Visual Acuity
Examination
- Checks acuity with Snellen and from proper distance
- Checks acuity both eyes separately
-
Typically measured by Snellen acuity but there are many optotypes (letters, tumbling E, pictures)
-
May be tested at any distance started by 6 meters (20 feet)
-
Recorded as fraction (numerator is testing distance, denominator is distance at which person with normal vision would see figure) e.g., 6/60
-
Measured without & without glasses (BCVA & UCVA).
-
Occlude one eye, children need to be patched
- 20/20 to 20/400, CF (counting fingers), HM (hand motion), LP (light perception), NLP (no light perception)
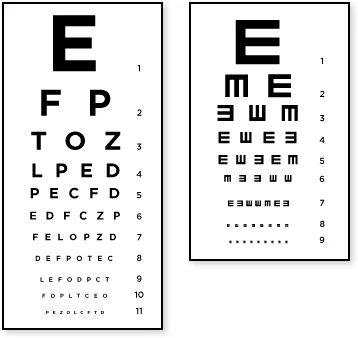
Examples of Visual Acuity Charts
- (A) Snellen chart.
- (B) Landolt C chart.
- (C) Illiterate E chart.

Hand-Held Eye Chart
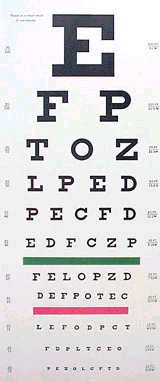
- Hold card approx 14” from pt’s nose
- Read smallest line
- Ask pt to cover one eye
- Cover other eye and repeat
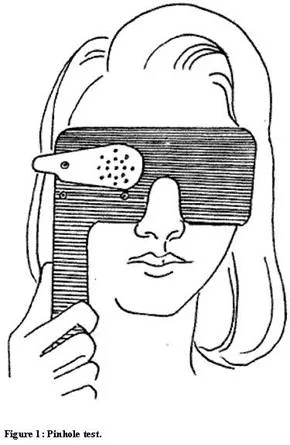
Pinhole View
-
Difference between refraction or not
-
Use: 1 A 1
-
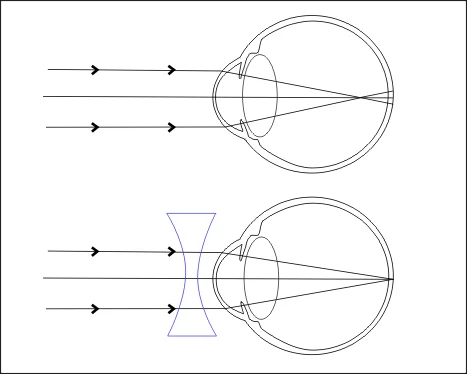
The pinhole (PH) exam can show refractive error
- Need a pinhole occluder
- Central rays of light do not need to be refracted
Near Visual Acuity
Examination
- Ask patient to wear glasses
- Hand-held card at 14 inches or 40 cm
- Assess both eyes separately
- Direct the patient to read the smallest letter that he can see
Hand Held Acuity Card

Near Vision
