulla of pancreas or bile duct or deuodenmum??)))))
Internal Obstruction - External obstruction - carcinoma head pancreas, LN’s in portal triad
- Jaundice, pleuritis, (Itching??)
- ALP, GGT high
types of stone and its location list?
stool & urine color depending on hepatics
Investigations
CBC (leukocytosis; obstruction, RBCs) LFT (ALT AST ALP GGT Amylase…) Coagulation profile (increased prothrombin in obstruction - deficient liver vit K) Lipid Profile Viral profile
U/S - size CBD (gallstone, carcinoma), acoustic shadow, thickness wall, distended, collapse, tumor in pancreas
ERCP - endoscopy, deuodenum, ampulla vater, dye is injected - to see any strictures or stone - stone can be retrieved - retrograde
MRCP - Diagnostic - intra/extra hepatic biliary tract imaging
CT - cancer, staging, malignancy
PTC - TANSEEM; used in severe cases of bilirubin to decompression - ?? -
Diff
Management of obstructive jaundice
Depends on the cause
- Choledicocholethiasis - ERCP if fails open surgery
- Carcinomas - chemotherapy, surgery depending on stage/operable diseases
- Head Pancreas carcinoma - whipples surgery
note
gallbladder palpable - carcinoma ? Corviesar law? - distendended gallbladder suggested carcinoma
not palpable - in stone due to reccurent stones resulting in fibrosis
Charcot Triad (jaundice, Tenderness, RUQ, Fever)
Pentad (Triad + confusion + Hypotention)
typical presentation head pancreas - painless progressive jaundice
CCTD 3 Breaking Bad News
nevus melanoma - biopsy positive for cancer
be sensitive - Empathy - no sympathy im sorry, hold patient, RIP
How to break bad news Greet patience, introduce, explain that you have took biopsy.
sit on right angle, no table in between, lean forward
ask if there any family members or loved ones who can be present
make summary on all findings and results - ask his ideas on his illness the result is out
warning shot chunke chenke
avoid jargons
ask if to continue the conversation
Premature assurance never do it - say كل ضغيره / علم عند الله / , explain further investigations, and medical plans.
Explain the procedures that could help
Sign posting (options of treatments) biopsy excision cancer chemotherapy treatment
i will be with you
tell old patient news perferabbly to ease treatment process, will etc…
CCTD EXAM
CCTD 1 Ex Abdomen
Abdomen examination
- Introduction
- Position & Exposure (Midchest-Midthigh)
Inspection
Go in-front patient check for
-
hernias (Cough)
-
Umbilicus
-
Scars / Surgical / tattoos
-
Deformities
-
Distention; 5 S’s (normally mild convex)
- Fluid; Ascites
- Fat
- Flatus; Gas
- Fetus
- Fibroid - Mass
-
Hair distribution
-
Abdominal movement with respiration
- Male - Abdomino thoracic
- Female - intercostals stronger
- Obstruction (intestinal / Gastric) perlstatic movement
- Pulsation (tumour / )
- Hernia (Cough - Bulging appear)
- Positive expansile impulse
- Umbilicus (Position “Central, shifted; due tumor”, evert, invert, discharges; pus, urine, fistula, etc…, skin; hair distribution, scars, cushing, cullen’s sign, caput medusa “central Portal HTN” peripheral IVC obstruction)
Visible Mass comment ??
- size
- Contour (scaphoid; obstruction, distended; fluid fat fetus flatus fibroid)
- shape (Smooth, Irregular)
- Skin overlying (cyanosis, scars, erythema)
- Pulsation - Pulsatile or not
Palpation
Do you have any pain in abdomen - start far away from site of pain - look at the patient eyes to check any tenderness
Superficial Palpation
- Tenderness
- Gaurding
- Palpable mass
Deep Palpation - after inspiration palpate the areas
- Organomegaly
- Hepatomegaly - Edge + Tenderness +liverspan
- Pyelomegaly - ballotment? - (costo-vertebral angle)
- Splenomegaly - Oblique growth (Renocolic; splenic flexture)
- Cholecystitis - Murphy’s sign (Catch breathing)
Percussion
Resonance tympanic,
AUsc Perstaltic movement, aneryusm,
CCTD 2 Ex Neck mass
6 minute exam Greet, introduce, explain procedure, take consent, assure privacy, chaperone, Position & Exposure
Local Examination
- at same level
- check from sides (to check visible pulsations, bulging)
- Movement from swallowing (pretrachial fascia; thyroid, hyoid, pretrachial prelaryngeal LN ????CC)
- Protrusion of tongue
Comment on lesion if found
- Site (right neck swelling)
- Size (0.2x0.8 Meters use ruler)
- Shape (Irregular regular)
- Surface (feel surface Nodular or Smooth)
- Depth (Deep or superficial - check contraction after squeeze hand)
- Colour (strawberry, portwine?, purple, orange, chronic inflammation; hyperpigmentaiton, redness; active inflammation )
- Temperature ( Hot; Abscess, Malignancy , Cold, Normal; Lipoma)
- Tenderness (Painful or Painless)
- Edge (Ill-defined or well-defined) feel the edge?
SSSSC TTED
Palpation
-
from behind patient, three fingers against one side of lobe pushing the other against it - ask patient to swallow while palpations (put it below lower pole/edge of mass to exclude retrosternal goiter - if its positive non palpable its retrosternal goiter) - (((solitary if one sided????))) - comment on lesion as previously mentioned S4 DECTT
-
Temperature of each side - compare with sternum
-
Tenderness - by staring at patient eyes from behind
-
Comment on lesion
-
Tracheal Position
-
Carotid/ superficial temporal Pulsation
-
LN’s Neck (submental, submandiublar, pre-pot auricular, sub-occipital, anterior cervical, posterior cervical?, supraclavicular )
Mass Pull skin to see if its attached to skin (such as sabbecous cyst) (video?)
put your fingers in between sternocleidomastoid to seperate mass (video?) - attached to muscle
Composition: Solid, fluid or gas
- consistency (Hard/Firm/Soft like?) (soft if pheripheral??)
- fluctuation (Fluid; Cyst - Pseudocyst; without epithelium Push two fingers against another in between pressing from above) (Cystic push in central)
- fluid thrill ()
- translucence (Torch; hydrocele - any cyst vs hernia)
- resonance
Paget’s test? - two finger step toeing - if area is tender can be used if the swelling is very small - or illdefinedCC
vascular
-
pulsatility (Transmitted/True? - aneurysm, varicose) - Expansile vs transmission (two finger))
-
compressibility (Tumour/Hernia/)
-
bruit (Turbulence/Murmur - thrill if palpable)
- Reducibility (Renal Hernia, cough)
- Relations to surrounding structures – mobility/fixity
- Regional lymph glands (Malignancy/Infection — Primary / Secondary
PercussionCC
- Percuss from sternum with one hand - any dullness - retrosternal goiter
AuscultationCC
Thrill, carotid auscultation
CCTD 3 Peripheral vascular dis.
ACT - examination of lower limb - ask vitals
Intro
Greet, Introduce (5th year med), assure privacy (curtain, nurse), explain procedure, position (mention good position - supine semisitting) & exposure (from lower abdomen - cover genatelia)
ulcer found in LT Found
General appearance
conscious alert man, well built, healthy, looks comfetable laying on bed, connected to vitals signs, no iv canulla, no oxygen, no foleys
“Now i will do focused examination after general apperance”
General examination
no pallor (check eyes for pallor - look up), hand no tar staining
Inspection
Inspect infront bed patient, to inspect, check between foot fingers, raise legs to see any hidden ulcer
General findings of Peripheral vascular disease (typically pale hair loss atrophy erythema skin break down wound nail changes )
theres gauze medial on surface of foot, the gauze is soaked with (pus yellow, clear fluid) dressing is clean? (clean) - ask examiner if you can remove the gauze..
Comment on ulcer for size Floor + Edge (surface) shape Surrounding
squeeze distal from both sides - to see any accumilated pus inside ulcer
Floor by inspection feel base by palpation
Palpation
check tenderness & temperature on all levels of lower limb from foot tibia thigh right and left
Pulse examination (examine one side each)
- dorsalis pedis (assessed tarsal bone lateral to hallicus longus)
- Posterior tibial (medial malleous two cm midway)
Capillary Refill
- compress finger (hold finger then compress nail bed - 2-3 seconds)
Beurgers test Assure no lower limb pain before doing the test 10 degrees 10 seconds - add repeat until pallor appears
looking for change of color - will turn pale positive
if pale sit down then drop lower limb down - if foot become red hyperemia indicates positive sign
do the next lower limb
Percussion
no percussion
Auscultation
mid inguinal point ASIS - auscultate the femoral artery
medial surface of foot midside of the thigh - site of adductor/hunter canal - where femoral come deep to superficial
?? systolic lower upper limb
i will finish examination with neurological exam & upper limb peripheral
investigations
CBC Sample Urine
Q&A
if you dont feel pulse (weakflow)
- check next level
- use hand held doppler (will assess flow in vessel - gives sound)
other notes
chronic - diffucult hx due no pain
CCTD 4 - Liver Mass
General appearance
…
Abdomen examination
- Introduction, explain, consent, wash, chap, vitals.
- Position & Exposure (Midchest-Midthigh - cover genetalia)
Inspection
Go in-front patient check for
-
hernias (Cough)
-
Umbilicus
-
Scars / Surgical / tattoos / discoloration
-
Deformities
-
Distention; 5 S’s (normally mild convex)
- Fluid; Ascites
- Fat
- Flatus; Gas
- Fetus
- Fibroid - Mass
-
Hair distribution
-
Abdominal movement with respiration
- Male - Abdomino thoracic
- Female - intercostals stronger
- Obstruction (intestinal / Gastric) perlstatic movement
- Pulsation (tumour / )
- Hernia (Cough - Bulging appear)
- Positive expansile impulse
- Umbilicus (Position “Central, shifted; due tumor”, evert, invert, discharges; pus, urine, fistula, etc…, skin; hair distribution, scars, cushing, cullen’s sign, caput medusa “central Portal HTN” peripheral IVC obstruction)
Visible Mass comment ??
- size
- Contour (scaphoid; obstruction, distended; fluid fat fetus flatus fibroid)
- shape (Smooth, Irregular)
- Skin overlying (cyanosis, scars, erythema)
- Pulsation - Pulsatile or not
Palpation
Do you have any pain in abdomen - start far away from site of pain - look at the patient eyes to check any tenderness
Superficial Palpation (palm completely covering abd)
- Tenderness
- Gaurding
- Palpable mass
Deep Palpation - after inspiration palpate the areas - move palm on against of organ
- Organomegaly
- Hepatomegaly - Tenderness +liverspan (confirm with chest percussion, then reconfirm percussion on abdomen for dullness after palpation) - Edge (sharp round?) surface (nodular, smooth?)
- Pyelomegaly - ballotment? - (costo-vertebral angle)
- Splenomegaly - Oblique growth (Renocolic; splenic flexture) (use tips of hand on direction oblique more to palpate the spleenomegaly)
- Cholecystitis - Murphy’s sign (Catch breathing)
How to differentiate kidney, spleen
-
Spleen has notch, enlarges Diagonally/Oblique, moves with respiration, not palpable, under rib cage cant go above it
-
Kidney enlarges Vertically, largely unrelated, Palpable , Ballottable, does not move with respiration
Percussion
Resonance tympanic,
AUsc Perstaltic movement, aneryusm,
CCTD 5 - Breast Lump
Examination
- conesnt
- vital signs
- general apperance
- postion expoosure
- upper umblical above
Inspection
-
assymetry - level
-
affected areas
-
vissible masses
-
Discharge, ulcers
-
texture of nipples (peduea orange; thick edematous skin - due lymphatic drainage blockage)
-
nipple retraction due mass behind niple - (could be physiological)
-
cooper ligament holding structure of breast -
-
skin dimpling - due fibrosis of malignant cells infliltration to cooper ligament
-
raise arm and to waist
-
infammary lines, protraction of pectrolaris muscle to see any dimpling
Palpation
clockwise palpation to check any masses/tenderness solid hard mass, irregular margin, immobile.
- location - inner uper quadrant
- size?
- consitency?
- tenderness?
- hotness/temprature?
- margin?
palpate aeoral complex
Check for Lymph Nodes palpable lymphoadenopathy - axilla & Cervical describe how many, features, tenderness in each side
TNM stages
T tumor site N lymph nodes involved M metastisis
General examination
- respiratory,
- abdomen
- spine
examine the back spine, bone abdomen for organomegaly
staging for diff? 5x5 mass hard immobile irregular mass with nipple retraction, axilla/supraclavical negative
early stage breast cancer
surgical duct excision
Investigations
Surgical
- CBC
- Coagulation profile (INR, Prothrombin)
- LFT (metastases) & KFT (contrast)
- Electrolyte (calcium; malignant hypercalcemia)
- Albumin
Diagnosis
- mammography (more fatty - old age 40 and above)
- U/S (more dense - young) differentiate cyst, mass, suspicious LN
calcification, structure, surgical plan for calcification mastectomy in this case due phrophylaxis
loboectomy if only lump mass found at place.
grade of mammorgam birad 1-6 scores classifcation - indications for biopsy depending on features of the mass
5-6 likely only for biopsy (in this case) Do fine needle aspiration / core needle biopsy
- Core bipsy?, receptors, ER, Progestrin, HER
- FNAC - breast cancer cell not diagnostic
invasive ductul carcinoma grade 2
- CT abd chest, all
- Nuclear PET Scan
approach is multideplicintary NEO??
before surgery - new adjuvant therapy
surgery
-
loboctomy -
-
axilla is negative in all imaging - take sentinel lymph node biopsy (first group of LN, pick with gamma probe, then study when frozen - check if theres metases for indicatiative axilla dissection) - sentinel is used when no evidence but cancer
-
2 & 3 suspectious LN - METS - Axillary dissection
post surgery treatment - adjuvant therapy
Staging
- ?
risk factors to know 3 years of contraceptive use early menopause (ask age of menarche) Nullaparity famiily hx of genitoutinary cancers - BRCA - HERN2nue? previous cancer
Systemic review Unremarkable
ask for
- Bone
- Lung
- Liver
- B symptoms
CCTD SKILL
CCTD 1 SK Suturing
Scrubbing
-
Remove all foreign body’s - scratch previously
-
Hand - palm palm, palm dorsum, between fingers, interlock, thumb, tips, forearm (up to down from proximal to distal until elbow) - three times (last forearm till wrist?) - raise arm DUA/MONK
-
Gown - ???CC
- given by nurse - give hug to sleeves - find two behind and connect
- If no nurse is present - let it go, hold from tip, go to sleeve - Closure from behind, connect two threads contra
Hold card give it to dr. - Release short thread from card, holded, going direction of anti-clockwise , then knot long thread after twirl maneuver
-
Gloves - after raising hand covering wrist -
- Open Bag from outside - RT & LT THUMB up roof- Wear inside out
- Put thumb to the roof same direction to opening
- RT traction then leave it dont pull - right hold from inside
- LT - pull completely, then pull RT from inside
- Fix both after completion
if given by nurse
-
tell nurse right or left -
-
put hand to direction to the glove from thumb
-
then push in same direction
-
take scrub from OR
-
Head cap
-
Face mask
-
Gown
-
Shoes cover
Dont touch anything blue/green - i.e. sterile instruments
scrub w/ you - closer to field - intrested
Suturing
- Needle Holder - Ring finger w/ thumb
- Needle distal 1/3 to 2/3 & Straight 90 degree
- Movement - Supination + Pronation
Forceps - hold like pencil
CCTD 2 SK Nasogastric tube insertion
Nasogastric Tube & enteral feeding
Indications for GI Intubation
- To decompress the stomach and remove gas and fluid
- To lavage the stomach and remove ingested toxins
- To diagnose disorders of GI motility and other disorders
- To administer medications and feedings
- To treat an obstruction
- To compress a bleeding site
- To aspirate gastric contents for analysis
paralytic illeus, gastric lavage (suction) better in Double lumen Medication, nutrition (delivery)
contraindicationsCC
Absolute
- Facial trauma and/or basilar skull fracture
- Esophageal stricture
- Alkaline ingestion
Relative
- Coagulopathy
- Prior gastric surgery (e.g., gastric bypass)
- Recent nasal surgery
complications
- Clogged Tube- most common
- Oral mucosal breakdown
- Nasal irritation/ulceration
- Dumping Syndrome.
- Aspiration during feeding : ensure head of bed is elevated at least 30 degrees while feeds are being administered
- Dehydration- diarrhea is a common problem.
- Electrolyte imbalance: hyperkalemia and hypernatremia
- Gastric mucosa ulceration
Items
- nasogastric tube or (single lumen tube) or (laven) - can be used as suction and feeding - better for double lumen
- Double lumen tube (salim sump??) - better in suction due venting
confirm tube by x-ray from the blue lines in the nasogastric tube
ACTING - not i will do
greet amm ahmad, introduce your self, explain the procedure (reach nose to stomach for suctioning or medications), take permission, wash hands, close curtain, take nurse to assist, hand client glass water keep it in vicinity.
know reason why to put nasogastric tube - suction or delivery mainly?
ask patient previous nose administration, if he knows size of the nasogastric tube.
-
if theres any pain raise your left arm (OBTAIN SIGN) stop procedure.
-
Position 45 degrees - Position the patient in a semi-sitting or high fowlers position. If comatose-semi fowlers, expose upper trunk
-
take distance from nose to lobe behind ear, to side of neck, till the xiphoid process
-
Lubrication - best lidocaine appliance patient to his own nose
-
ask patient which nose is used previously -
-
inspect for most patent (septal defect, polyps, lesions) other way (close nose take breath check for most patent) - Emphasize the need to mouth breathe and swallow during the procedure
-
flexion of head whilist insertion - ask patient to swallow, Gently insert tube through nostril to back of throat (posterior naso pharynx). Have patient flex head toward chest after tube has passed through naso pharynx If resistance is met or client starts to cough, lacrimation, choke or become cyanotic stop advancing the tube and pull back.
-
Confirmation - check correct placement A) with suction (May not be accurate - may be no acid) (comment on food characteristics)
B) pH TEST - 5.5 ph in stomach normally with test pH automatic or strip - empty fluid in the field -
C) BUBBLES take the stethoscope heart the stomach, push air to listen for any bubbling in epigastrium
D) X-ray GOLD STANDARD to check - a tube passing center of chest, passing diaphragm, tip below tip of diaphgramgm ((THREE FINDINGS SHOULD BE PRESENT))
E) CAPNOGRAM - high reading of CO2 means the nasogastric tube could be in the lung
-
Fix it - Secure the tube with tape or commercial device
X-ray placement
1- follows straight course through midline to below diaphram
2- tube not follow bronchus path
3- not coiling
4- tip tube below diaphragm
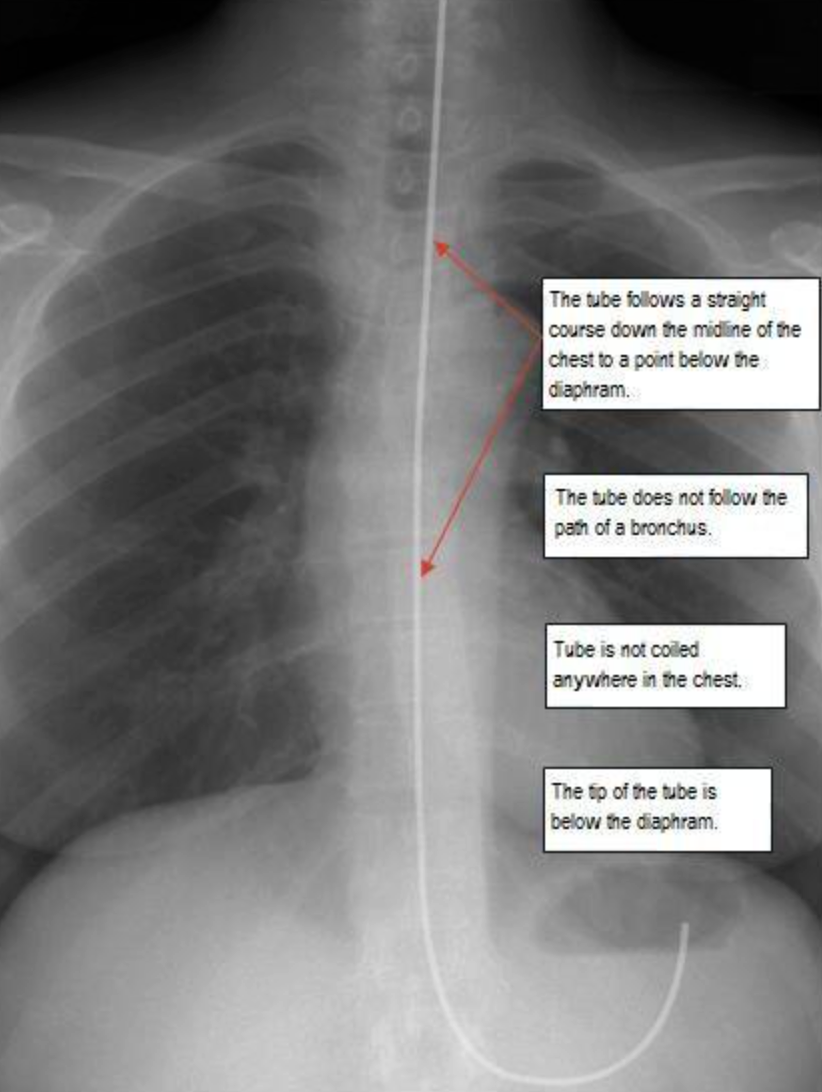
Fix it
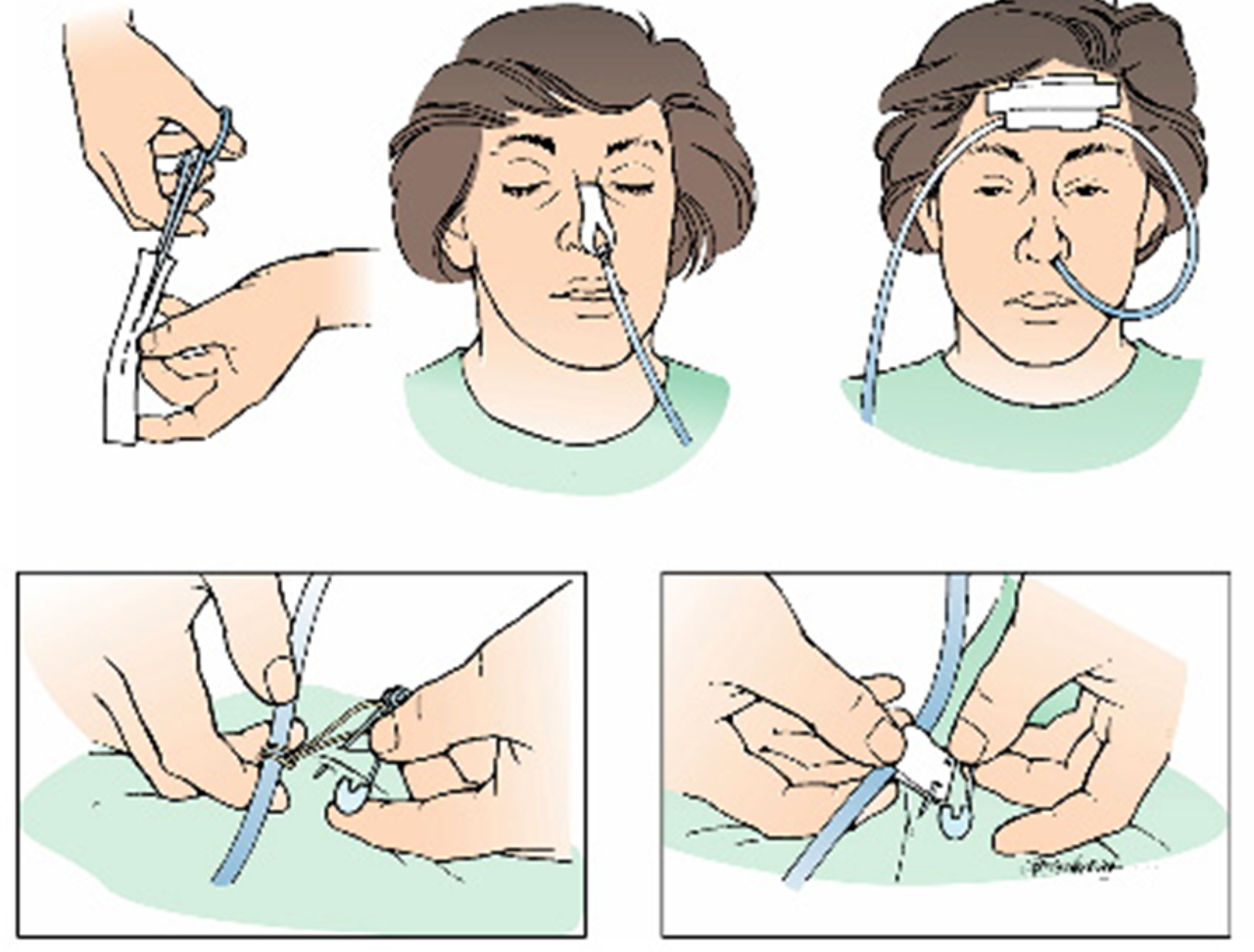
Intubating the patient with an NG tube????
-
Assessment:
-
Who needs an NG:
- Surgical patients (bowel obstruction, Ileus, …)
- Ventilated patients
- Neuromuscular impairment .
- Patient with swallowing disorders (post CVA, …)
-
Assess patency of nares.
-
Assess patient medical history:
- Nosebleeds
- Nasal surgery
- Deviated septum
-
Anticoagulation therapy
-
Assess patients’ gag reflex.
-
Assess patient’s mental status.
-
Assess bowel sounds.
CCTD 3 Urethral Catheterization
Indication of Urinary Catheter insertion
A urinary catheter is used in many different situations:
- Decompression;
- BPH
- A urinary catheter may be inserted to drain the bladder before or during a surgical procedure, during recovery from a serious illness or injury, or to collect urine for testing
- A urinary catheter may be used for a person who is incontinent of urine, if the person has wounds or pressure ulcers that would be made worse by contact with urine
- A urinary catheter is necessary when a person is unable to urinate because of an obstruction in the urethra
Contraindication
-
Known or suspected urethral injury in case of pelvic fracture (absolute)
-
Signs to suspect urethral injury (blood at meatus , gross hematuria ,perineal hematoma ,high riding prostate gland) - (absolute contraindications)
-
Urethral stricture, recent urethral or bladder surgery (relative) Combative or uncooperative patient (relative)
Complications
- Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Trauma to urethra & bladder
- Paraphimosis
- Undesirable catheter retention
Caring for a Person with an Indwelling Urinary Catheter
-
Indwelling urinary catheters are connected by a length of tubing to a urine drainage bag
-
The tubing is secured loosely to the person’s body near the insertion site using a catheter strap or adhesive tape
-
Securing the tubing to the person’s body prevents the catheter from being accidentally pulled out during repositioning
equipments - catheter tray
-
Gel
-
syringe (with distilled water - to inflate ballon of catheter - capacity in cath)
-
sponges
-
Cotton swaps
-
tape to anchor tubing
-
forceps
-
foley’s catheter (two way/indwelling) (12cm pedia - 16-18cm adults)
-
or three way catheter (continuous irrigation & drainage)
-
Sterile drainage tubing with collection bag
-
Bath blanket
Procedure
In Males
-
Greet patient, explain full procedure, take confirmation, nurse
-
before starting make sure everything is prepared
-
Open instrument and make it ready for use
-
ready the catheter - bifidone - saline - gin
-
Supine for males. (position and exposure)
-
Wear sterile gloves
-
Apply Drape
-
Non dominant hand will hold the skin, labia/penis
-
Retract skin,
-
Take cotton with bifidone then clean meatus circular away from point to scrotum in circular motion, do not return to same area throw cotton, wear new gloves after first - take another one with same motion - repeat three times -
-
inject lidocaine intro penile urethra
-
Keep holding with you non-dominant hand
-
then inject lidocaine gel lubricant in urethra
-
with your right hand, hold folly’s catheter then pull 90 degree from non-dominant whilist holding penis - put the catheter fully inside.
-
you can add extra lidocaine to catheter; Then insert with nondominant hand keeping it completely straight, then push catheter all the way until end - in females until urine flows
-
Then drop your non domininant hand
-
Confirm urine is flowing before inflating the balloon
-
Inflate balloon, then pull catheter to hold it in place, then connect the bag, tape the cath from side.
-
We keep bag below patient
Document the patient file time, did procedure go perfectly, is there any hematuria?
In Females
- non dominant hand to hold
- then use cotton with your right hand to clean around and inside the labia
- If it goes inside vagina, then throw it out and change the catheter
- 5-7 cm insertion - then when you see urine come out - push it more 2 cm then inflate the balloon
- attach by side of thigh
- keeping the bag below the patient, by the side of the bed
CCTD4 Per rectal/digital/ protoscope
Introduce, explain, permission, chap, privacy, wash, gloves
Position & Exposure
- PR is part of abdominal exam - Mid chest to Mid thigh
- SIMs position / left lateral debicutus position
Inspection
first pull buttocks check any abnormality
-
Fissure on posterior - lumbar side
-
Fistula - due abscess formation of tract // many fistulas due crohn, TB, investigate more to the patient.
-
Hemorrhoids
-
Abscess
-
Discharge / Redness / Any change
Palpation
Tell the patient that you will introduce your finger, ask patient to relax
-
apply gel to your finger then palpate anus until relaxation
-
Introduce part of finger - then ask patient to grip on finger to check on sphincter tone (neurological problem, truama, etc..)
-
Rotate 360 degree of finger while insertion and exerion
- hemorrhoids visible onlyCC ?
- smooth?
- Pathologies? (pulops, tumors)
- Prostate (groove - normal sulcus of medial, BPH | lateral cancer sign)
- Look your fingers afterward (blood, stool, pus, discharge - comment)
Anoscope
it has two parts - shaft & obturator
- lubricate
- relax - go deeper
- introduce anoscope straight toward the umbilicus, you will see polyps
- pull obturator afterwards
check protosxope for any abnormality
End
ask if patient needs any help, thank the patient document in patient files