FM
Therapeutic
Approach to chest Pain
Introduction (Accurate Diagnosis Remains A Challenge)
- 5 Million (9%) ED visits
- Second most common cause of ED presentation among adults in the US
- Chest pain is the chief compliant for 1-2% of OPC and 70% of ED visits.
- Cardiac etiology found in < 1/3
- 2% of patients with acute MI are unrecognized and discharged from ED.
Common Causes of chest pain
- Cardiac causes
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome - Prolapsed Disc
- Psychological Pain
- Pulmonary Causes; Pneumonia, Spontaneous Pneumothorax
- Gallbladder disease, Pancreatitis, Transverse Colitis
- Peptic Ulcer, Esophageal Reflux, Spasm
- Costochondritis ,Cervical disk disease , Trauma or strain,
- Herpes Zoster
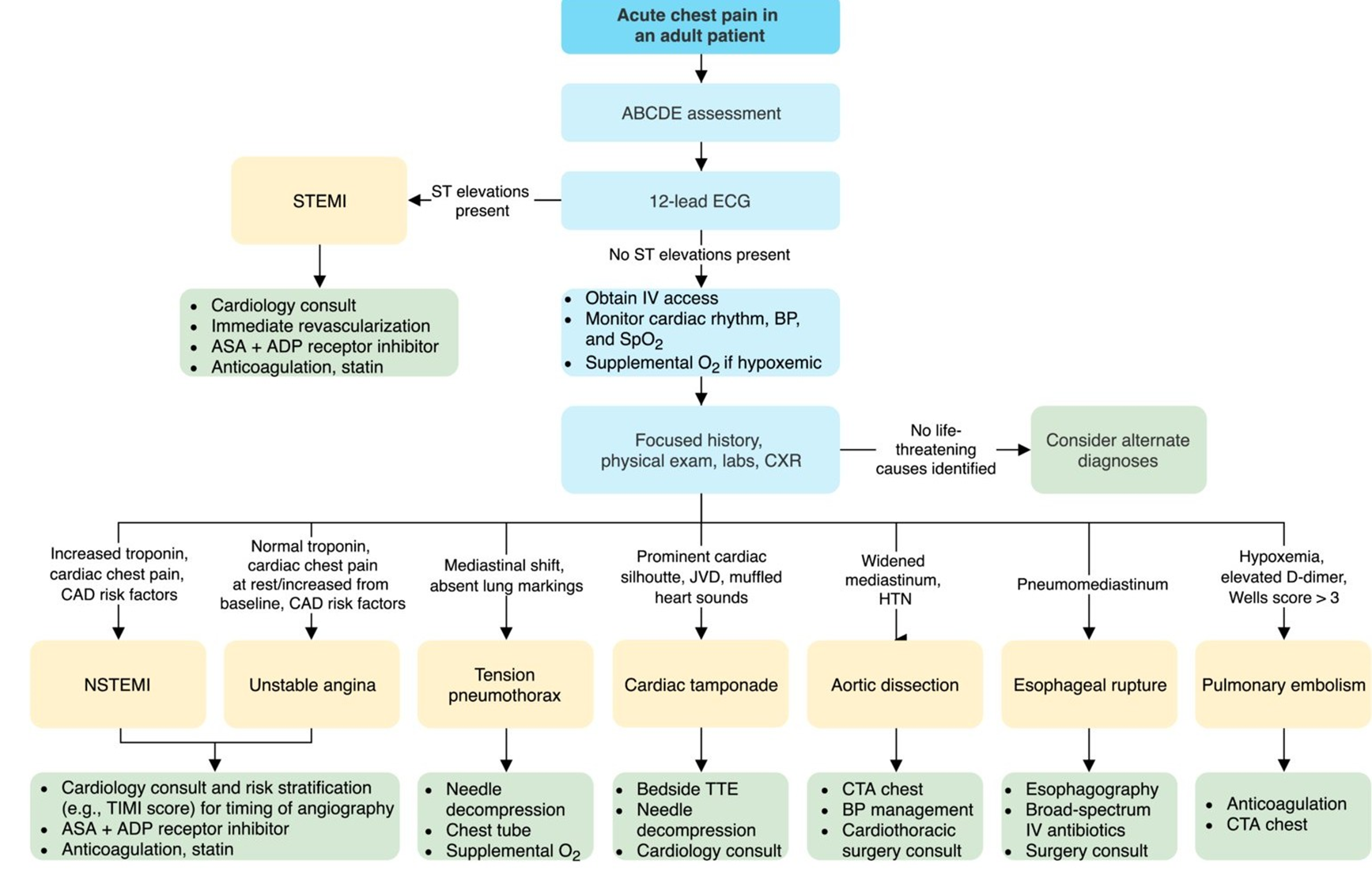
HISTORY IS THE KEY TO THE DIAGNOSIS OF ETIOLOGY OF CHEST PAIN
CLINICAL APPROACH TO CHEST PAIN HISTORY
LIFE THREATENING CAUSES
- Oesophageal Rupture
- Acute coronary syndrome
- Dissecting Aortic Aneurysm.
- Cardiac tamponade
- Pulmonary embolism
- Tension Pneumothorax
Risk Factors?????

- Mitral Valve Prolapse
- Pneumonia
- Costochondritis
- Esophagitis
- Herpes Zoster
- Gallbladder Disease
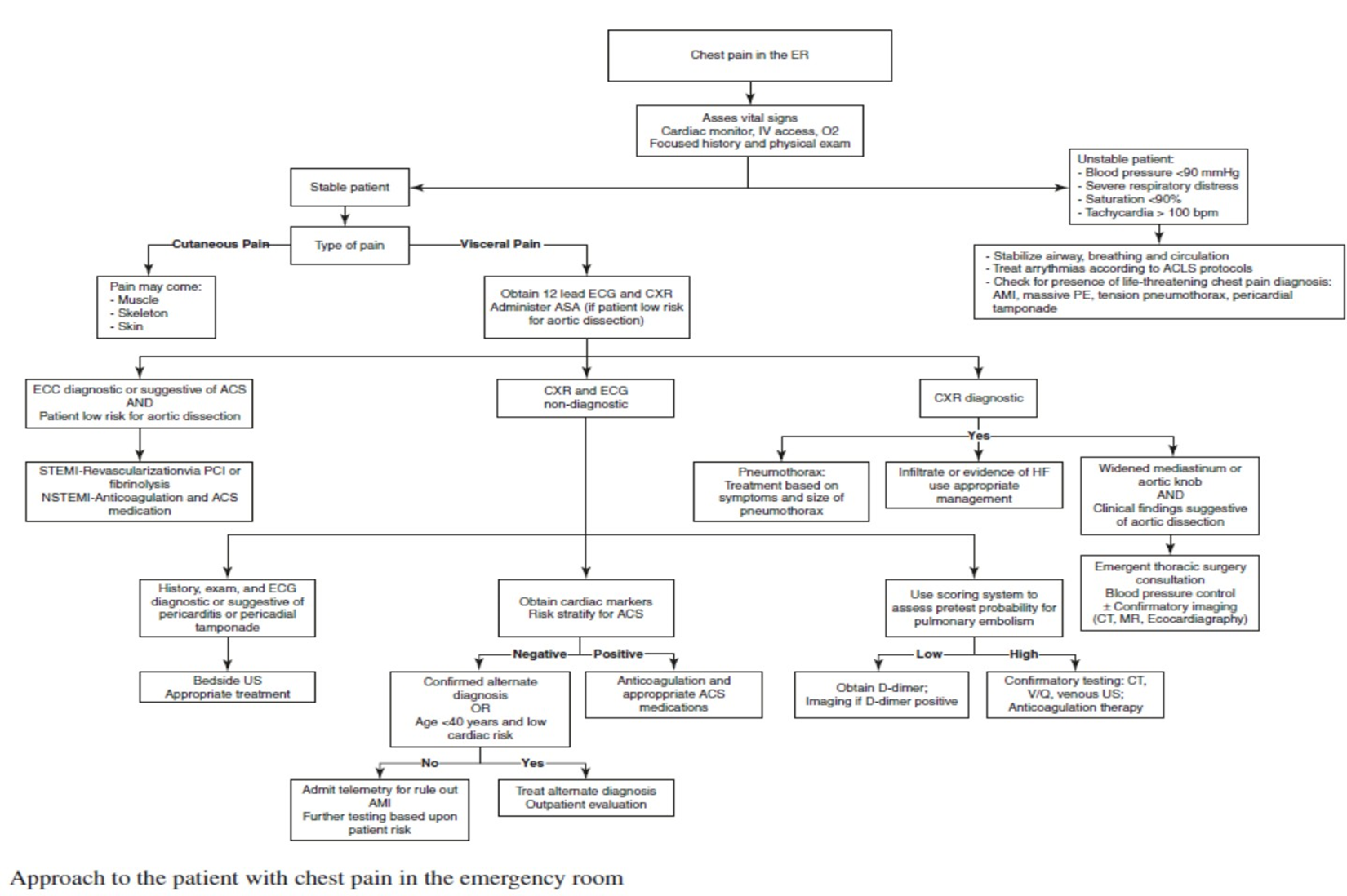
Approach to chest pain