it is 3 stages
I. Stage of Diabetes without retinopathy:
II. Stage of non proliferative retinopathy( Background retinopathy):
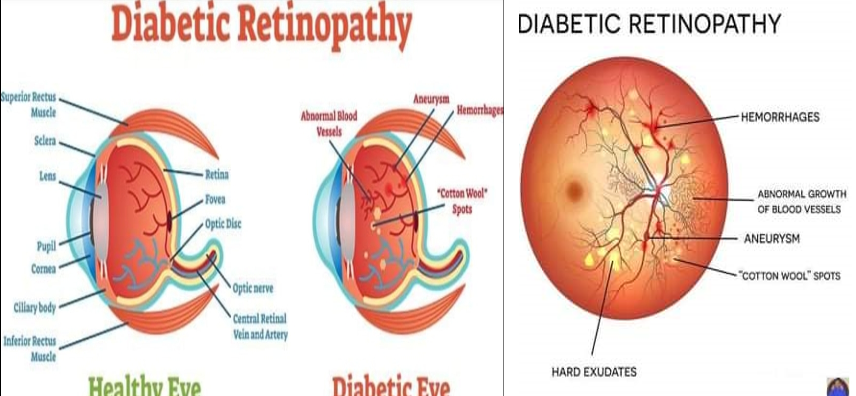
III. Stage of Proliferative retinopathy : due to damage of retinal capillaries leading to ischemia which stimulate release of VEGF and formation of new capillaries
Clinical presentation:
- Asymptomatic
- Blurred vision,floaters,blindness
pathological lesions:
- Microaneurysm - earliest sign.
- Hemorrhage. Dot’s (microaneurysm) and blot’s (hemorrhages)
- Macular edema.
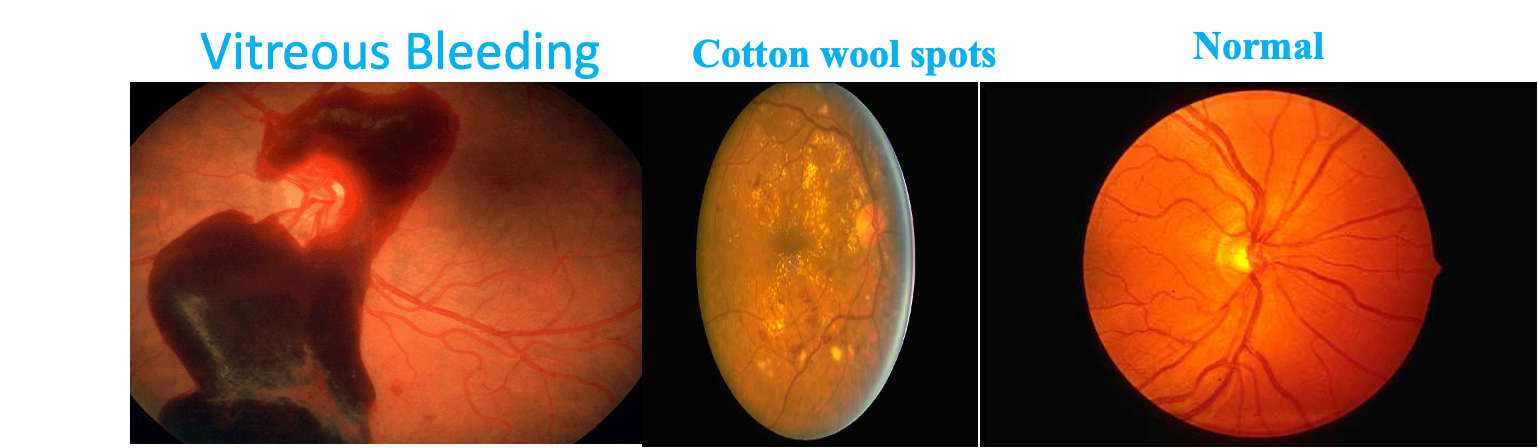
- Vascular occlusion leads to large ischaemic areas producing infarcted areas (cotton-wool spots).
Other Eye Complications:
- Cataracts,glaucoma at earlier age than non diabetic persons.
- Vitreous Bleeding.
Management of Diabetic retinopathy
I. Asymptomatic patients :
-blood glucose regulation
-yearly eye examination
II- Symptomatic patients
-
Metabolic control: A- glycemic control HBA1C ﹤7% B- Blood pressure ﹤130/80mmHg
-
Antiangiogenic factor: using monoclonal antibodies that bind to vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF).
-
Retinal laser photocoagulation with local anathesia: specialy in patients with proliferative retinopathy stage.
-
surgery: e.g vitrectomy specialy if there is hemorrhage interfere with vision