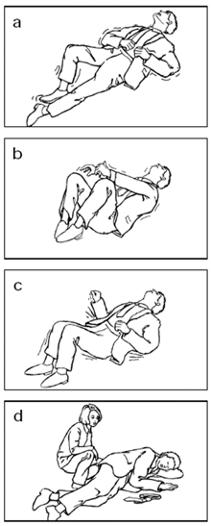
- Status epilepticus >15m
HISTORY OF SEIZURES
- Any clinical event caused by abnormal electrical discharge in the brain –
- Role of inhibitory neurotransmitter, gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) and various excitatory neurotransmitters (acetylcholine, amino acids such as glutamate and aspartate)
- Epilepsy is the tendency to have recurrent seizures (fits)
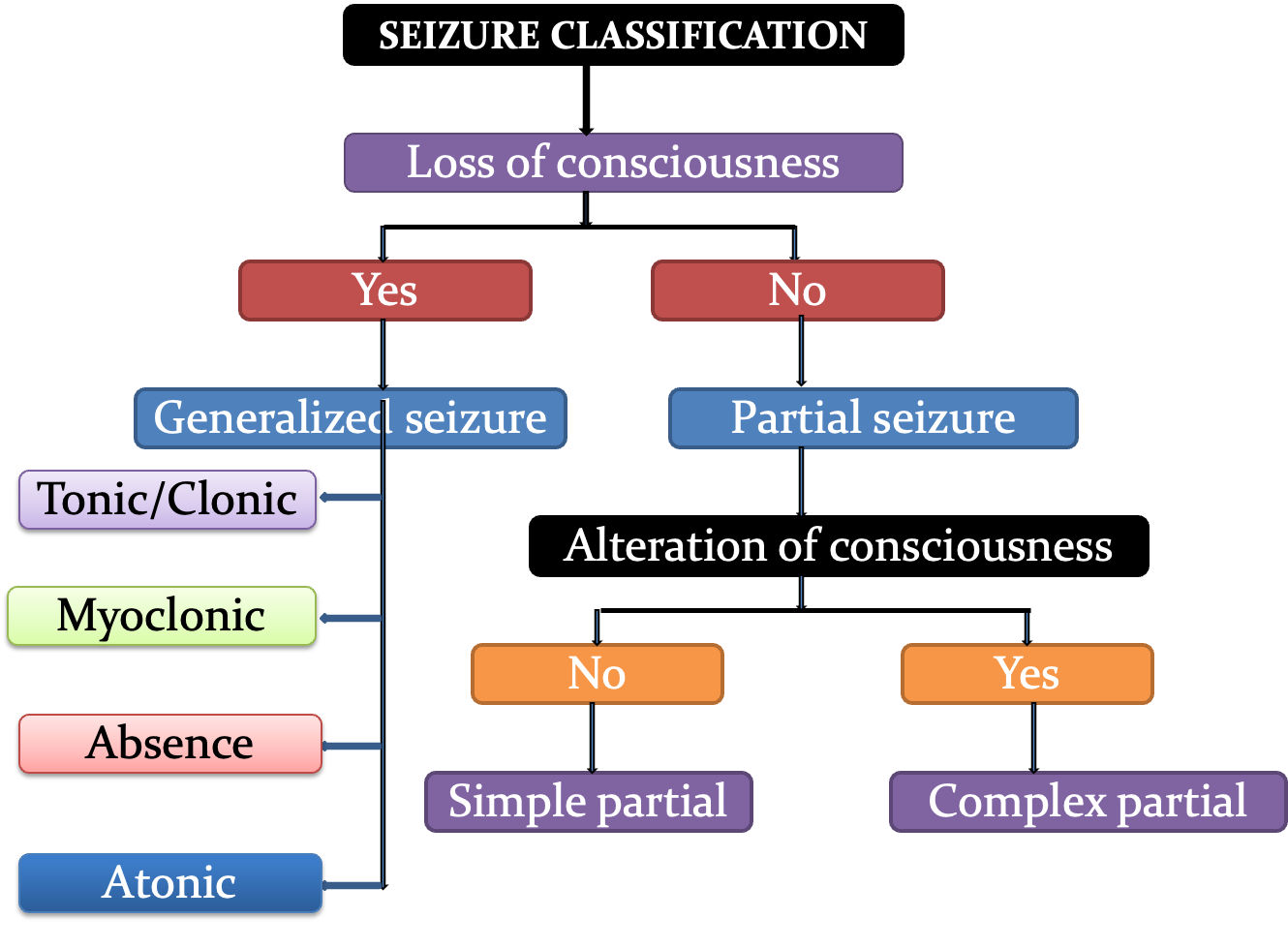
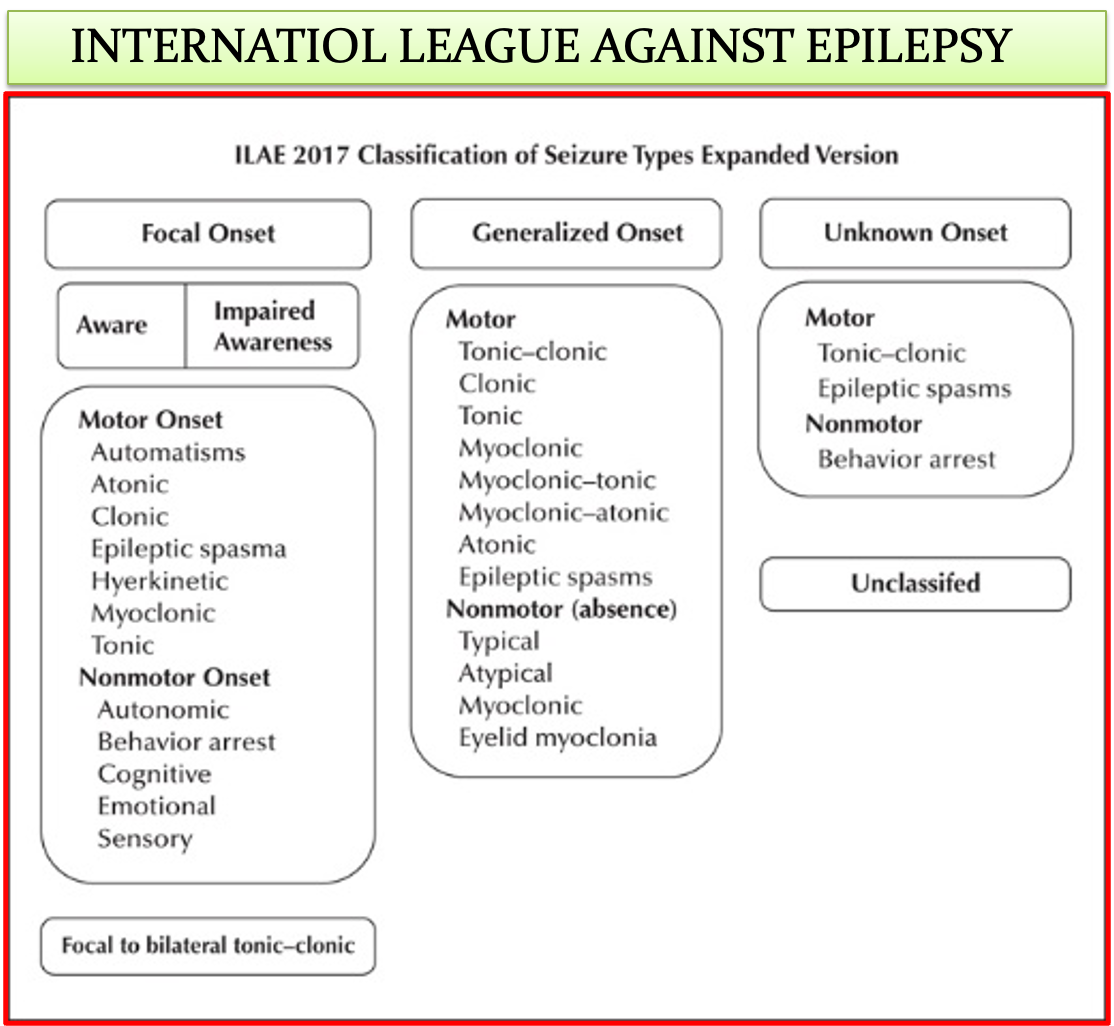
SEIZURE CLASSIFICATION
Depending on the source of the seizure within the brain:
Localized – Partial - seizures
- Simple partial - if consciousness not affected
- Complex partial - if consciousness is affected
Generalized seizures
- All involve loss of consciousness
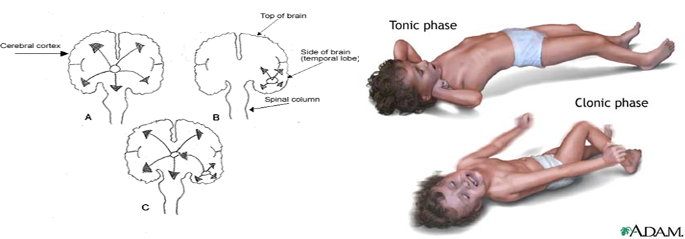
- Further divided according to the effect on the body -include absence, myoclonic, clonic, tonic, tonic–clonic, and atonic seizures.
- Partial seizure may spread within the brain. This is known as secondary generalization
HISTORY OF SEIZURES
- Obtain a description of the seizure/s:
- From patient and witness (NB blackouts, faints, fits, loss of consciousness)
- What happens at the onset of the fit?
- What happens during the fit?
- Does the patient fall or remain standing or sitting?
- How does the fit end?
- Confusion or other post-ictal symptoms?
- Is there incontinence, any injury or tongue biting?
- Change in seizure pattern
- Frequency of seizures?
- When do the seizures occur?
- Head trauma or brain illness (especially in adult onset epilepsy)
- Birth history (especially in early onset seizures)
- Family history of seizures
- What medication is taken?
- History of past/ current medication, compliance and response to medication
SEIZURE AND SYNCOPE