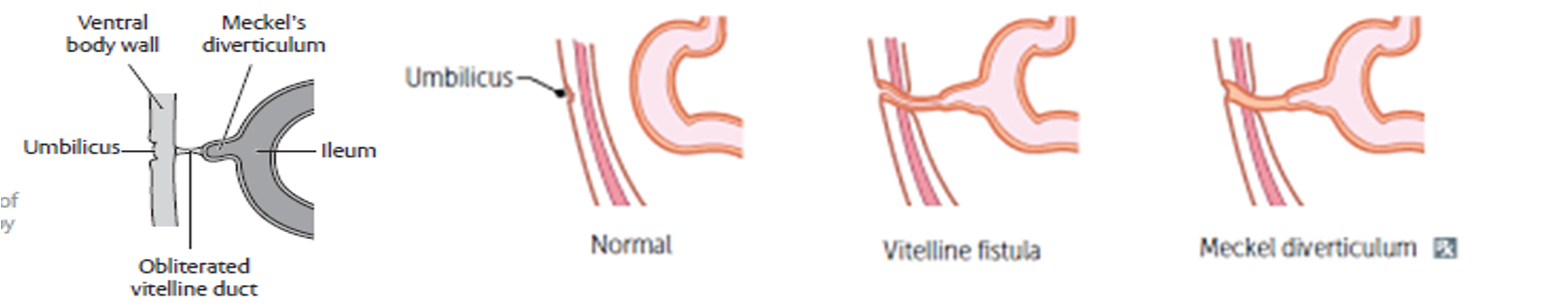
Meckel’s diverticulum
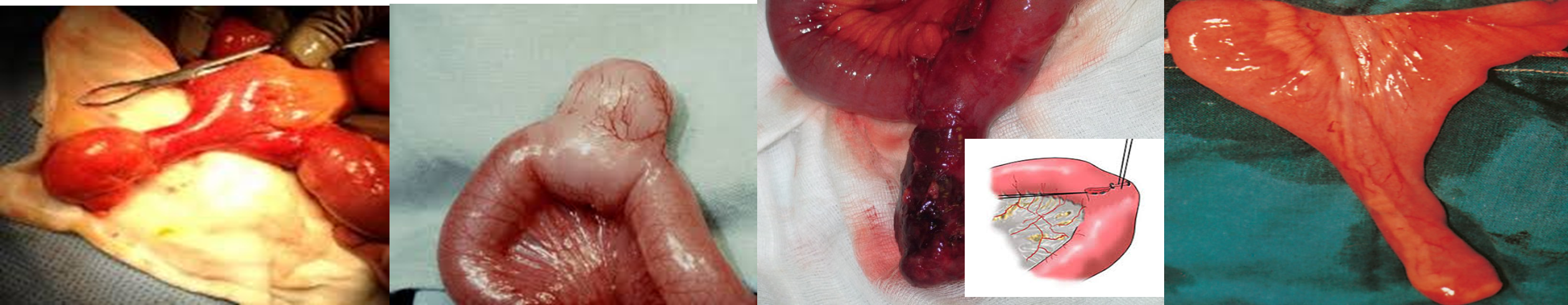 Acutely inflammed Meckel’s diverticulum
Acutely inflammed Meckel’s diverticulum
Embryological remnant of Vitello-intestinal duct. Arise from antimesentric border of ileum Occurs in 2% population, 2 feet from ileocecal valve and 2 inches long and 2 times common in men.
Presents as :
- Persistent vitello-intestinal fistula
- Acute diverticulitis
- Perforation and peritonitis
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding due to ectopic gastric mucosa.
Complications:
- Bleeding: due to ileal mucosal ulceration.
- Obstruction
- Volvulus of the intestine
- Intussuception
- Stricture due to diverticulitis
Clinical manifestation:
- Asymptomatic (95%)
- 50% are younger than 10y/o
- Symptomatic (5%)
- Bleeding (Most common in children)
- Intestinal obstruction most common in adult (Intussusception- twist)
- Diverticulitis mimics appendicitis
Diagnosis:
- For asymptomatic usually discovered as an incidental findings in radiographic imaging, endoscopy, or intraoperatively.
- Radionuclide scans (99m Tc-pertechnate) for ectopic gastric mucosa or in active bleeding
- Angiography to localize site of bleeding
Management:
- Observation: Asymptomatic and incidentally: left as such.
- Excision: Narrow necked, inflamed or symptomatic diverticulum is excised
Acutely inflammed Meckel’s diverticulum