IM
Grave’s disease:
- most common
- Autoimmune disease
- Overactivity of the gland due to TSH Receptor Stimulating antibodies or TRAB (these antibodies are specific for Grave’s)
- On exam, gland is diffusely enlarged, bruit present, non tender
- Other autoimmune diseases may also be present
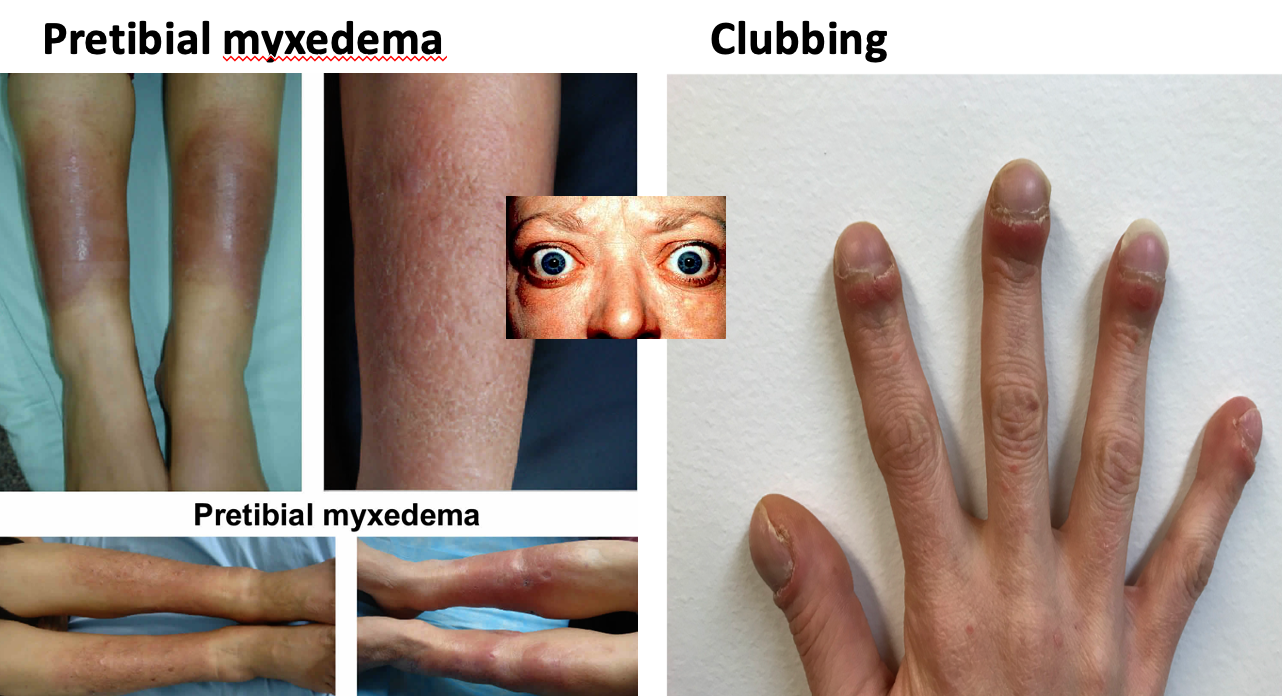
3 Features seen in Grave’s dis. only 1) Exophthalmos (proptosis)
- Also called Grave’s ophthalmopathy
- Protruding eyes
- Lid retraction
- Lid lag
- Ophthalmoplegia (?)
- Leads to corneal drying
2) Pretibial myxedema
- Plaques of thick scaly skin in lower legs
- Topical steroids may help
3) Clubbing of fingers (thyroid acropachy)
CM
` Graves disease (Thyrotoxicosis) 60-80% of 1ry causes Most common cause of hyperthyroidism.
Etiology:
A primary hyperthyroid disease which results from production of a thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin(TSI) ? IgG that activates TSH receptors on thyroid gland resulting in over production of thyroid hormones (T3 & T4) by thyroid gland.
Clinically:
Thyroid gland is diffusely enlarged + Thyrotoxic manifestations:
- Increased heart rate & hypertension
- Nervousness & inability to sleep (insomnia)
- Sensitivity to heat (increased BMR), flushed skin & excessive sweat
- weight loss with increased appetite
- Exophalmos of the eye in late severe cases
Diagnostic Laboratory Investigations:
- Plasma Free T3 & free T4 are elevated ↑
- Serum TSH is markedly reduced ↓
Treatment:
- blocking hormone production by antithyroid drugs
- Radioactive iodine Ablation
- Surgical removal of the thyroid gland (subtotal thyroidectomy)
